General Flashcards
(50 cards)
What’s it called when you create a conditional to stop a program from breaking?
- checks the passed-in parameters, and returns with an error if they’re not suitable.
- checks the state of the object, and bails out if the function call is inappropriate.
- checks for trivial cases, and gets rid of them quickly.
guard clause
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using pseudocode
AD
- Can brainstorm without worrying about syntax
DIS
- can’t check logic
- still too detailed for complex programs.
You want to write code without having to worry about syntax, what do you use?
PSEUDOCODE is writing code without worrying about syntax. Casual pseudocode uses plain words to think out the code steps Casual example: Given a collection of numbers. Iterate through the collection one by one. - save the first value as the starting value. - for each iteration, compare the saved value with the current value. - if the current number is greater - reassign the saved value as the current value - otherwise, if the current value smaller or equal - move to the next value in the collection After iterating through the collection, return the saved value.
Formal pseudocode uses specific KEYWORDS to think out the code. Formal example:
START # Given a collection of integers called “numbers”
SET iterator = 1
SET savedNumber = value within numbers collection at space 1
WHILE iterator <= length of numbers
SET currentNumber = value within numbers collection at space “iterator”
IF currentNumber > savedNumber savedNumber = currentNumber
ELSE skip to the next iteration iterator = iterator + 1
PRINT savedNumber
END
PesudoCode for:
start of the program
set a variable that we can use for later
retrieve input from user
display output to user
retrieve a value from a variable
show conditional branches in logic
show looping logic
end of the program
START
SET
GET
READ
IF/ELSE
IF
ELSE
WHILE
END
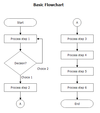
(Flow chart) Shape of:
Start and Stop
Processing Step
Input/Output
Decision
Connector
https://d1b1wr57ag5rdp.cloudfront.net/images/flowchart_components.jpg
Start and Stop, oval
Processing Step, rectangle
Input/Output, parallelogram
Decision, diamond
Connector, circle
Difference between declarative syntax vs imperative syntax?
What’s a metaphor.
When should you use one over the other?
Declarative programming is when you say what you want,
and imperative language is when you say how to get what you want step by step
“I declare that I want this”
“It is imperative that you do each of these things”
Imperative goes to a restaurant and orders a 6oz. steak (cooked rare), fries (with ketchup), a side-salad (with ranch), and a Coke (with no ice). The waiter delivers exactly what he asked for, and he’s charged $14.50. On the other hand,
Declarative goes to a restaurant and tells the waiter that he only wants to pay around 12 dollars for dinner, and he’s in the mood for steak. The waiter returns with a 6oz. steak (cooked medium), a side of mashed potatoes, steamed broccoli, a dinner roll, and a glass of water. He’s charged $11.99.
Declarative is higher level and easier to understand. Use it first. Like pseudocode.
Then use imperative to see how to do it.
Do it top down.
Install 3 lint packages locally
(They do not recommend installing globally)
use it to check the code in terminal
npm install eslint eslint-cli babel-eslint –save-dev
npx eslint file_name.js
Hotkey to change all variable names
F2
What is a template literal?
What are the things it allows called? (1 thing, 2 terms)
Template literals are literals delimited with backticks (`), allowing embedded expressions called substitutions.
With backticks, string literals allowing embedded expressions within:
${ }
install readline sync so you can have input in terminal
npm install readline-sync –save
What is the difference between a statement and an expression.
{edit with info from this: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eWTuFoBYiwg}
Statement vs Expression
Expressions produce a value, and that value will be passed into the function. Statements don’t produce a value, and so they can’t be used as function arguments.
Statement- group of words, numbers and operators that commands an action for the computer to perform
Expression- Any unit of code that can be evaluated to a value is an expression.
console.log((/* Some chunk of JS here */)
Error is a statement. Works is an expression
For example:
a = b * 2;
This statement (is this a statement? It runs in console.log) has four expressions in it:
• 2 is a literal value expression.
• b is a variable expression, which means to retrieve its current value.
• b * 2 is an arithmetic expression, which means to do the multiplication.
• a = b * 2 is an assignment expression, which means to assign the result of the b * 2 expression to the variable a (more on assignments later).
1 statement
console.log(“Hello”);
4 expressions
console
console.log
“Hello”
console.log(“Hello”)
What does a block do?
How is it noted/created?
Blocks have two functions:
- to group statements so that they can be treated as one statement;
- and to define scopes for names to distinguish them from the same name used elsewhere. In a block-structured programming language, the objects named in outer blocks are visible inside inner blocks, unless they are masked by an object declared with the same name.
a block is defined by wrapping one or more statements inside a curly-brace pair
{ .. }
What all will evaluate to false (are falsy) when converted to boolean?
How many things?
null
undefined
NaN
0
false
‘’ (empty string)
What is returned from:
2 && 1
0 && 2
2 && 0
3 || 2
2 || 0
0 || 2
1
0
0
3
2
2
Return equality with implicit conversion or explicit equality
Return non-equality with implicit conversion or explicit equality
== implicit equality
=== implicit equality
!= implicit non equality !== implicit equality
In what order are method chains processed?
‘string another string’.toUpperCase().toLowerCase()
will return:
string another string
Chains are processed one at a time from left to right.
How to actually test truthiness (2 ways)
!!
Boolean()
What does a ; indicate?
; indicates the end of a statement
statements can be separated with a ;
A new line
implicitly indicates an end of statement (;)
T or F
It depends:
A new line implies a semicolon in most case
console. log(‘affs’)
console. log(‘affs’)
But sometimes it doesn’t:
alert(3 +
1
+ 2);
Sometimes JS assumes right or wrong
Enable/modify features added in ECMAScript 5 (ES 5)
what are some of these features?
‘use strict’
Strict mode helps out in a couple ways:
It catches some common coding bloopers, throwing exceptions.
It prevents, or throws errors, when relatively “unsafe” actions are taken (such as gaining access to the global object).
It disables features that are confusing or poorly thought out.
Difference between var, let and const
Let has block scope
var has function scope
const has block scope, cannot be reassigned, and must be initialized or will throw an error
Most important things when naming a variable:
Use human-readable names like userName or shoppingCart.
Stay away from abbreviations or short names like a, b, c, unless you really know what you’re doing.
Make names maximally descriptive and concise. Examples of bad names are data and value. Such names say nothing. It’s only okay to use them if the context of the code makes it exceptionally obvious which data or value the variable is referencing.
Agree on terms within your team and in your own mind. If a site visitor is called a “user” then we should name related variables currentUser or newUser instead of currentVisitor or newManInTown.
For :
const birthday = ‘18.04.1982’;
const age = someCode(birthday);
should birthday and/or age be capitalized?
Just BIRTHDAY because it is hard coded before run time
age has to be calculated still and won’t be known until the function plays.
Is null the absence of a value?
No. It is not an undefined value. It is a value DEFINED to be “nothing”, “empty” or “unknown”.
Null is not a “reference to a non-existing object” or a “null pointer” like in some other languages.


