Final Flashcards
(122 cards)
How long does Chlorohexidin last?
8-12hrs
Which procedure would be best indicated to perform shortening of the oral commissure after?
total hemi-mandibulectomy- incision is so far back and now you don’t have that side of the mandible there for
support
Which graft requires a bed of granulation tissue before placement?
punch graft
What is the main indication for ‘Tubing the flap’?
It is a second option instead of bridging incision
Older dog, crown of tooth fractured off and pulp is exposed, what should you do?
Complete root canal and seal over
A dog comes in the next day and owner said tooth was loose. Based on the image, what occurred?
tooth luxation
Which of the following surgery would be indicated for the above procedure? (tooth luxation)
extract the tooth- not viable more than 30mins
Dog with prosthetic hip and coming in for GI obstruction surgery, and you give him Abx 30 mins prior to the procedure,
what kind of Abx administration is this?
prophylactic abx
Wet to dry bandage is indicated for which situation?
Infected traumatic wound with Debris – wet-to dry (adherent bandage) is used for microdebridement.
Based on this pic, which would stimulate granulation tissue the fastest?
VAC
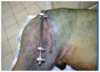
Image of salivary mucocele sx and had 2 arrows, what are these arrows pointing to?
Digastricus muscle and lingual nerve
Which of the following surgical procedures is indicated for this (picture) labial flap?
Single advancement pedicle flap
What is an axial pattern flap?
Transpositional flap
What is the diagnostic tool of choice for foreign body causing obstruction?
US
Dog gets a traumatic wound and you decide to wait a day to close it?
delayed primary closure- bc there is no granulation tissue formation before you suture
Which option is most likely to reduce number of bacteria in a wound with moderate pressure?
20-60cc and 18G needle
Which NOT an advantage of active drains over passive drains?
a. Decreased risk of infection
b. Decreased risk of maceration around drain opening
c. Ability to quantify drainage
d. Risk of part of the drain breaking off during removal is less
d. Risk of part of the drain breaking off during removal is less
Which allows you to decrease dead space while advancing skin?
Walking sutures
What is the elevator within, as a landmark for extraction? (Image of an elevator in the tooth furcation)
Furcation – in extraction of multi-rooted teeth, we section the tooth at the furcation of roots (bw them)
In male dogs, you sometimes stop the incision cranial to the prepuce for a celiotomy. T/F
false- No, you pull the prepuce laterally and make incision slightly paramedian but don’t stop cranial to it
Lesion in the mid-rectum, not in the abdominal cavity OR anal canal. Which of the following approach would you use?
dorsal approach
Dog with hemoabdomen. The owner wants to know what is the % chance it’s a BENIGN tumor?
25%
75%- chance of malignant tumor
Which of the following is NOT an indication for Nephrouretectomy?
a. Hematuria secondary to blunt trauma to the abdomen
b. Avulsion of the renal pedicle
c. Unilateral renal adenocarcinoma
d. Unilateral uncontrollable pyelonephritis
e. Idiopathic renal hematuria
a. Hematuria secondary to blunt trauma to the abdomen
If you perform a bilroth 2 and … , what do you have to do?
a. Cholecystectomy
b. Cholecystoduodenostomy
c. cholecystojejunostomy
c. cholecystojejunostomy- bc the duodenum was removed