Final Flashcards
(53 cards)
In mice, albino coat (a) is recessive to agouti coat color (A) and short whiskers (s) are recessive to long whiskers (S). The genes controlling these traits are 6 map units apart. In the cross As/aS x as/as, what proportion of offspring are predicted to have agouti coats and long whiskers?
A. 0.03
B. 0.06
C. 0.47
D. 0.94
E. 1.00
F. 0.00
A. 0.03
In potatoes, dotted leaf (D) is dominant over undotted leaf (d), and smooth tuber (S) is dominant over wrinkled tuber (s) fruit, which is covered with fine hairs. A farmer has two tall and smooth tomato plants, which we will call plant A and plant B. A plant breeder crosses a heterozygous potato plant with dotted leaves and smooth tubers with a plant with undotted leaves and wrinkled tubers and the following numbers of progeny:
DdSs-122; Ddss-6; ddSs-4; ddss-124
What is the map distance between the leaf type and tuber type genes?
A. 4 mu
B. 2 mu
C. 8 mu
D. 16 mu
E. 50 mu
A. 4 mu
In potatoes, dotted leaf (D) is dominant over undotted leaf (d), and smooth tuber (S) is dominant over wrinkled tuber (s) fruit, which is covered with fine hairs. A farmer has two tall and smooth tomato plants, which we will call plant A and plant B. A plant breeder crosses a heterozygous potato plant with dotted leaves and smooth tubers with a plant with undotted leaves and wrinkled tubers and the following numbers of progeny:
DdSs-122; Ddss-6; ddSs-4; ddss-124
What is the arrangement of alleles in the heterozygous plant?
A. DS/ds
B. Ds/dS
C. Dd/Ss
D. DD/ss
A. DS/ds
The spliceosome recognizes the 5’ and 3’ splice sites when:
A. RNAs within the spliceosome bind to consensus sequences at the junctions of introns and exons
B. proteins within the spliceosome
C. proteins within the spliceosome
D. RNAs within the spliceosome
A. RNAs within the spliceosome bind to consensus sequences at the junctions of introns and exons
In eukaryotes that cap their mRNAs, the first nucleotide used as a template during transcription:
A. could be any nucleotide
B. is always a C
C. is always a G
D. is always an A
E. is always a T
A. could be any nucleotide
When an mRNA from a rat was hybridized to the corresponding single stranded DNA, it produced the following structure. This structure suggests:

A. the presence of three exons
B. the presence of one exon
C. the presence of two exons
D. the presence of three introns
E. alternative splicing
A. the presence of three exons
The mRNA needed to direct the synthesis of a 400 amino acid polypeptide is predicted to be _____ nucleotides long.
A. >1200
B. 400
C. 600
D. 800
E. 1200
F. 1203
A. >1200
Based on how each of the following molecules works, which of the following proteins must have the ability to join broken DNAs back together?
A. single strand binding protein
B. DNA helicase
C. DNA topoisomerase
D. DNA polymerase III
E. DNA polymerase I
C. DNA topoisomerase
The 5’-3’ exonuclease activity possessed by some DNA polymerases is used by these enzymes in:
A. proofreading
B. primer removal
C. DNA chain elongation
D. ligation of DNA strands
E. transcription
B. primer removal
If eukaryotes had circular chromosomes, which of the following molecules would no longer be needed?
A. primase
B. topoisomerase
C. single-strand binding protein
D. telomerase
E. DNA helicase
F. DNA polymerase
D. telomerase
The nucleosome found on newly replicated DNA molecules:
A. contain nucleosomes either that
B. are derived entirely from the amino
C. contain some subunits of the pre-existing nucleosomes remain intact and other parts are assembled from newly synthesized histones.
C. contain some subunits of the pre-existing nucleosomes remain intact and other parts are assembled from newly synthesized histones
A promoter is:
A. a transcription factor
B. a consensus sequence in RNA
C. a sequence important in promotion
D. an enhancer
E. a sequence in DNA
E. a sequence in DNA
The looping of long stretches of DNA is often important in:
A. transcription initiation in bacteria
B. transcription termination in bacteria
C. binding of rho to RNA
D. transcription initiation in eukaryotes
E. transcription termination in eukaryotes
D. transcription initiation in eukaryotes
Which of the following statement about mitochondria and chloroplasts is FALSE?
A. Plants have chloroplasts and mitochondria
B. The vast majority of mitochondria
C. Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain the vast majority of the genes needed for organelle function
D. Mictochondria go through cycles
E. There are well-documented organisms
C. Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain the vast majority of the genes needed for organelle function
The form of inheritance in which differences in phenotype are not due to differences in DNA sequences or environments, but do to stable alterations of chromatin structure is known as:
A. neogenetics
B. Mendelian genetics
C. molecular genetics
D. organelle genetics
E. epigenetics
E. epigenetics
Histone proteins are:
A. negatively charged
B. positively charged
C. non-polar and non-charged
D. polar and non-charged
B. positively charged
The molecule below is a:
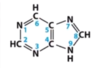
A. pyrimidine
B. purine
C. deoxyribose sugar
D. ribose sugar
E. cytosine
B. purine
Where would a nitrogenous base be attached to the following molecule?

E
Imagine that a bacterial gene is added to an efficient in vitro transcription system (a test tube system that allows transcription). However, transcription of this gene cannot be initiated. What is a plausible explanation fo the problem?
A. There is a mutation 10 nucleotides upstream from the normal transcription start site
B. histones that were on the DNA
C. there is a mutation in the in vetro
D. rho has not been added
E. bacterial TATA-binding protein
A. there is a mutation 10 nucleotides upstream from the normal transcription start site
The following image is an electron micrograph of DNA molecules that are being transcribed. Which arrow points closests to a promoter?

C
In the following diagram of a replication bubble, which strand or strands of template DNA would support the synthesis of the lagging strand or strands of newly synthesized DNA? (multiple answers)

A and D
What will be the sequence of newly synthesized DNA made form the following primer/template combination?

A. 5’ATGCGA3’
B. 5’ACTGC3’
C. 5’CGTCA3’
D. 5’AGCGTA3’
B. 5’ACTGC3’
The results of the following study suggest that:

A. DNase is ineffective at digesting
B. it is only possible to purify DNA
C. DNase is specific for globin gene
D. changing the association of DNA with proteins is an important element in regulating gene expression
E. nucleosome is not assembled
D. changing the association of DNA with proteins is an important element in regulating gene expression
Imagine creating a set of reproductively isolated populations of the same species with the same initial frequency of a particular allele. These reproductively isolated populations are allowed to continue for many generations. Considering only the effect of genetic drift, the variance in allele frequency between a set of populations like these is predicted to be smallest when the reproductively isolated populations are:
A. small
B. large
C. inbred
D. outbred
B. large





