facts Flashcards
why/ when to give potassium along with IV insulin
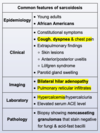
hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (exacerbation of DM) glucose < 600 with normal electrolytes and serum osmolality > 350 have to give potassium if < 5.3 bc even though lab K is normal, its actually low bc of urinary K release (inc glucose= osmotic diuresis)
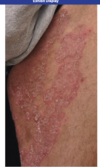
sore throat, cough worse at night, morning hoarseness, inc need for albuterol inhaler after meals dx?
in this dx - what would be alarm sx (6) and how do they change management approach
GERD (often associated w asthma bc micro-aspiration of gastric contents w GERD leads to inc vagal tone and bronchial reactivity = asthma)
alarm sx= get endoscopy!!
- weight loss, hematemesis, melena, persistant vomiting, dysphagia, anemia

osteoporosis risk factors (6)
old age low weight postmenopausal smoking excessive alc intake sedentary lifestyle
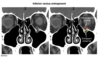
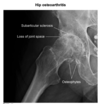
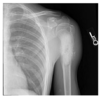
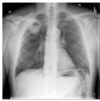
pointing at what, what is this called
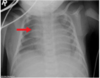
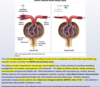
thymus: sail sign
effect of hyperALD on system pH
tPa- what is the actual medication
IV altepase
what is kleptomania
impulse control disorder starts in adolescence, the impulse to steal little things. instant relief when they do it followed by guilt or shame.
gallstone pancreatitis
in addition to pancreatitis signs, what suggests specfically gallstones pancreatitis and how do you diagnose
in addition to epigastric pain that shoots to the back and inc amylase:
inc BMI, ALT>150, inc Alk Phose suggest GB Pancreatitis
get a RUQ US to confirm
what is the gold standard for diagnosing celiac’s and why that specifically?
colon biopsy revealing villous atrophy
anti-TTG ab might actually be negative because celiac ds is associated with IgA deficiency. so a negative anti-TTG ab does not rule out celiac
precocious puberty vs premature thelarche/adrenarche
bone age

what is the histopathological change seen in diabetic nephropathy

what is the finding
what disease is this finding associated with

thymoma (an anterior mediastinal mass)
-Myasthenia Gravis: will present with dysphagia and unable to swallow = bulbar dysfunction
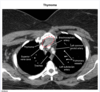
what is the pathiphysiology of myasthenia gravis
autoAb from the thymus against n-Ach R in the neuromuscular junction –> impaired action potential at receptors –> M wkness
will have weakness that is worse throughout the day, often presents with fatiguable chewing or dysphagia
treatment for:
- asx gallstones
- gallstones with biliary colic
- acute gallstones w cholecystitis, hemodynamically stable patient
within 72 hours dec mortality and length of hospital stay compared to delayed surgery

dx + treatment of toxic megacolon
dx= colonic dilation > 6cm on CT, loss of haustra
trx= if pt is stable, can do IV fluids, bowel rest, nasogastric decompression, broad spectrum Ab
TM secondary to UC–> IV glucocorticoids is first line therapy
MC cause of viral gastroenteritis
norovirus
presents w non-bloody non-bilious V, abd pain, and waterry diarrhea
develops 2-3 days after the event (school event, cruise..)
what is the time frame needed for a diagnosis of major depressive disorder
2 weeks

what are the sx of organophosphate poisoning
what is the treatment

risk factors and organisms that cause emphysematous cholecystitis
- DM, vascular compromise, immunosuppression
- C. dif, E. coli

5 big risk factors for avascular necrosis
- femoral head fracture
- glucocorticoids
- excessive alc use
- SLE
- sickle cell
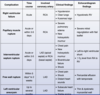
how does acetazolamide effect the renal tubule?
which diuretics can cause hypokalemia?
which diuretics are K-sparing?
which diuretics can cause metabolic acidosis?
- acetozolamide= prevent proximal reabsorption of bicarb
- hypokalemia = thiazide diuretics
- K sparing= spironolactone/eplerenon, amiloride
- can cause metabolic acidosis= amiloride (dec gradient for H+)
- amiloride = direct inhibit ENaC: can also cause hyperkalemia
- vs spironolactone= x ALD receptor= indirect ENaC inhibit: spare K but no cause met acid
–if develop hyperK –> switch to another BP agent i.e. CCB amlodipine

primary sclerosing cholangitis
- lab markers
- complications/inc risk for what else
PSC
- inc alk phos (+bilirubin), inc GGT
- 90% pts have IBD –> need to get colonoscopy to rule it out if you have PSC
- inc risk for colon CA, cholangiocarcinoma, biliary CA
- inc risk for biliary strictures, cholelithiasis, cholestasis –> dec ADEK, osteoporosis
- preferred INR range for warfarin in setting of a fib.
- going into surgery/in hemorrhage, how do you adjust the INR
- preferred for a fib: btwn 2-3
- bring INR back to ~1= give prethrombin complex concentrate (factors 2,9,7,10,protein c&s) + IV vitamin K
how do you calculate the “number needed to treat” to have X effect
NNT= 1/(absolute risk reduction)
ARR= (risk of control) - (risk of experimental group)
(i.e. 24% placebos got asthma, 17% treated got asthma –> ARR= 24-17 = 7.2 % –> NNT= 1/0.072 = 14)
hodgkin lymphoma
peak age
clin presentation
histo findings
- yound adult (30s) or >60
- 40% have B sx (weight loss, night sweats, fevers)
- most present for painless LAD (cervical + mediastinal), or a mediastinal mass found on CXR
- hepatosplenomegaly
- inc LDH
- histo= giant cells w bilobed nuclei in germinal centers
how does a PET scan work, what will results look like
sends radiotracer that will be taken up by cells with high metabolic activity = neoplastic cells
BUT also includes the brain, kidneys (and thus bladder), and liver so these places will also light up even if no mets there
characteristic heart changes in takotsobu cardiomyopathy : what is the timeline
literally acute, within a day can happen
present with balloon shape on echo = segmental mid- , apical, and basilar hypokinesis
ARDS timeline and CXR findings
= takes 6-72 hours after the inciting event to develop (while the inflammatory response develops)
presents with diffuse, bilateral infiltrates
what is flail chest, how does it happen
fractures of 3+ adjacent ribs in 2+ areas
the groups of fractured ribs start moving paradoxically and will also injure the lung underneath
=flail chest with increased work for breathing and dec oxygenation –> respiratory failure –> mechanical ventilation
when to use ERCP, MRCP, HIDA Scan
what imaging modality is best for visualizing the pancreas for CA or inflammation
- ERCP = suspected choledocolithiasis
- MRCP= visualize the biliary and pancreatic ducts to asses for biliary obstruction or cholangiocarcinoma
- HIDA scan= look for cholecystitis in suspected patients
- best for viewing pancreas for CA or inflammation = CT abd
does celic ds increase risk for colon CA
no!
mild inc risk for small bowel cancer, but not even enough to screen for it
pediatric septic arthritis
- MC pathogens
- management
MC pathogens
- <3 months = s. aureus, Grp B strep, G- bacilli
- > 3 months= s. aureus, Grp A strep
management
- get an arthrocentesis to confirm dx and get a culture
- AFTER getting culture, start empiric abx for that organism
- bc of long term damage, need prompt surgical drainage to decompress and clear debris
how to calculate
- relative risk
- relative risk reduction

