Gas exchange and smoking Flashcards
Where is ciliated epithelium found in the gas exchange system?
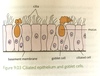
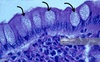
Lining the trachea, bronchi and larger bronchioles. The epithelium of the trachea, bronchi and larger bronchioles also contain goblet cells.
What function does ciliated epithelium have?
The epithelial cells are covered with cilia, which beat back and forth to sweep the mucus and trapped particles and pathogens up the airways towards the mouth where they are swallowed. This action helps prevent the particles and pathogens entering the lungs and causing infections. Any bacteria that are swallowed will be killed by stomach acid.
Where are goblet cells found in the gas exchange system?
Trachea, bronchi and larger bronchioles
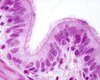
What function do goblet cells have?
Secrete mucus onto the surface of the ciliated epithelium
Where are mucus glands found in the gas exchange system?
Below the epithelium of the trachea and bronchi
What function do mucous glands have?
Secrete mucus into ducts that open through the ciliated epithelium in order to trap particles and pathogens.
Where is cartilage found in the gas exchange system?
In the wall of the trachea (in C-shaped rings) and in the wall of the bronchi (as irregular blocks)
What function does cartilage have in the gas exchange system?
Gives upport to the walls of the trachea and bronchi. During inhalation the pressure inside the airways falls, and the cartilage prevents them from collapsing, holding open the airways to allow easy flow of air.
Where is smooth muscle found in the gas exchange system?
In the walls of the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles
What function does smooth muscle have in the gas exchange system?
Smooth muscles cells undergo contraction and relaxation which alters the diameter of the respiratory airways (trachea, bronchi and bronchioles). This is particularly important in bronchioles, which widen during exercise to allow more air to enter the alveoli.
Where is squamous epithelium found in the gas exchange system?
Alveoli
What function does squamous epithelium have in the gas exchange system?
It is thin to give a short diffusion pathway for gas exchange. Alveoli provide a large surface area
Where are capillaries found in the gas exchange system?
In all parts of the gas exchange system - many around the alveoli
What function do capillaries have in the gas exchange system?
They provide a large surface area for exchange between blood and air in the alveoli
What is ventilation or mechanical respiration?
Breathing air in and out of the lungs
What is cellular respiration?
The chemical processes that occur inside cells to transfer energy from molecules, such as glucose and fat, to ATP.
What is gas exchange?
Diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide between air in the alveoli and the blood.
What structures form the airways of the gas exchange system?
The trachea, which branches into two bronchi which branch into numerous bronchioles
How does the structure of bronchi differ from that of the trachea?
They have a similar structure, but the cartilage is in blocks in the walls of the bronchi instead of in rings as it is in the trachea. Bronchioles have no cartilage.
What are these cells?
Ciliated epithelium
What are these cells?
Goblet cells
What are these structures?

Mucous glands
What is this tissue?

Cartilage
What is this tissue?

Smooth muscle
Look carefully at the micrograph
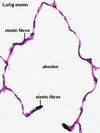
Elastin fibers
What are these cells?

Squamous epithelium of alveoli
Study the attached micrograph

Draw a plan diagram of an alveolus
What is the gas exchange surface of the lung?
The squamous epithelium of the alveoli