General & OChem Review Flashcards
Coordinate covalent bonds
unlike covalent bonds, are formed between two atoms when both of the shared electrons are donated by the same atom. Such coordinate bonds are often formed between electron-poor metal ions and molecules called ligands that contain one or more electron-rich atoms with available lone-pair electrons.
Coordination Number
number of coordinate bonds formed between the central metal ion and its nearest neighboring atoms. When all of these nearest neighboring atoms are from separate molecules or ions, the number of ligands will equal the coordination number. However, if two or more of these nearest neighboring atoms are joined to the same coordinating ligand unit, then the number ligands will not equal the coordination number.
Boyle’s Law
*all BOYS want is the V and P* Inverse relationship between V and P: as V increases, P decreases and vice versa -when T is constant -when n is constant P∝1V PV = k
Charles’s Law
*King Charles was Fat (Volume) and Sweaty (Temperature)* Describes direct proportional relationship between Volume and Temperature: ex. as V increases so does T V∝T and V/T is a constant
Avogadro’s Law
*Avogadro’s (mole) is too big to fit in my house* Direct proportional relationship between Number of Moles and Volume V∝n and V/n is a constant.
Guy-Lussac’s Law
*Good Luck under Pressure & Heat* Direct proportional relationship between Pressure & Temperature P∝T and P/T
Representative Elements
-Group 1, 2 -Group 13-18
Density
d= m/v - if volume decreases, density increases
Relationship between density, volume, temperature
-if temperature decreases –> volume decreases –> density increases
Density in an isolated system
-if volume decreases and density increases the level of fluid in a system will be relatively unchanged -if density increases and there is something in the fluid –> object will now float because density has increased relative to what it was before
Enantiomers
Mirror Images

Diastereomer
Differ at the Stereocenter, similar to enantiomers except for the connections
-Ex. Alpha and Beta glucose are an example of a diasteromer (subcategory of an epimer)
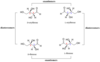
Stereoisomer
- Have identical molecular formulas and arrangements of atoms
- They differ from each other only in the spatial orientation of groups in the molecule
- Simplest forms: cis and trans isomers created by restricted rotation about doulbe bond or ring system
Ex. C4H8

Structural Isomers/ Constitutional Isomers
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different physical and chemical properties

Catecholamines
Monoamine Neurotransmitter

Prostaglandins
Physiologically active Lipid structure
Involved in inflammation: prevent needless clot formation and regulate the functioning of smooth muscles

Thromboxanes
Potent hypertensive agent and helps with platelet aggregation

Phospholipids
- hydrophilic head
- hydrophobic head
- glycerol + phosphate head
- fatty acid tails

Isopropyl Alchol
C3H7OH

Methanol
CH3OH

Carbon Dioxide
CO2

Carbonate
CO3 (2-)

Formaldehyde
CH2O (double bond characteristic for O)

Ka Values for Amino Acids
- amino acids with acidic side chains: isoelectric point is the 2 lowest Ka values
- pKa = average of two lowest values


