Foundation: C7 - Organic Chemistry Flashcards
Alkanes are hydrocarbons
- What elements are hydrocarbons made from?
- What type of bonds do alkanes contain? How can you tell?
- Hydrocarbons are made from hydrogen and carbon.
- Alkanes contain covalent bonds.
Covalent bonds are between non-metal atoms and hydrogen and carbon are both non-metals.
Name the first four alkanes in order of size starting with the smallest.
Mice Eat Peanut Butter
- Methane
- Ethane
- Propane
- Butane
What is the general formula for alkanes
CnH2n+2
For example:
Methane has 1 carbon atom so it has (2x1)+2 = 4 hydrogen atoms.
Ethane has 2 carbon atom so it has (2x2)+2 = 6 hydrogen atoms.
- What is the chemical formula for Methane.
- Draw the displayed formula (a drawing showing all the atoms and bonds for Methane.)
- CH4
- Diagram below
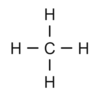
- What is the chemical formula for Ethane.
- Draw the displayed formula (a drawing showing all the atoms and bonds) for Ethane.
- C2H6
- Diagram below

- What is the chemical formula for Propane.
- Draw the displayed formula (a drawing showing all the atoms and bonds for Propane.)
- C3H8
- Diagram below
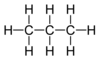
- What is the chemical formula for Butane.
- Draw the displayed formula (a drawing showing all the atoms and bonds for Butane.)
- C4H10
- Diagram below

Describe the realtionship between the length of a hydrocarbon and…(the first one has been done for you):
- How runny the hydrocarbon is (The shorter the hydrocarbon the runnier it is).
- The boiling point of the hydrocarbon.
- How flamable the hydrocarbon is.
- How viscous (sticky) the hydrocarbon is.
- The shorter the hydrocarbon the runnier it is.
- The shorter the hydrocarbon chain the lower its boiling point.
- The shorter the hydrocarbon the more flammable it is.
- The longer the hydrocarbon the more viscous it is.
Explain why shorter hydrocarbons have lower boiling points than longer hydrocarbons.
They have weaker intermolecular forces.
So it takes less energy to break these
Explain why shorter hydrocarbons are runnier/less viscous than longer hydrocarbons.
They have weaker intermolecular forces.
Methane has a lower melting and boiling point than propane. Explain why.
Because methane is a shorter molecule.
So the intermolecular forces between the methane moleculse are weaker.
It therefore takes less energy to break them.
Which alkane (methane, ethane, propane or butane) is..
- Most flamable
- Most viscous (most sticky)
- Methane is most flamable because it is the shortest.
- Butane is most viscous because it is the longest.
Name 3 fossil fuels
Crude oil
Coal
Natural gas
What was crude oil made from
Plankton that died millions of years ago
And was exposed to high temperature and pressure
Where is crude oil found
In layers of rock below the sea and the ground
Fossil fuels are non-renewable/Finite.
What does non-renewable/Finite mean
That we are using them faster than they are made/they will eventually run out.
What is fractional distillation used for?
Seperating the hydrocarbons in crude oil.
Explain how fractional distillation works.
- Crude oil is heated until the hydrocarbons evaporate/vaporise.
- The hydrocarbons rise through the column.
- The hydrocarbons condense and are extracted in different parts of the column (fractions).
- Longer hydrocarbons condense (turn back into a liquid) in the lower parts of the column.
Why do shorter hydrocarbons cool and condense in the upper part of the fractional distillation column?
Because they have lower boiling points.
Why do longer hydrocarbons cool and condense in the lower part of the fractional distillation column?
Because they have higher boiling points.
What are the different hydrocarbons extracted from crude oil used for?
- Used as fuels
- Used for making polymers (plastics)
- Used as solvents (e.g in paints)
- Used for making lubricants
- Used for making detergents
What is cracking used for?
Why is this important?
Breaking long hydrocarbons into short hydrocarbons.
Because short hydrocarbons are more useful than long hydrocarbons.
What are the products of cracking used for?
- Used as fuels (e.g petrol)
- Alkenes made in cracking are used for making polymers (plastics)
Describe what happen during catalytic cracking.
- The hydrocarbons are heated until they evaporate/vaporise
- Then they are passed over a catalyst
Describe what happen during steam cracking.
- The hydrocarbons are heated until they evaporate/vaporise
- Then they are mixed with steam and heated to very high temperatures.
TRIPLE:
Name the first 4 alkenes
Ethene
Propene
Butene
Pentene
Eat Peanut Butter Penitently
TRIPLE:
What functional group do alkenes have
C=C
TRIPLE:
Name the first 4 alkenes
Ethene
Propene
Butene
Pentene
Eat Peanut Butter Penitently
TRIPLE:
What is the general formula for alkenes
C2H2n
TRIPLE:
What is the chemical formula for
- Methene
- Ethene
- Propene
- Butene
- Pentene
- Methene: Doesn’t exist
- Ethene: C2H4
- Propene: C3H6
- Butene: C4H8
- Pentene: C5H10
TRIPLE:
Alkenes are unsaturated.
What does unsaturated mean?
There are double bonds between some of the carbon atoms.
TRIPLE:
Draw the displayed formula for
- Ethene
- Propene
- Butene
TRIPLE:
Why do alkenes burn with a smoky flame?
Because they undergo incomplete combustion.
TRIPLE:
What is the word equation for incomplete combustion of alkenes.
Alkene + oxygen → carbon + carbon monoxide + carbon dioxide + water (+ energy)
TRIPLE:
Alkenes react via addition reactions. What happens during an addition reaction.
The carbon carbon double bond open up to leave single bonds that new atoms are added to.
TRIPLE:
What molecule is formed when enthene reacts with bromine.
Draw a diagram to show this reaction.
Dibromoethane
Click here for a diagram: http://igcse-chemistry-2017.blogspot.com/2017/07/427-describe-reactions-of-alkenes-with.html
TRIPLE:
Testing for alkenes: Describe the test you would use to test if something is an alkene.
Add bromine water (bright orange)
If an alkenes is present the bromine water becomes colourless
TRIPLE:
What is formed when ethene reacts with water?
Ethanol
Ethene + water → ethanol
TRIPLE:
What are addition polymers (e.g polythene) made from?
Monomers with double covalent bonds (unsturated monomers).
TRIPLE:
How are the displyed formula for the monomers and polymers in addition polymers different (see below)?