name a complication associated with treating hemophilia with Factor 8 replacement therapy
inhibitor development:
- the body begins to recognize the infusions as foreign material and makes Abs to the infusions
- presents as breakthrough bleeds despite long standing control with treatment, or hemorrhage unresponsive to trx = inc PTT, n PT
- trx for this= provide infusions of factors that bypass the need for factor 8 in the first place = recombinant factor 7, activated prothrombin complex (so you don’t need factor 8 to make 10 to make thrombin)
strongest predictor of nursing home placement for parkinson’s patients
risk of this predictor increases with what
how do you trx the onset of this predictor
psychotic sx, MC visual hallucinations and paranoid delusions
=a late stage sx of PD, but risk increases when you add/replace carbidopa/levidopa with the dopamine agonists= pramiprexole, ropinorole
=preferred trx=
- FIRST dec carbidopa/levidopa dose
- IF NO IMPROVE –>low potency antipyschotics w minimal D antagonism = queitiapine, clozapine, pimavanserin
MC pediatric elbow fracture
what kind of injury is it associated with
what adjacent structure is MC injured with this kind of frx
supracondylar humerus fracture
falling on an outstretched arm
brachial A with displaced bone (humeral shaft forward)
- ulnar nerve is more distal

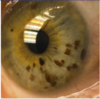
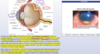
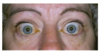
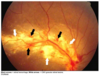
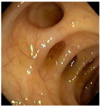
what pathology is this fundoscopic exam associated with

diabetic retinopathy
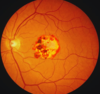
what pathology is this fundoscopic exam associated with


CSF diagnostic findings that suggest MS
oligoclonal IgG bands on LP

describe x-ray findings for acute respiratory distress secondary to foriegn body aspiration

what drugs are associated with macrocytic anemia
alc
hydroxyurea
zidovudine
chemo drugs

dx of babesiosis = sx? lab changes? blood smear?

clinical difference in ulnar N injury at the wrist vs elbow
at wrist= 4th+5th digit numbness and parasthesias and intrinsic hand weakness = clumsy
at elbow= ^^ plus grip strength weakened and weaker hand flexion
what pathology is associated with this fundoscopic exam

CMV retinopathy
in a patient w hx of a single episode of unipolar depression: once you start an antidepressant and sx have remitted, how long do you have to stay on the med?
recommend additional 6 months= continuation phase trx
what is this called
complications if left untreated?


“episodic inconsolable crying w hips flexed up with asx periods of play inbetween” is classic presentation of what
intussussception

what clinical signs are sufficient to diagnose diabetic nephropathy without getting a biopsy,etc?
-persistant albuminuria and/or dec GFR AND 1+:
- prolonged hx of DM dx > 5 years
- retinal neovascularization (diabetic retinopathy) bc they are both microvascular complications of DM and so are usually associated
what is the difference between Steven Johnson and toxic epidermal necrolysis
causes- 3 drugs, 2 classes, 3 path
the body surface amount only
<10% = SJS
>30%= TEN

what is waterhouse-freidrichson syndrome
vasomotor collapse secondary to adrenal hemorrhage in the setting of meningococcemia
= adrenal gland failure
presents w meningitis, purpura and petechiae, sudden hypotension–> resp failure–> 100% mortality
CONSIDER THIS in a patient with history of ulcerative colitis and now has a cholestatic pattern of enzyme abnormalities
what test will i do to confirm the dx
primary sclerosing cholangitis (90% pts have UC)
MRCP= rapid and noninvasive–> will show the beaded duct
vs PBC associated w celiac ds, CREST, hashimoto
list the 3 inactivated (killed) vaccines
polio
Hep A
influenza
(inactive HIP)

list the two inactivated toxin vaccines
diptheria
tetanus
DT= dead toxin

list the 5 live, attenuated vaccines
measles
mumps
rubella
varicella
rotavirus
(live motor= VRRMM)

list the 6 conjugated vaccines
Hep B
H influenzae B
HPV
Pertussis
Pneumococca
Meningococcal
what disorders are associated with causing gout
myeloproliferative disorders
tumor lysis syndrome
CKD

explain how an acute aortic aneurysm can lead to pulmonary edema and orthopnea
tear upwards–> aortic regurge –> backflow into lungs

differentiate btwn the diff stages of HTN in pregnancy
(vs n renal changes in preg)
–> gestational HTN= >140/>90 new onset HTN at 20+ wks
NO PROTEINURIA on 24 hour urine
–>pre-eclampsia= HTN + proteinuria / end organ damage
–>pre-eclampsia _w severe feature_s=
- new onset HTN >160/>110
- OR HA/visual hanges / pulm edema
- OR Cr>1.1
- OR inc AST/ALT or plts<100,000
- severe features = greater morbidity = eclampsia, abruptio placentae, fetal demise
–>eclampsia= HTN + proteinuria + new- onset seizures
vs n renal changes = inc BUN, inc Cr
- (bc of inc GFR + BM permeability)
- nin preg = 0.4-0.8
classic ecg and CXR findings for PE
how sensitive?
MINORITY OF PTs
ecg= prominent S lead 1, prominent Q lead 3, inverted T L3
- S1Q3T3
- afib is also associated w PE
cxr=
- hampton hump= lateral wedge
- westmark sign= space of dec markings surrounded by normal markings
- , palla’s sign= prominent R descending pumonary A
in a presentation of bilateral trigeminal neuralgia, suspect this
MS
post-traumatic hemorrhagic shock is likely due to bleeding from where
- external bleeding
- chest (can lose up 40% BV)
- abd: up to entire BV, into perotineum
- pelvis: up to entire BV, hidden in retroperitoneum
- thigh: 1-2 L per thigh
post traumatic ischemic stroke would present as how
-bradycardia and flacid paralysis and hypotension (loss of sympathetic tone)
or Cushing’s Triad
- HTN
- bradycardia
- irregular respiration
in which patients is succinylcholine not recommended for use as anesthesia (i.e. in rapid procedures)
why
what should be used instead
- succinylcholine should not be used w patients at risk for hyperkalemia = extensive skeletal muscle injury, burn injury, disuse muscle atrophy, denervation syndromes (i.e. stroke, Guillan-Barre, polynueropathy)
- succinylcholine is a depolarizing NMSK agent can cause hyperkalemia, the above conditions will also cause inc K and will upregulate Ach-R. this leads to inc risk of cardiac arrhythmias w use of succinylcholine
- instead use non-depolarizing NMSK agent= vecuronium, rocuronium
is patent ductus arteriosus cyanotic at birth
NO
transposition of the great vessels presents how? treatment?
- presents with cyanosis at birth with a loud single S2 and a narrow mediastrinum (egg on a string CXR)
(tachypnea and subcostal retractions)
- treat with prostaglandins to keep open a PDA that is required to live
what is the etiology of a metaphyseal corner fracture
occurs from forced pulling or twisting of the arm
red flag for child abuse

