Functional Hierarchy of Motor System Flashcards
(34 cards)
What is in control of spinal reflexes?
Brainstem nuclei
What are the brainstem nuclei controlled by?
Cerebral cortex
Basal Ganglia
Cerebellum
These control the brainstem nuclei and instruct voluntary nucleus
Give an account of the function of the following descending systems:
Motor cortex
Braistem centres
Basal Ganglia
Cerebellum
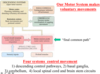
Motor cortex: Planning, initiating and directing voluntary movements
Basal ganglia feeds into the motor cortex (caudate nucleus and putamen feed into the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra, the latter two then feed into the thalamus before being transmitted to the motor cortex)
Basal ganglia is responsible for gating proper initiation of movement
Brainstem: Basic movements and postural control
Cerebellum: feeds into the brainstem, sensory motor coordination of ongoing movement
What is the effect of lower motor neurone lesions?
Lower Motor Neurones at spinal levels directly innervate muscles to initiate reflex and voluntary movements
So lesions cause flaccid paralysis and muscle atrophy
What regulates alpha motor neurone activity?
Upper Motor Neurones in the brainstem or cortex synapse with multiple lower circuit neurones to regulate a motoneurone activity
What do upper motor neurones from the cortex control?
Complex spatiotemporal skilled movements
Brainstem is responsible for basic movement and postural control
What do upper motor neurone lesions cause?
Lesions cause spasticity, some paralysis, may be transient.
Lesions in many posture-regulating pathways - spastic paralysis
Corticospinal lesions - weakness (paresis), rather than paralysis
Which motoneurones are proximal shoulder muscles and finger muscles attached to?
- proximal shoulder muscle are mapped to medial motoneurones
- finger muscles are mapped to much more lateral motoneurones
What is the spinal cord descending input?
The spinal cord receives descending input via neurons in the brainstem AND direct cortical input via Corticospinal / Pyramidal tract.
Where does vestibular sensory input enter?
Informs us of balance - enters at the brainstem
Movements in response to visual, olfactory, auditory, emotional, intellectual cues result in nerve entry to what structure?
Cortex

What sensory organ is responsible for the stretch reflex?
Muscle spindle
What spinal cord segment is responsible for the following reflexes?
Biceps jerk, Triceps jerk, Patellar tendon, Achilles tendon reflex
Biceps jerk C6 Triceps jerk C7 Patellar tendon L4 Achilles tendon reflex - S1
What condition may result in a loss of ankle jerk?
Diabetes
What is the sensory organ for the flexor reflex?
Noiceceptors in skin muscles and joints
How does the flexor reflex work?
- Increased activity in the flexor muscles of the affected part via a number of excitatory interneurones.
- At the same time, via a number of excitatory and inhibitory interneurones, the antagonistic extensors are inhibited
●
FLEXOR REFLEX - ipsilateral flexion in response to pain

How do we prevent falling over when the noiciceptor is activated, which in turn has activated our flexor and inhibited out ipsilateral extensor?
The contralateral limb extends via:
- several excitatory interneurones which cross the spinal cord and excite the contralateral extensors
- at the same time, via several interneurones, there is inhibition of the contralateral flexors
this helps to maintain an upright posture by extending the limb to bear the body weight.
- sensory information ascends to the brain in the contralateral spinothalamic tract.
Why do noiciceptor fibres conduct more slowly than muscle spindle afferents?
•Nociceptive sensory fibres have smaller diameter than muscle spindle afferents and so conduct more slowly
What organ is involved in excessive load to a muscle?
Golgi tendon organ
What causes inhibition of relfexes?
Reflexes can be over-ridden with conscious thought
How many synapses does an alpha motor neurone receive?
Over 10,000
Many are from descending cortical excitatory and inhibitory inputs, with continual integration of EPSPs and IPSPs
How can the golgi tendon organ inhibition of a flexor be inhibited?
Descending voluntary excitation of a motoneurones can override the inhibition from the GTOs and maintain contraction.
How can the stretch reflex be over-ridden?
Strong descending inhibition hyperpolarizes α-motoneurones and the stretch reflex can not be evoked.
What are y-motoneurones dependant on?
Entirely dependant on descending pathways


