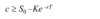Financial Engineering Flashcards
Optimal Hedge Ratio
(Page 57)

Basis Risk
- Basis is usually defined as the spot price minus the futures price
- Basis risk arises because of the uncertainty about the basis when the hedge is closed out
Measuring Interest Rates
•When we compound m times per year at rate R an amount A grows to A(1+R/m)m in one year

Continuous Compounding formula etc.
- In the limit as we compound more and more frequently we obtain continuously compounded interest rates
- $100 grows to $100eRT when invested at a continuously compounded rate R for time T
- $100 received at time T discounts to $100e-RT at time zero when the continuously compounded discount rate is R
Contiuous Compounding Conversion formulas

If the spot price of an investment asset is S0 and the futures price for a contract deliverable in T years is F0, then….
F0 = S0erT
where r is the T-year risk-free rate of interest.
In our examples, S0 =40, T=0.25, and r=0.05 so that
F0 = 40e0.05×0.25 = 40.50
Forward price when an Investment Asset Provides a known Yield/Return
F0 = S0 e<em>(r–q )T</em>
where q is the average yield during the life of the contract (expressed with continuous compounding)
The value of a Forward Contract
•A forward contract is worth zero (except for bid-offer spread effects) when it is first negotiated
•Later it may have a positive or negative value
•Suppose that K is the delivery price and F0 is the forward price for a contract that would be negotiated today
•By considering the difference between a contract with delivery price K and a contract with forward price F0 we can deduce that:
–the value of a long forward contract, ƒ, is
*(F<sub>0</sub> – K )e<sup>–rT</sup> * –the value of a short forward contract is
(K – F0 )e–rT
Forward vs Futures Prices
•When the maturity and asset price are the same, forward and futures prices are usually assumed to be equal.
•
•When interest rates are uncertain they are, in theory, slightly different:
–A strong positive correlation between interest rates and the asset price implies the futures price is slightly higher than the forward price
–A strong negative correlation implies the reverse
Forward Stock Index Pricing
- Can be viewed as an investment asset paying a dividend yield
- The futures price and spot price relationship is therefore
F0 = S0 e<em>(r–q )T</em>
where q is the average dividend yield on the portfolio represented by the index during life of contract
Index Arbitrage
- When F0 > S0<em>e(r-q)T</em> an arbitrageur buys the stocks underlying the index and sells futures
- When F0 < S0e(r-q)T an arbitrageur buys futures and shorts or sells the stocks underlying the index
- Index arbitrage involves simultaneous trades in futures and many different stocks
- Very often a computer is used to generate the trades
- Occasionally simultaneous trades are not possible and the theoretical no-arbitrage relationship between F0 and S0 does not hold (19 October 1987)
Futures and Forwards on Currencies
- A foreign currency is analogous to a security providing a yield
- The yield is the foreign risk-free interest rate
- It follows that if rf is the foreign risk-free interest rate
F0=S0e(r-rf)T
Consumption Assets Formula
Storage is Negative Income

The Cost of Carry

Valuation of an Interest Rate Swap
- Initially interest rate swaps are worth close to zero
- At later times they can be valued as the difference between the value of a fixed-rate bond and the value of a floating-rate bond
- Alternatively, they can be valued as a portfolio of forward rate agreements (FRAs)
The Put-Call Parity
- Both are worth max(ST , K ) at the maturity of the options
- They must therefore be worth the same today. This means that
c + Ke -rT = p + S0
Reasons For Not Exercising a Call Early (No Dividends)
- No income is sacrificed
- You delay paying the strike price
- Holding the call provides insurance against stock price falling below strike price

Bull Spread Using Calls

Bull Spread Using Puts
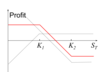
Bear Spread Using Puts
Figure 11.4, page 240

Bear Spread Using Calls
Figure 11.5, page 241
What is a Box Spread?
- A combination of a bull call spread and a bear put spread
- If all options are European a box spread is worth the present value of the difference between the strike prices
- If they are American this is not necessarily so (see Business Snapshot 11.1)

Butterfly Spread Using Calls
Figure 11.6, page 242