increased PTT that does not correct with a mixing study suggests what
this pathology is associated with what other symptoms
a coagulation inhibitor (rather than factor deficiency)
MC = lupus anticoagulant, present in antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
- APAB has inc PTT but not PT
- associated w livedo reticularis, IBS, migrains
infections can lead to (inc/dec/no change) in platelet levels
inc = thrombophilia
who dat

in what clinical setting does malignant hyperthermia present
vs. another syndrome that can cause pt to present w T>104 and neuro changes
vs post dural HA
- malignant HTN presents in ppl geneticall predisposed who are anesthetized w halothane or succinylcholine
- vs exertional heat stroke: exertion outside in heat, inc risk w obesity, dehydration, use of : anticholinergics, anti-psychotics, tricyclics
postdural HA
- post partum: after neuroaxial anesthesia (epidural) –> occipital HA, worse w sitting or standing bc of CSF leak, but NO focal neuro signs
- trx= epidermal patch
management of newborns with erb-duchenne palsy
observation and PT: 80% of pts have spontaneous recovery within 3 months
-if no improve in 3-9 months, can get surgery but its not necessarily curative
anti-CCP Abs are associated with
Rhematoid Arthritis
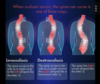
what manuevers increase + decrease the intensity of the murmur in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
what is the etiology of the murmur
HOCM = LV wall thickening, MC in basal AV septum (asymmetric septal hypertrophy)’
- systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve –> anterior (abn) motion of mitral valve leaflets towards the IV septum –> LVOT obstruction during systole –> crescendo-decrescendo murmur
increase
- Valsalva
- abdrupt standing
- nitroglycerin
decrease
- sustained hand grip
- squatting
- passive leg raise

how does the valsalva change heart fluid dynamics
which murmurs does it inc and which dec
dec preload
- dec LV volume = inc murmur: hypertrophic cardiomyopathy + mitral valve prolapse
dec flow across stenotic valve= dec murmur: aortic stenosis
how does a sustained handgrip affect cardiac fluid dynamics
which murmurs does it inc and which dec
= inc afterload + BP
- inc = aortic regurge, mitral regurge, VSD
- dec= hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and aortic stenosis
how do the following affect aortic stenosis murmur
- valsalva
- squatting
- sudden standing
- sustained handgrip
- valsalva (dec flow across stenotic valve)= softer
- squatting = no change
- sudden standing (dec flow across stenotic valve)= softer
- sustained handgrip (dec P gradient) = softer
how do the following affect mitral valve prolapse
- valsalva
- squatting
- sudden standing
- sustained handgrip
- valsalva (dec LV volume) = louder
- squatting (inc LV size) = softer
- sudden standing (dec LV volume) =louder
- sustained handgrip = no change
what are the top 5 (in order) lifestyle interventions that will decrease BP?
- DASH diet
- weight loss
- aerobic excercise
- dec Na
- dec alc

MC post-op pumonary complication
atelectasis = impaired cough, shallow breathing
treatment of osteomyelitis in
- healthy kids
- sickle cell ds
healthy kids:
- probs NOT MRSA = nafcillin/oxacillin or cefazolin
- probs IS MRSA = clindamycin / vancomycin
sickle cell kids
- clindamycin + ceftriaxone
- or vancomycin + cefotaxime
- (to cover MRSA + salmonella)
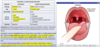
child with acute onset respiratory distress, dysphagia, and drooling
epiglottitis
acute, due to narrow airway : need intubation
cranial N palsies associated with subarrachnoid hemorrahge
= aneurysm rupture (sudden onset, i.e. on toilet)
CNIII= down and out, ptosis = MC
CNII= unilat vision loss, bitemporal hemianopsia

workup of a suspicious thyroid nodule in pregnancy
get a serum TSH and US to check for suspicious anatomy (irregular margins, internal vasculature, microcalcifications)
- if suspecting malignancy, get a FNA
- if shows v aggressive, can do thryoidectomy in second trimester, otherwise wait until after pregnancy
- just don’t give radioactive iodine for imaging or trx bc that is teratogenic
what is the dexamethasone test used for
to assess for cushing’s sydnrome (inc cortisol)
- sx= M weakness, fasical flushing, supraclavicular fat pads
- = adrenal tumors or ACTH secreting pituitary tumors

differentiate btwn presentation for cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellularcarcinoma
cholangiocarcinoma
- inc Alk phos > inc AST/ALT
- inc CEA, CA 19-9, n AFP
- inc direct bilrubin, GGT, ALP
- hx of PSC secondary to UC, or hx of fibrocystic liver ds
- acholic stools, dark urine, pruritis, RUQ heaviness/mass,
hepatocellular carcinoma
- inc AST/ALT > inc ALK phs
- n CEA, CA 19-9 , 50% have inc AFP
- hx alchoholism, chronic viral hepatitis
- RUQ pain, cachexia
management of pneumothorax
- spontaneous = tall, thin, young men vs. tension
- small (<2 cm) & stable = observe, O2
- large & stable = needle thoracostomy, chest tube
- unstable = chest tube > emergent needle decompression
finding and dx
management?

adbominal perforation
i.e. hx of GERD..postprandial, sudden worsening w lots of epigastric pain –> perforated peptic ulcer
- FIRST emergent surgical exploration to clear up secretions = dec mortality
- THEN.. IV PPI, fluids, nasogastric suction

blood smear and mean age groups for ALL vs CLL
-blood smear and population for burkitt lymphoma
ALL
- blast cells on blood smear (small nucleoli and scant cytoplasm)
- children
CLL
- smudge cells (fragile lymphocytes)
- ~70 yo
burkitt
- starry sky appearance
- EBV pts
exertional heat stroke vs heat exhaustion
both have <104T w sweating, N/V, HA, dizzy, tachycardia, hypotension
exertional heat stroke = AMS
heat exhaustion= no CNS dysfunction
single MC cause of neonatal meningitis within first 7 days
Group B strep –> can lead to sepsis w high mortality
- low chance of transmission if mom is prophylaxis
- but if C section and mom not given prophylaxis, she can still go home and give it to baby
- listeria presents a lot like GBS but 1. GBS is more common 2. mom would have had flu like sx w listeria infection from food
MC lung cancer in teens + YA, and how does it present
bronchial carcinoid tumor
presents w recurrent pnuemonia or hemoptysis

what kind of MI is most likely to lead in eccentric hypertrophy of the heart
how can this be prevented
anterior MIs (affecting the LV) are more likely to lead to dilated cardiomyopathy (eccentric hypertrophy) via neurohormonal signalling of cardiac remodeling
- one of the neurohormonal pathways = RAAS
- trx w ACE-I post anterior-MI can help prevent dilated cardiomyopathy –> ischemic heart disease –> death
exposure to a house fire can lead to inhalation poisening from what two substances
carbon monoxide
cyanide
- HA, vertigo, dizzy, N/V, tachy, hyperventalation (dec paCO2), inc LDH
dx?


