Genomic Imprinting & Epigenetics Flashcards
What is meant by androgenesis?
a form of quasi-sexual reproduction in which a male is the sole source of the nuclear genetic material in the embryo
What is meant by parthenogenesis?
reproduction from an ovum without fertilization
What types of reproduction are shown in the following diagrams?

1 shows normal mammalian development requiring 2 parents

What is the chromosomal makeup of a hydatidiform mole?
they are androgenetic
complete hydatidiform moles are mostly homozygous 46,xx
What is a hydatidiform mole and how does it form?
it is formed by proliferation of abnormal trophoblastic tissue
it is a growth of abnormal placental tissue or a fertilised ovum, without an embryo being present
What is a main risk associated with hydatidiform moles?
they can develop into a malignant trophoblastic tumour
What is an ovarian teratoma?
What is it derived from?
it is parthenogenetic
it is derived from oocytes which have completed their first or both meiotic divisions
What is the composition of an ovarian teratoma like?
it is diploid and consists of a wide spectrum of tissues
it is predominantly epithelial, but may contain hair, teeth, bone and thyroid tissue
it contains NO skeletal muscle or membranes/placenta
When do parthenogenetic embryos die and why?
they die due to failure of development of extraembryonic structures
e.g. trophoblast and yolk sac
When do androgenetic embryos die?
they die at the 6 somite stage
they have well-developed extra-embryonic membranes but poor embryo development
Why do uniparental conceptions fail?
- there are different roles of maternal and paternal genes in determining developmental fate
- genomic imprinting involves parents “imprinting” their genes with a memory of the paternal or maternal origin
What is meant by genomic imprinting?
How is it brought about?
a mechanism that ensures the functional non-equivalence of the maternal and paternal genomes
it is not encoded in the DNA nucleotide sequence
it depends on modifications to the genome laid down during gametogenesis
Which genes are affected by genomic imprinting?
it affects the expression of a small subset of 100-200 genes which are evolutionarily conserved
What are the facial and mental symptoms of Angelman syndrome?
facial dysmorphism:
- prognathism, wide mouth, drooling
- smiling/laughing appearance
mental handicap:
- microcephaly
- absent speech
What is prognathism?
an extension or bulging out (protrusion) of the lower jaw (mandible).
It occurs when the teeth are not properly aligned due to the shape of the face bones
What is the other main symptom of Angelman syndrome?
it is a seizure disorder that involves ataxic, jerky movements
What are the symptoms of Prader-Willi syndrome affecting appearance?
small hands and feet
hyperphagia
- excessive eating and strong desire for food
- leads to obesity
infantile hypotonia:
- decreased muscle tone due to:
- feeding problems
- gross motor delay
male hypogenitalism/crytporchidism:
- partial or complete failure of the gonads to develop
What are other symptoms associated with Prader-Willi syndrome?
- mental handicap
- stereotypical behaviour
What is the cytogenetic abnormality seen in both Angelman syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome?
deletion of chromosome 15
this is always de novo, meaning recurrence risks are very low
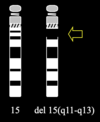
What is the difference in the genetics in Angelman syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome?
In Angelman, the deletion is on the maternal chromosome 15
In Prader-Willi, the deletion is on the paternal chromosome 15
What are the 2 molecular mechanisms in Prader-Willi syndrome?
70% of cases caused by a deletion
25% of cases caused by uniparental disomy
they are indistinguishable clinically as both lack a paternal 15qq11-13 contribution

What are the molecular mechanisms involved in Angelman syndrome?
75% of cases are caused by a deletion
1% of cases are caused by uniparental disomy
2-5% of cases are caused by a point mutation in the UBE3A gene

What is meant by uniparental disomy?
2 copies of a chromosome come from the same parent, instead of 1 copy coming from the mother, and 1 copy coming from the father











