Geometry Flashcards
(148 cards)
Collinear
Three or more points on same line
Line
Defined by two distinct points and contains an infinite number of points
Segment
A line bounded at both ends
Segment Bisector
A line that goes through the midpoint of a segment, dividing the segment into two equal parts
Perpendicular AKA
AKA Orthogonal
Perpendicular lines
Meet at 90* right angles
Perpendicular line slopes
Negative reciprocals
Parallel line slopes
Identical slopes
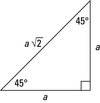
Distance Formula
√ (x2-x1) ^2+ (y2-y1)^2
Slope
(x2-x1) / (y2-y1)
Midpoint (between two points)
[(x1+x2)/2 , (y1+y2)/2]
Angle
The intersection of two non-identical lines
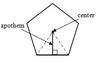
Angle Bisector
A line through the vertex that divides the angle into two equal angles (point is equidistant from sides).
Vertex
The point of intersection
Coplanar Angles
Lie in the same plane but are not necessarily adjacent
Adjacent Angles
Share a common side
Vertical Angles are…
Congruent (Angles opposite each other where two lines cross)
Acute angle
Less than 90*
Right angle
Equals 90*
Obtuse angle
Greater than 90*
Linear pair
Two angles that form a straight angle
Congruent figures
Same shape and same size
Congruent Triangles proofs
Side-Angle-Side, Side-Side-Side, Angle-Side-Angle, or Angle-Angle-Side
Similar figures
Congruent angles and proportional sides