sudden onset of abd pain, dehydration, and elevated K in a young person who suddently and severely dec carbs and calories
dx?
diabetic ketoacidosis
- type 1 DM in young pt (maybe they didn’t know), DKA can be precipitated by low calorie/carb
- insulin resistance= less K being taken up by cells bc usually insulin and K go in together
=inc total body K even tho you are also increasing excretion via kidneys (hyperosmolarity)
for who is the PPSV23 vaccine recommended
- >65
- <65 if they have comorbid conditions that inc risk of pneumococcal infection = chronic liver/lung/heart disease, DM, smoking
describe the clinilcal exam findings for varicocele
-“irregular mass seperate from and superior to the testes” that does NOT transilluminate, worse with standing long persiods and valsalva, decreases w lying supine
BUN: Cr > 20 suggests what
pre-renal azotemia
=AKI due to hypovolemia (i.e diuretic use that causes dec BP…)
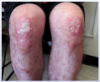
what is the medical name for eczema
atopic dermatitis
second hand smoke is a risk factor what 3 childhood illnesses
dental caries
pneumonia / other lower resp tract infections
middle ear ds
what is the meaning of
- HBs Ag
- HBe Ag
- HBc Ab IgG
- HBc Ab IgM
- HBs Ab
- HBc Ab
the vaccine only has Hbs protein
to have Hbc Ab you have to have had HBV
+AntiHbc, +AntiHbs = previous resolved infection

sudden onset severe epigastric pain and vomiting with hx of postprandial RUQ pain +nausea, PE reveals diffuse tenderness and stool guaiac is positive
how to confirm diagnosis
perforated peptic ulcer (probs undx PUD)
- DIFFUSE tenderness (peritonitis), positive guaiac points to PUD
- get an upright Xray abd+chest –> will show abd free air: emergent surgery
- cholecysitits would have pain specifically in RUQ, no peritonitis, would NOT have a + stool test
what lab values suggest hypovolemia
inc Hgb, inc BUN + Cr
w dry mucus membrane
ECG findings for LV hypertrophy
LV hypertrophy
- high voltage QRS complex
- inverted T waves V5-V6 (lateral)
- ST segment depression V5-V6 (lateral)
presenting difference between neuroleptic malignant syndrome and serotonin syndrome
- NMS= generalized M rigidity
- SS= hyperreflexia, myoclonus, tremor
left sided flank pain, hematuria –> varicocele in testes
what is the dx?
renal vein thrombosis
L gonadal V drains into L renal V so it will all back up and you get L sided engorged veins
-due to underlying hypercoagubility (i.e. from nephropathy, RCC)
- most sensitive test for diabetic nephropathy
- screening requirements
- urine albumin: creatinine ratio (will detect earlier, smaller changes in albumin clearance)
- annual test in diabetics: starting at dx with Diabetes type 2 and 5 years post-dx with Diabetes type 1
knee swelling and pain: xray shows punched out lesions with a rim of corticol bone
dx?
what will arthrocentesis show?
gout
inflammatory effusion with negative bifringent needles
hypercalcemia of malignancy is a paraneoplastic syndrome of which CAs
Cushings is a paraneoplastic syndrome of what CAs?
PTHrP releasing tumors
- squamous cell CA head, neck, lung, renal, bladder, ovarian, breast
ACTH releasing tumors (inc melanin + cortisol)
- neuroendocrine tumors : MC = small cell lung CA > medullary thryoid CA, bronchial carcinoid tumor
urine dipstick results for acute pyelonepthritis
positive nitrates and positive leukocyte esterase
- what kind of study asseses a disease group (against control) to compare risk factor frequency
- what kind of study assesses a risk factor group (against a control) to compare current disease prevalence
- what kind of study follows a risk factor group (against a control) to compare future disease prevalence
- CASE STUDY= asseses a disease group (against control) to compare risk factor frequency
- CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY= assesses risk factor group (against a control) to compare current disease prevalence
- PROSPECTIVE STUDY= follows a risk factor group (against a control) to compare future disease prevalence
which patients should be considered for a carotid endarterectomy procedure (as opposed to just clopidogrel + lifestyle changes)
patients with carotid artery stenosis who
- have a history of TIA/stroke from the effected carotid vessel within the last 6 months
- AND have 70%+ stenosis = high grade stenosis
risk factors for primary nocturnal enuresis
first step in eval of primary or secondary enuresis
family history
boys 5-8
NOT psych stuff
SECONDARY enuresis= psych stuff or underlying medical condition
first step = urinalyses
- after, address behavioral concerns or underlying medial conditions

- risk factors for apical bleb rupture
- risk factors for extensive lung atelectasis
CP, dyspnea, hypoxia, unilat dec breath sounds
- apical bleb rupture: spontaneously occurs in pts with hx COPD, lung ds = usually no tracheal deviation, only if large enough
- lung atelectasis: preceded by insulting factor = aspiration, malignancy, pnuemonia (severe, w mucus plug) : associated with tracheal deviation
preferred imaging modality to diagnose ureterolithiasis
stone stuck in the ureter (can’t sit still, referred pain down to groin, sudden onset..)
- best = abd US
- spiral CT abd/pelvis WITHOUT contrast
what kind of imaging would you get if you have suspicion of subclavian vessel injury (i.e. displaced fracture of clavivle and hemodynamic instability/bruising and bleeding)
CT of the CHEST, w IV contrast
will show injury to the subclavian vessels, as well as any possible lung /pleura injury (i.e. pneumothorax)
heparin incuded thrombocytopenia (HIT) increases risk of what kind of blood complciations
arterial / venous THROMBOSIS
- (dec plts bc spleen attacks the Abs on the plts, but the Abs actually cause activation so inc thrombosis)
- NOT bleeding probs
- i.e. low molecular weight heparin = enoxaparin
x fibrillin 1 –> ?
x fibrillin 2 –> ?
x collagen –>
x fibrillin 1 –> marfan’s
x fibrillin 2 –> congenital contractural arachnodactyly (tall, arachnodactyly, multiple contractures of large joints)
x collagen –> ehler’s danlos
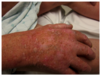
fever, sore throat, cervical LAD, rash that develops after taking amoxicillin
dx?
INFECTIOS MONO
rash post amoxicillin= Hallmark
alcoholic hepatitis will lead to what characteristics lab changes? (3)
- AST= 2(ALT) (but less than 500)
- inc GGT (enzyme found in hepatocytes)
- inc ferritin (an acute phase reactant)
what is this sign called and what is the dx