- Monomers contain bouble bond: Polymer has single bonds only and additional bonds at each end.
- The n is in front of the monomer: The n is at the bottom right in the polymer.
See the diagrams at the bottom of this web page: https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/guides/zqxbxfr/revision/1
TRIPLE:
Name the first 4 alcohols
- Methanol
- Ethanol
- Propanol
- Butanol
TRIPLE:
What fuctional group do alcohols have
-OH
TRIPLE:
What is the general formula for alcohols?
CnH2n+1OH
TRIPLE:
What is the displayed formula for propanol?
See image below.

TRIPLE:
What are the main uses of alcohols?
- Used as solvents (they dissolve many things that don’t dissolve in water).
- Used as fuels
TRIPLE:
Give the word equation for complete comustion of methanol.
Methanol + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
TRIPLE:
What are formed when alcohols react with oxygen (oxidation)?
Carboxylic acids
TRIPLE:
Give the word eqution for ethanol production from fermentation?
What organism is used in this process?
sugar → ethanol + carbon dioxide
Yeast
TRIPLE:
What functional group do carboxylic acids have?
-COOH
TRIPLE:
Name the fisrt 4 carboxylic acids
- Methanoic acid
- Ethanoic acid
- Propanoic acid
- Butanoic acid
TRIPLE:
What are formed in reactions between carboxylic acids and alcohols?
E.g Ethanoic acid + Ethanol →
Esters (and water)
Ethanoic acid + Ethanol → Ethylethanoate + water
TRIPLE:
In condensation polymerisation, whenever a new bond is fomed a small molecule is lost. What small molecule is usually lost?
Water
TRIPLE:
How many products are fomed in addition and condensation polymerisation?
- Addition polymerisation: 1 product (the polymer)
- Condensation polymerisation: 2 products (the polymer and water)
TRIPLE:
What type of functional groups are involved on addition polymerisation and condensation polymerisation?
- Addition polymerisation: C=C double bonds
- Condensation polymerisation: Two reactive group on each monomer.
TRIPLE:
- Name two polymers found in humans
- Name three polymers found in plants
- Proteins and DNA.
- Starch, cellulose, proteins, DNA.
TRIPLE:
What monomers are proteins made from?
Amino acids
TRIPLE:
What functional groups do amino acids have?
- Carboxyl groups: -COOH
- Amino groups: -NH2
TRIPLE:
What monomers is DNA made from?
Nucleotides
TRIPLE:
TRIPLE:
Describe the industrial production of ethanol using ethene.
- Ethene is mixed with steam
- And passed over a catalyst
- The mixture passes through a condensor
- Ethanol and water condense (turn into liquids) and are removed
- Ethanol and water are seperated using fractional distillation

TRIPLE:
Under what conditions does alcohol production using yeast (fermentation) happen fastest?
- 37oC
- Slightly acidic
- Anaerobic
TRIPLE:
What is made when alcohols react with sodium?
Hydrogen gas.
TRIPLE:
What is formed in a reaction between a carboxylic acid and a metal carbonate?
Carboxylic acid + metal carbonate →
Salt + water + carbon dioxide (the same as any acid reacting with a carbonate)
Carboxylic acid + metal carbonate → salt + water + carbon dioxide
TRIPLE:
ethanoic acid + sodium carbonate →
ethanoic acid + sodium carbonate → sodium ethanoate + water + carbon dioxide
TRIPLE:
What type of catalyst is used in a reaction between carboxylic acids and alcohols (ester production)?
Ethanoic acid + Ethanol → Ethylethanoate + water
An acid catalyst
Usually concentrated sulfuric acid



