Forearm, wrist and hand orthopaedics and trauma Flashcards
What is the name given to a fracture of the radius with dislocation of the ulna at the distal radioulnar joint?
Galeazzi fracture dislocation
What is a Monteggia fracture dislocation?
A fracture of the ulna occurs with dislocation of the radial head at the elbow
What is the management for a Monteggia fracture dislocation and why?
ORIF, even in children
Manipulation alone has a high recurrence rate
What is Dupuytren’s contracture?
A proliferative connective tissue disorder where the specialized palmar fascia undergoes hyperplasia with normal fascial bands forming nodules and cords progressingto contractures at the MCP and PIP joints
What is the pathology involved in Dupuytren’s contracture?
Proliferation of myofibroblast cells and the production of abnormal collagen (type 3 rather than type 1)
What proportion of cases of Dupuytren’s contracture are bilateral?
50%
Which fingers are most commonly involved in Dupuytren’s contracture?
Ring and little fingers
Which gender is more affected by Dupuytren’s contracture?
Males 10:1
What can cause Dupuytren’s?
Familial - autosomal dominant inheritance
Alcoholic disease
A side effect of phenytoin therapy
Common in diabetics
What other fibromatosis is Dupuytren’s associated with?
Peyronie’s disease, which affects the penis
Plantar fibromatosis affecting the feet (Ledderhose disease)
When is surgical treatment for Dupuytren’s disease offered?
If contractures are interfering with function
Up to 30° of contracture can be tolerated at the MCP joint and but the PIPJ readily stiffens and any contracture here is usually an indication for surgery
What surgical management is avaliable for Dupuytren’s contracture?
Removal of all diseased tissue (fasciectomy)
Division of cords (fasciotomy)
What causes trigger finger?
Tendonitis of a flexor tendon to a digit can result in nodular enlargement of the affected tendon, and can get stuck in a fascial pulley, holding the finger in a ‘trigger’ position
What fascial pulley is usually involved in trigger finger?
A1
What will relieve the symptoms of trigger finger in most patients?
Injection of steroid around the tendon
Which site of the hands is very common for development of OA in post-menopausal women?
Distal interphalangeal joints
Which metocarpal joint is commonly affected by OA, especially in women?
1st - base of thumb
Which joints in the hands tend to be spared by RA?
DIP joints
What are the three stages of RA in the hands?
Synovitis and tenosynovitis
Erosions of the joints – inflammatory pannus denudes the joints of articular cartilage
Joint instability and tendon rupture – patients can progress to subluxation and chronic tenosynovitis predisposes to extensor tendon ruptures
What are the deformities of the hands seen in RA?
Volar MCPJ subluxation
Ulnar deviation
Swan neck deformity
Boutonniere deformity
Z-shaped thumb
What is a swan neck deformity?
Hyperextension at PIPJ with flexion of DIPJ
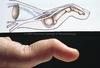
What is Boutonniere’s deformity?
Flexion at PIPJ with hyperextension of DIPJ

Which procedure may prevent tendon rupture in the hands in RA?
Tenosynovectomy (excision of synovial tendon sheath)
What procedure may be required for distal radio-ulnar joint RA?
Resection of the distal ulna