teeth appear worn and smooth: what should you suspect?
nocturnal bruxism
= grinding their teeth at night, maybe don’t even know it
possible causes for acquired platelet dysfunction
- ASA use
- uremia
- advanced liver ds
- cardiopulmonary bypass
of the infectious genital ulcers, which are painful and which are not painful
painful
- HSV
- haemophilus ducreyi (chancroid)
NO pain
- syphillis (chancre)
_BOTH PAINLESS AND THEN PAINFU_L
Chlamydia serotype L1-L3 = lymphogranuloma venereum = first is painless and small so often missed, but then it comes back as a painful buboe
pernicious anemia is due to a decrease in what
- etiology
- inc risk factor for which CA
-dec Vit B12!
– due to Ab against intrinsic factor = no absorb Vit B12 in stomach
—Ab against intrinsic factor also injures parietal cells –> chronic infl –> inc risk of gastric CA
in setting of rib fracture, what is most essential for preventing pulmonary complications
adequate anelgesia
- pain from rib frx will lead to shallow breathing (small tidal volume) + atelectasis
- –> inc risk of pneumonia
(rib frx typically heal w/o surgery (especially if nondisplaced : only do surgery if have flail chest, etc)
trx of Lyme disease in pregnant patients
early Lyme and late Lyme ds
- early Lyme = erythema migrans
- early Lyme in non-pregnant= doxycycline (can cause fetal tooth discoloration and skeletal deformities)
- early Lyme in pregnancy-use amoxicillin
- severe, late Lyme ds= sx like carditis, meningitis
- should be treated with ceftriaxone which is also safe to use in pregnant patients
- what ds is this
- what are these findings called
- what testing must be done when these findings are seen on exam + sx of the ds?

- OSTEOARTHRITIS
- bouchard’s nodes (PIP) and Heberden’s nodes (DIP)
- can present with pain in the 1st ICP (i.e. base of thumb) or distal IPJ (furthest joint)
- NO FURTHER EXAM= OA is a clinical dx
- an xray would show osteophytes and dec joint space but is NOT NECESSARY

in brain death
- which reflexes are lost
- will the HR inc after atropine injection
- will there be a respiratory response to PaCO2 > 70
- lose all brainstem reflexes, DTRs intact bc they orginate in the spinal cord and are not connected to the brainstem
- no HR will not inc: atropine dec vagal tone–> inc HR BUT in brain death there is no vagal tone to begin with so the HR won’t change
- no respiratory responses present = apnea test
an acute increase in Cr requires what
renal US to assess for AKI
(can also get urinealyses but US is key)
nodulocystic acne of the arms and upper back (including face) in a young woman should make you suspect what?
what info is needed to make the dx
PCOS : is a result of hyperandrogen (inc T)
dx of PCOS requires clinical/lab findings of increased T and hx of menstrual irregularity
what is the etiology of a concussion
neuronal functional disturbance, no structural intracranial injury
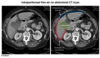
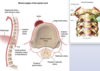
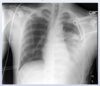
- what is seen in this image
- what is the dx? inc risk of what neurologic complication secondary to this image finding?

chiari 1 malformation (present in teen/YA)
-inc risk of syringomyelia (compression from tonsils)

pathogenesis of alzheimer
cerebral amyloid deposition
how are amino acids affected by thiamine (B1) /cobalmin (B12) deficiencies
- dec amino acid metabolism
- dec demethylation of tetrahydrofolate
diagnosis and etiology
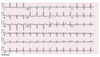
wolf parkinson white- accessory AV pathway,
most pts asx, might have intermittant palpitations w diaphoresis from an arrhythmia

what is an excessive amount of cow’s milk for babies/children to have (into toddlers..)
-inc risk of what?
> 24 ounces of cows milk is too much –> iron deficiency anemia
- cows milk does not have a lot of iron in it, and excessive amounts replaces iron-rich food in the diet
- iron from cow’s milk has decreased bioavailability
down syndrome is associated with what abdominal abnormalities
- umbilical hernia
- duodenal atresia: “double bubble” sign on imaging, polyhydramnios on US
- hirschsprung
what is a normal liver span
6-12 cm at midclavicular line
-describe presenting sx of acromegaly
- neurohormonal
- CV, pulm
- MSK, bones
- head&neck
- how do you diagnosie
- trx?
DIAGNOSTIC STEPS
- 1st- check fasting IGF-1 (insulin-like GF)
- if elevated –> 2nd = oral glucose test to check for suppressed GH levels
- inadequate GH suppression –> brain MRI
- pituitary mass–> resection
- no pituitary mass–> search for extra-pituitary sources of GH= ectopic, tumors

inc levels of thyroglobulin post-thyroidectomy –> dx?
= thyroid cancer recurrence
- thyroglobulin = precursor to T3/T4=
- produced by normal thyroid OR papillary/follicular thyroid CA

which medications cannot be taken along with lithium
AEs of lithium?
those that affect renal function –> lithium toxicityn
- NSAIDs
- ACE-I, ARBs
- tetracyclines
- metronidazole
AE =
- nephrogenic DI, chronic insterstitial nephritis
- hypothyroid, hyperPTH
- worsens physiologic tremor (resting, worse w stress (+posture held against gravity)
- nonprogressive, symmetric, fine tremor at rest
- weight gain
- leukocytosis
- acne, worse psoriasis, hair thinning
- goiter in pregnancy, teratogenic = ebstein anomoly
**can cause dystonia: BUT dystonic tremor is a tremor associated w dystonic M contractions i.e. torticollis**

most significant risk factor for getting TB in people living in the US
having emigrated from an endemic area
child with encephalitis sx and hepatomegaly (w inc AST, ALT, inc ammonia), normal temp
consider what dx
treatment?
reye syndrome = child given NSAID
=l_iver damag_e + rapidly progressing encephalopathy
- vomiting, lethargy, seizure, coma
- no jaundice even w hepatic enzyme
also have dec glucose, inc PT/PTT/INR
- trx= supportive
findings and diagnosis?
pt coughing up blood, sometimes brown sputum w 3 days of fever, pleuritic CP.
present w ground glass opacities in the same area of the nodules, gram stain -
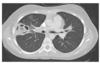
chronic pulmonary aspergillosi
- image shows a cavitary lesion in the upper lung with a fungus ball in it
*

etiology of acute limb ischemia after an LAD STEMI
-LAD STEMI = inc risk for LV aneurysm –> dec EF + inc stasis –> LV thrombus formation –> risk of emobilization –> stroke OR acute limb ischemia
newborn with cyanosis and the following xray
dx?
trx?

