General Surgery Flashcards
How can you differentiate the following in terms of pain, fever and jaundice?
Biliary Colic
Acute cholecystitis
Ascending cholangitis
Colic: Intermittent pain
Acute cholecystitis: Constant pain + fever
Ascending cholangitis*: Constant pain + Fever+ jaundice/raised bilirubin
*Also have confusion and hypotension
What is the first line imaging for biliary pathology
USS to exclude obstruction
What is the treatment for the following?
Biliary Colic
Acute Cholecystitis
Ascending cholangitis
Colic: Cholecystectomy within 6 weeks
Cholecystitis: Cholecystectomy in 1 week
Cholangitis: Urgent ERCP (24-48hrs)
How can the following be differentiated from colic/acute cholangitis/ascending cholangitis?
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Primary biliary sclerosis
Cholangiocarcinoma
Have RUQ pain and jaundice
No fever
PSC/PBC cause itching
RUQ mass +/- shoulder/umbilical nodes in cholangiocarcinoma
What is the first and definitive line investigation in PSC/PBC?
USS for obstruction
MRCP for biliary tree visualisation
What is the first line and definitive imaging in cholangiocarcinoma?
USS
CT
What condition gives a ‘beaded’ appearance on MRCP?
PSC
What RUQ pain condition is most associated with ulcerative colitis?
PSC
How does PSC and PBC differ in terms of immune markers?
PSC: p-ANCA
PBC: AMA-2, raised IgM
What can be used to treat itch due to raised bilirubin?
Cholestyramine
Outline the treatments for
PSC
PBC
Cholangiocarcinoma
PSC: Liver transplant
PBC: Ursodeoxycholic acid transplant
Cholangiocarcinoma: Typically palliative measures (can potentially resect if really
What are the causes of acute pancreatitis?
I GET SMASHED
Idiopathic
Gallstones
Ethanol (alcohol)
Trauma
Steroids
MUMPS/malignancy
Autoimmune
Scorpion sting
Hypercalcaemia
ERCP
Drugs
What scoring system is used for severe pancreatitis?
Glasgow criteria: PANCREAS
PaO2 < 8
Age >55
Neutrophils >15
Calcium < 2
Renal (urea > 16)
Enzymes LDH +++
Albumin <32
Sugar >10
Severe pancreatitis >=3
What are the investigations for acute pancreatitis?
1st: Amylase/lipase (>=3x is diagnostic)
GS: CT with contrast
USS to check for obstructive cause
What is the management of acute pancreatitis?
Slow enteral (NG tube) feeding IV Fluids and analgesia
Milder pancreatitis symptoms 3 weeks post acute pancreatitis indicates what?
Pseudocyst
Milder symptoms and amylase raise
Conservative management
How do you investigate chronic pancreatitis?
- CT with contrast for calcification
- Faecal elastase for malabsorption if above unclear
How often should chronic pancreatitis have Hb1AC monitored?
Annually
Painless jaundice indicates what?
Pancreatic cancer until proven otherwise
What is the first line and GS investigations for pancreatic cancer?
1st: USS for obstruction
GS: High-res CT
What cancer marker is relevant to pancreatic cancer?
CA 19-9 (also cholangiocarcinoma)
How do you manage pancreatic cancer?
2 week referral
Whipple’s or stenting for palliative cases
Umbilical pain that shifts to RIF worse on movement and pressing LIF is likely
Appendicitis
Rovsing’s sign is the LIF pressing causing RIF pain
Appendicitis symptoms + high fever + peritonitism indicates
Perforation
How is appendicitis diagnosed?
Clinical history + raised WCC diagnostic
+ Urine analysis for pregnancy + renal colic
+ CT if another diagnosis more likely
What is the treatment for appendicitis?
Prophylactic Abx + laparoscopic appendectomy
What are the features of bowel obstruction?
Green, bilious vomiting
Constipation +/- tinkling bowel sounds
Abdominal distention + pain
How can you differentiate between small and large bowel obstruction
Small // Large
Adhesions, post-op ileus, hernia, intussusception // Malignancy, stricture, volvulus
What are the investigations for suspected obstruction
- AXR for gross cause
- Contrast CT for more detail
CXR to exclude obstruction
How does an ileus present differently to a volvulus
Ileus has absent rather than tinkling bowel sounds
How does a caecal and sigmoid volvulus present image differently?
Caecal foetal sign
Sigmoid coffee bean
White line tends to be on side of volvulus

How does bowel lumen dilation help diagnose obstruction
How does bowel lumen dilation help diagnose obstruction 3/6/9 rule
>3cm: Small
>6cm: Caecal
>9cm: Sigmoid
Patient presents with severe, sudden onset general abdominal pain. They are systemically well but have a history of AF, what is the likely diagnosis?
Mesenteric ischaemia
How can the following causes of bowel ischaemia be differentiated?
Acute mesenteric ischaemia
Chronic mesenteric ischaemia
Ischaemic colitis
AMI: Acute pain, disproportionate to Obs
CMI: Colicky pain, rarer
IC: Transient pain, bloody diarrhoea, ‘thumbprinting on X-ray’. Cocaine use in young people
How do you image for bowel ischaemia
USS for obstruction
CT for diagnosis
+ lactic acidosis and raised WCC on blood
What is the management for acute mesenteric ischaemia and ischaemic colitis?
AMI: Emergency surgery
IC: Supportive
What hernias are found in the following places?
Superior and medial to pubic tubercle
Below and lateral to pubic tubercle
Symmetrical bulge under umbilicus
Asymmetrical bulge under umbilicus
Superior + medial: Inguinal
Below and lateral: Femoral
Symmetrical bulge under umbilicus: Umbilical
Asymmetrical bulge under umbilicus: Paraumbilical
How can you determine if an inguinal hernia is direct or indirect? Why is this significant?
Reduce and press 2/3 between ASIS and pubic symphysis then get patient to cough
Indirect will be restrained
Direct will not
Indirect more likely to be bowel so run risk of bowel strangulation
What is the management of an umbilical hernia in a child?
Observe for resolution until 2
If unresolved then operate
Fresh painless PR bleeding and altered bowel habit in patient without lumps or itch on PR exam indicates what
Diverticular disease
LIF pain (sometimes RIF), fever and systemically unwell +/- PR bleeds points towards what colorectal issue?
Diverticulitis
How do you investigate diverticulitis?
CT with contrast
mixed PR bleeding and altered bowel habit in elderly patient with microcytic anaemia suggests what?
Colon cancer
Who must get referred for suspected colorectal cancer?
>=40yrs: abdo pain + weight loss
>=50yrs: Unexpected bleeding
>=60yrs: Change in bowel habit/microcytic anaemia with low ferritin
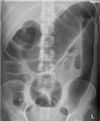
What does this AXR show

Small bowel obstruction

Valvulae conniventes: White lines going FULL WIDTH across bowel
What does the following x ray show?

pneumoperitoneum
Can see wall above diaphram on both sides
What are the causes of post-op pyrexia?
Wind: Pneumonia, atelectasis (1-2 days)
Water: UTI (>3 days)
Wound: Infections (>5 days)
Walking: DVT (>1 week)
Wonder drugs/What did we do
+ abscess
What blood changes are seen in TPN?
Low phosphate, magnesium, zinc
High glucose
What points towards toxic megacolon over sigmoid volvulus?
History of UC/IC
More systemically unwell
Diarrhoea, abdo pain, joint pain +/- neuro or cardiac deficits is caused by what?
Whipple’s disease (Tropheryma whipplei)
PAS positive macrophages
Co-trimox


