Genetics Flashcards
(105 cards)
What is DNA?
A molecule that carries genetic information (deoxyribonucleic acid)

What is the purpose of a chromosome?
It contains a molecule of DNA where genetic information is stored DNA is more precisely in long fibers called chromatin which is the material that makes up a chromosome
What is a gene?
It is a segment of a DNA molecule that codes for a particular trait; found at a specific location on a chromosome. -Genes also code for proteins -Mistakes in genes=mistakes in proteins
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA consists of a long chain of subunits called Nucleotides. DNA is a molecule composed of two Polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix that carries genetic instructions.(It is a double helix)
What is the composition if a nucleotide?
DNA consisting of a long chain of subunits (smaller units)

What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
- A ring-shaped sugar called deoxyribose
- A phosphate group
- A nitrogenous base (made of carbon and nitrogen)
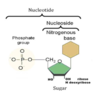
What is the sugar-phosphate backbone (handrails)?
Nucleotides link together by phosphodiester bonds to create a polynucleotide chain.
What are nitrogenous bases (the stairs)?
The nitrogenous base form base-pairs via hydrogen bonding and join the two complimentary strands in DNA.
What are nitrogenous bases joined to?
The DNA backbone by a glycosyl bond..
What are the 2 types of nitrogenous bases?
Pyrimidine bases (single ring) and Purine bases (double ring)
What are all the pyrimidine bases?
Uracil (U) (found in RNA) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C)
What are all the purine bases?
Adenine (A) Guanine (G)
What nitrogenous bases bond with each other?
Adenine (A) always bonds with Thymine (T), Cytosine (C) always bonds with Guanine (G) *Note: The two strands are antiparallel (they start in opposite directions)
How many chromosomes do humans have?
Human body cells have 46 chromosomes (2 pairs of 23). 44 of the chromosomes are autosomes. 2 are sex chromosomes
What are the stages of the cell cycle?
- Growth Phase 1
- Synthesis Phase
- Growth Phase 2
- Mitotic Phase (Mitosis occurs here)

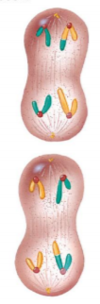
What are the stages of mitosis?
PMAT (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase)

What happens during prophase in Mitosis?
- -Chromosomes begin to shorten and thicken
- -Nuclear membrane dissolves
- -Centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell
- -Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres, which hold the sister chromatid together.

What happens during metaphase in mitosis?
-Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell

What happens during anaphase in mitosis?
-Sister chromatids are pulled apart by spindle fibers and move to opposite ends of the cell

What happens during telophase in mitosis?
- -Nuclear membranes form around the chromosomes on either end of the cell
- -The cell pinches in the middle (Then Cytokinesis takes place where it divides the cytoplasm of a parental cell into two daughter cells)

What are telomeres?
Every time DNA replicates, a small amount of DNA is lost. To help reduce this loss, the chromosomes have protective caps called telomeres. After many many many many divisions, the telomeres become too short and the cell can no longer divide.
What are genetically modified organisms (GMO’s)?
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) involves inserting a desired gene from one species into the DNA of another species. (Ex. healthy fats genes inserted into pigs to make them more healthy)
In which type of cells does mitosis occur?
Eukaryotic cells
What is the result of mitosis?
A parent cell has divided successfully into two identical daughter cells.