- respiratory distress syndrome
develops within minutes to hours, often in preterm
(associated w grunting, retractions, hypoxia)
- trx= continuous positive airway pressure ventilation

for which patients/disorders do you use the following types of psychotherapy?
- interpersonal psychotherapy
- supportive psychotherapy
- psychodynamic psychotherapy
- motivational interviewing
- dialectical behavioral therapy
- biofeedback

painless maroon colored stool in someone >60 yo who had a normal colonoscopy, consider what dx?
angiodysplasia
- often missed by colonoscopy bc of poor prep or was behind haustra
- associated with renal ds or vWF ds (which is oft associated w aortic stenosis)
- treatment is supportive: if have anemia, then cauterize the abn vessels
how does sample size affect type 1 and type 2 errors
inc sample size = inc power (prob of rejecting a false H0)
–> dec type II error (prob of FAIL TO REJECT a false H0)
–> inc type I error (prob of rejecting a true H0) = inversely related to type II

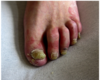
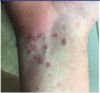
what is this finding called, and what is the etiology?

these are plantar hyperkeratotic warts! (painful)
HPV
trx of acute pancreatitis likely secondary to gallstones
(= non-drinker, w elevated liver enzymes and gallstones on imaging )
- once her sx and labs have resolved, –> early laparoscopic cholecestectomy (for stable pts)
- reduce risk of recurrance of gallstone pancreatitis
square, envelope shaped crystals in the urine and metablic acidosis in a pt with AMS –> dx? complications?
ethylene glycol poisoning (from anti-freeze)
- calcium oxylate stones
- high anion gap
- will also have high serum osmolality = >295
- complications = acute renal failure
vs methanol poisoning = AMS and HAGMA but no crystals : complications –> bilndness
differentiate between large fiber peripheral neuropathy and small fiber peripheral neuropathy in diabetic neuropathy
- large fiber = predominantely negative sx
- DCML
- small fiber= predominantely positive sx
- ALS

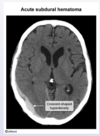
what is this finding called
etiology and classic presentation
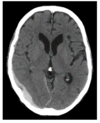
subdural hematoma = tearing of bridging veins
-often in old people w generalized cerebral atrophy: often after a fall (TBI), inc risk w anticoagulation
progressive confusion, weakness, unsteady gait
what are the two causes of “floppy baby” syndrome
- infantile botulinism
- werdning-hoffman = AR degen of anterior horn cells and CN motor nuclei
which antipsychotic has the highest risk of seizures as an adverse effect
clozapine
- agranulocytosis (aka neutropenia)
- seizures
- myocarditis
what is this finding called
what is the diagnosis
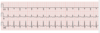
electrical alternans w short QRS

post-op pt presents for new onset anxiety and agitation +/- delirium, tachycardia, lid lag, tremor, inc BP, inc pulse rate, inc liver enzymes
clinical suspicion for what dx?
THYROID STORM
- precipitated by acute injury or surgery (inc wbc, fever, inc CK…)
- also precipirated by child birth, IV contrast
MC cause of cor pulmonale
=COPD
RHF caused by LHF/Congenital heart ds is NOT cor pulmonale
Cor pulmonalie can also be caused by: interstitial lung ds, OSA, pulmonary vasc ds, chest wall disorders
what is the dx

peaked T waves, shortened QT or widened QRS complex
P wave disappears,- conductive block
assocated w ESRD

pt comes in w normocytic anemia, back pain, and this xray of his arm (bc increasing arm pain)
what is the diagnosis

multiple myeloma
=osteolytic “moth eating” lesions
NOT JUST IN BACK, also long bones

thrombocytopenia
what conditions are associated with peripheral destruction of platelets vs splenic sequestration
- peripheral destruction (immune mediated)
- SLE, Antiphospholipid Ab
- TTP
- DIC
- splenic sequestration
- portal HTN, hepatic V thromobosis
- liver cirrhosis
- sickle cell ds
treatment with what kind of diuretic in the trx of ascites is associated with acute metabolic alkalosis with an inc BUN/Cr
=inc BUN/Cr, inc HCO3, dec K/H+
- loop diuretics = inc ALD and inc Na delivery to distal tubule to inc diuresis
next step in assessment in a pt w hypercoaguable state labs= inc Hgb, inc Hct, inc EPO
CT abd

mechanism of action of nitrates (sublingual nitroglycerin)
- systemic vasodilation (NOT coronary)
- dec preload, dec afterload
- = dec LV wall stress aka dec myocardial O2 demand
3 most common causes of chronic cough > 8 weeks
- upper-airway cough syndrome/ postnasal drip
- aka nasal secretions
- associated with chronic/multiple episode of rhinosinusitis (i.e. allergic rhinitis)
- asthma
- GERD
arthralias and an urticarial rash 1-2 weeks after taking abx
dx?
serum sicknless-like reaction

two days post-op w N, constipation, and diffusely tender abd. no bowel sounds.
dx?

paralytic ileus

elderly patient presents with back pain, inc WBC, dec Hgb
dx?

retroperitoneal hematome

laparoscopic procedures require CO2 insufflation of the abd
this comes along with what CV risk
=causes perotoneal stretching (so cameras can see)
-perotoneal stretch receptors will trigger inc vagal tone –> can cause severe bradycardia and possible transient AV block –> maybe even asystole
needs to be monitored by anesthesia
-CO2 embolization is v rare, associate with CO2 pushed into an artery/vessel –> end organ infarction/ hypotension/ obstructive shock
HAGMA
ethylene glycol vs methanol
both have v high osmol gap with bicarb v low (oftn < 6)
= alc substitutes
- ethylene glycol = renal damage, Ca oxylate stones
- methanol = blindness, optic disk hyperemia
compare presentations of 1st, 2nd, 3rd degree AV block and the management for each
observe for 1st
pacemaker for third degree, mobitz type 2

RA is associated with what kind of glomerular damage
AA AMYLOIDOSIS = nephrotic syndrome

syncopal episodes with muscle jerking that occurs at rest with no obvious trigger or prodrome suggests what
how to diagnose?
cardiac syncope
- muscle jerking can be in lots of syncope bc of cerebral hypoperfusion
- no prodrome preictal period rules out vasovagal or seizures to a high degree
- cardiac syncope =
- LV outlet obstruction (occurs with exertion)
- v tach = no warning sx, either monomorphic or polymorphic
- conduction impairment = preceding faint feeling, associated w ekg changes
dx= ambulatory ECG
what is the renal dx?

simple renal cyst= benign ; no treatment or follow up required

bicuspid aortic valve is associated with what type of murmur
when does it present and what does it sound like
aortic stenosis most frequently
- AS due to bicuspid valves usually presents 40s-50s
BUT bicuspid valve is the MC cause of aortic regurge in the US
- typically diagnosed in 30s-40s
- decrescend, early diastrolic murmur @L sternal border w patient leaning forward and holding exhalation
bicuspid aortic valve can also cause aortic root dilation which –> causes aortic regurge
MC cancers to mets to the brain
- which present as solitary met
- which present as multiple mets
lung> breast> unknown > melanoma> colon
- single: breast, colon, renal cell carcinoma
- multiple: lung CA, malignant melanoma
MC electrolyte abn associated with chronic alc use
why is this dangerous
hypomagnesemia
dec Mg –> inc K excretion by kidneys –> hypokalemia
(ROMK channels in kidney are regulated by Mg: v common ause of refractory hypoK is hypoMg)
def Mg -> induced PTH resistance –> hypocalcemia
hypoCa oftn refractory to trx unless also give Mg (phospohorous is n-low bc of depletion = vs other causes)
anemia of chronic disease is associated with what types of chronic diseases
= suppression of RBC production by inflammatory cytokines
=inflammatory ds like RA, SLE
NOT like OA…
what is the finding in this MRI and what is the diagnosis

HYPOXIC BRAIN INJURY
=hyperintensity of the globus pallidus bc it is very sensitive to hypoxic injury
-also associated w hypoxic brain injury is diffuse cerebral edema (later) and the sx of AMS, confusion, seizures, lactic acidosis from peripheral tissue hypoxia

how do you differentiate between angina due to aortic stenosis vs coronary A ds
AS angina = w severe AS, w <1 cm of valve area, often w a low pulse P

how does dec hepatic UDP glucoronosyltransferase activity present
=GILBERT SYNDROME
- mild jaundice with stress/illness/surgery/dehydration/vigorous excercise
- -presents in kids/teens/ YA
GILBERT is inc indirect bili with normal hgb
- vs g6pd= inc indirect bili w dec hgb
sudden onset painless vision loss in one eye with this fundoscopic exam
what is the diagnosis

acute mono-ocular painless vision loss= retinal A embolism
oftn from ispi carotid A or cardioembolic (a. fib)

post-op patient (days) with fever, pain at surgical incision site that is numb around the edges and has a dusky, friable subcutaneous tissue
necrotizing (fasciitis) surgical infection

what medications can cause a false positive amphetamine result on urine drug screen
atenolol
propranolol
bupropion
nasal decongestants

what medications can cause a false positive phencyclidine on urine drug screen
(false + PCP)
- dextromethorphan
- diphenhydramine, doxylamine
- ketamine
- tramadol
- venlafaxine
differentiate between allergic rhinitis and nonallergic rhinitis
- sx/triggers
- PE exam
- treatment
allrgic = specific allergens (pollen, cats..)
-nonallergic = no systemic sx, associated with the cold, season changes, etc.

a “magnetic” gait is a classic description of the gait associated with what pathology
normal pressure hydrocephalus
- early disease my present w ONLY gait changes +/- flat affect, but no cognitive or incontinence
- dx= ventriculomegaly and n opening pressure
vs PD= shuffling or festinating (short, quick steps)
describe the levels of PaCO2 and the A-a gradient in the following:
- alveolar hypotension (what conditions is this associated with)
- pulmonary embolism
- atelectasis
- pulmonary effusion
- pulmonary edema
- alveolar hypoventilation =
- inc PaCO2
- n A-a gradient
- PE, atelectasis, pulmonary effusion/edema
- dec PaCO2
- inc A-a gradient (aka VQ mismatch)
n A-a mismatch= <15

- what is the glasgow coma scale used for
- what are the parameters of measurement
- what is the scoring scale
- assess the severity of brain injury
- EVM = eye opening, verbal response, motor response
- GCS = 0-15
- mild injury = 13-15
- moderate injury= 9-12
- severe injury = <8

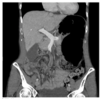
pt in the ER w progressive abd pain + distension, N/V, hx of alc abuse
dx?
trx?
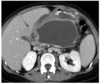
pancreatic pseudocyst = mature walled off pancreatic fluid collections (usually no necrosis or solid material) surrounded by thick, fibrous capsule and contains enzyme rich fluid, tissue, debris
- can –> amylase-rich fluid leaking into circulation and inc serum amylase
- complications = spontaneous infection, duodenal or biliary obstruction, pseudaneurysm (presents with embolism before drainage procedure), pancreatic ascites, pleural effusion
TRX
- asx= expectant management (symptomatic therapy, NPO)
- sx w abd pain/V/infection/pseudoaneurysm –> endoscopic drainage

what is this imaging finding called?
dx?
trx?

PORCELAIN gallbladder
dx= cholecystitis
- CXR= rim like calcifcation where the GB should be
- CT= calcified rim wall w central, bile filled dark gb
- the gallbladder irl is like bluis-grayish on the outside bc of the Ca deposition, and oftn filled w yellow, multifaceted gallstones
- (US shows thick GB wall filled w sludge, and surrounded by fluid)
trx= cholecystectomy
- chronic cholecystitis has inc risk of GB adenocarcinoma
describe appropriate resuscitation measures in patients with hemorrhagic shock/ ongoing hemorrhage
what is the danger of inappropriate resusc
- balanced resuscitation= “damage control”
- limit use of crystalloids (saline infusion) bc these will dilute coag factors –> coagulopathy = inc bleed
- replace the intravascular fluid with blood products = 1:1:1 ratio
- maintain permissive hypotension (65 MAP) until hemorrhage is controlled
danger of excessive fluid resuscitation with IV fluids =
- hypothermia (room temp is colder than body)
- acidosis (NAGMA, hyperchloremic)
- inc mortality from lethal triad = hypothermia, acidosis, coagulopathy
- inc risk of ARDS (dose dependent on amounts of fluid)
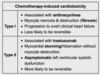
patients who survive cancer with treatment of radiation and chemo are at increased risk of what
specific myocyte changes w diff chemo?
-secondary malignancy= solid organ (breast, lung)
- associated w radiation
- secondary malignanc is the MC cause of CA related death in those cured of a CA
-CV ds = CAD, valve damage, PVD, cardiomyopathy
- leading non-malignant cause of death in hodgkin lymphoma survivors
- myocyte necrosis and fibrotic destruction associated w anthracyclines (-doxorubicin, -rubicin) –> progress to overt HF
- trastazumab= myocardial stunning/hybernation without destruction = asx LV systolic dysfunction, more likely to be reversible
- pulmonary fibrosis/bronchiectasis (radiation)
- hypothyoid (radiation)
- neuropathy (chemo)
what three causes of hypoxia (PaO2<75) do NOT correct with O2 supplementation
how do you improve oxygentaion then?
ARDS (due to associated pulmonary edema= intrapulmonary shunting as Nø inflammation fills the alveoli w proteinacious fluid)
- inc PEEP= positive end expiratory pressure= opens up the flooded alveoli and recruits them for ventilation = inc the amoung of lung that is actually doing O2 transfusion
- aka dec the intrapulmonary shunt effect
- associated w increase risk of barotrauma so have to be careful
massive pulmonary embolism
severe R–>L intracardiac shunt

patient, hx of bronchiectasis, with psoriasis, nephrotic syndrome, palpable kidneys, hepatomegaly, fourth heart sound on auscultation
what is the underlying pathology of the nephropathy
amyloidosis

psoriasis= chronic inflammatory disease
nephrotic syndrome palpable kidneys= amyloid dep
hepatomegaly = amyloid dep
S4 = vetriculomegaly = amyloid depo
pt with trouble swallowing liquids, tongue fasciculations, and when you tap on the chin with the mouth slightly open the jaw jerks forward briskly
dx?
ALS

describe estrogen levels in turner syndrome
estrogen is produced by the ovaries so in TS–> decreased estrogen
- results in amenhorrhea and poor breast development
- inc risk of osteoporosis and fractures (estrogen inhibits osteoclasts)
trx includes giving TS teens estrogen to promote sexual maturation and dec risk of osteoporotic fractures
what is the etiology of Reye Syndrome
child is given ASA –> liver toxicity and damage –> hyperammonemia –> buildup in CNS –> cerebral edema –> toxic metabolic encephalopathy = rapidly progressivve nausea, vomiting, lethargy, AMS/confusion
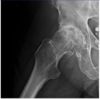
13 yo w progrssive hip pain, limping and pain on IR
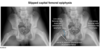
pt w insecurity about body and weight, enlarged parotid glands and scars on back hand BMI at 4th percentile
dx??
anorexia nervosa
-even if purge, AN vs BN = BMI
BMI<18.5= AN
describe the PFT pattern and diffusion capacity of the lung for CO for asbestosis and silicosis
restrictive PFTS
w dec DLCO
a well appearing infant <6mo w blood streaked, mucusy stools
what are the two possible dx?
anal fissure (hx constipation)
food-protein induced allergic prococolitis (n bowel movements: is associated w mom’s diet if being breastfed, clinical dx–> have mom cut out dairy + other foods till sx resolve)
(things like intestinal obstruction or necrotizing enterocilitis would present with an ill pt + tender abd)
testing sequence for suspected cushing’s disease
aka hypercortisolism and you gotta assess where the cortisol is coming from
-clinical presentation of hypercortisol
- 1st get:
- 24 hour urinary cortisol excretion
- late night salivary cortisol assay
- low dose dexamethason suppression test
- if two of these are abn = you have high cortisol:
- then do a high dose dexamethasone suppression test to differentiate between ACTH dependent or independent
- imaging to look for pituitary/ adrenal tumors, etc.
patient presents with infective endocarditis
- what is the trx?
- at what point would you consider surgical intervention
n trx= IV abx and O2 supplement prn
- if the pt is in acute heart failure, oft secondary to aortic/mitral regurge
- = acute SOB, bilat LE edema, pulm edema
- extensin of infection (i.e. abscess, fistula, heart block)
- IE is caused by a fungus or med- resistant pathogen
- persistant bactermia after abx trx
- persistent septic emboli
4 wks post MI pt presents w diffuse, severe abd pain, N/V onset suddenly 3 hours ago
labs= inc hgb, metabolic acidosis, inc leukocytes, inc amylase ; HTN, inc HR
dx?
mesenteric ischemia
dx= evidence of bowel infarction–> go to OR : it pt stable/suspicious, get CT angio

dx?
what is the etiology

narrow QRS + regular rhytym = paroxysmal SVT
=in young pt (<40) w normal heart, MC cause is AV nodal reentrant tachy
- two distinct conduction pathways in the AV node = fast w long refractory and slow with short refractory

describe the ECG of Vtach and what is the etiology
- abn electrical activity around ischemic scar tissue
- or abn automaticity of the ventricular conduction sytem = associated with dilated cardiomyopathy

disorganzied atrial activity originated from the pulmonary Vs results in what type of arrhythmia
a fib

what type of anemia is associated with a high homocysteinuria w high methylmalonic acid, and which is associated with a high homocysteinuria w n methylmalonic acid
high methylmalonic acid = combalamin= Vit B12
“folate MTMA falls* *cobalamin= both up*

pt presents s/p MVC w pelvic fracture, blood at the urethral meatus, and a high rising prostate
what should you be concerned about and what is the next best step in assessment
posterior urethral injury
get a retrograde urethrogram ASAP
*upward movement of bladder/prostate can cause urethral tearing, MC at bulbomembranous junction*
-other sx= inability to void,, perineal bruising
what are two potential longterm consequences of myopia
=near sightedness
-SEVERE myopia is associated w inc risk of
- macular degenration
- retinal detachment

differentiate the clinical picture of bell’s palsy from an acute stroke
how do you diagnose bell’s palsy
bell’s palsy is paralysis of one side of the face, including the lower and upper face
- also sudden onset = difficulty eating, drooping smile, trouble closing eye, foreheard involved pupils equal and reactive though
- a stroke would not include the upper case as well bc of the different innervations
bc >50% of U&L face palsies are due to bell’s and because the prognosis is so benign –> = clinical diagnosis
- further testing is NOT recommended in pts w classical presentation
- may rule out other causes through H&P usually

- MC oppurtunistic infections after transplant are:
- what are common post drug toxicities and malignancies
MC opp infections=
- CMV pnuemonia (bilat infiltrates, fever, acute onset)
- pneumocystis pneumonia (bilat infiltrates, fever, indolent onset)
- invasive molds (Aspergillus)
**NEW ONSET PULMONARY INFILTRATES: have to rule out acute transplant rejection during the workup for infection (can be concurrent) –> bronchoscopy, lung biopsy

pt presents for confusion and AMS.
fever, dec BP, inc pulse and respirations
diffusely tender abd pain, distended, tympanic abd to percussion, rigid to palpation
dx?
how to trx?

perforatd viscus
- *hx of colon surgery –>adhesions–> SBO –> perforation*
- present w recent anorexia, AMS, pt cannot tolerate being upright, sx of peritonitis
dx= clinical signs plus xray (CT w contrast if xray -)
trx- immediate surgical exploration to repair

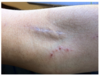
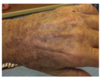
3 days after cardiac cath and stent, patient presents in hospital with vague, abd pain, 3 blue R toes and 1 blue L toe, and this skin finding
- dx?
- etiology? risk factors?
- treatment

- cholesterol embolism
- presents with livedo reticularis, ulcers/gangrene, blue toe syndrome due to peripheral shower emboli, kidney injury, stroke/olfactory hallucinations (due to cerebral emboli), Hollenhurst plaques (golden yellow spots in eye)
- dx= eosinophilia, dec C3
- = emboli from atherosclerotic plaque in aorta
- inc risk w HTN, hypercholesterol, DM
- presents days-weeks after a cardiac/vascular surgery
- trx= supportive