Facial Aging & Rhytidectomy Flashcards
What are the five anatomical layers of the face
- Skin: firmly attached to the underlying SC w cutis retinacula
- Subcutaneous/Superficial fat compartments (5)
- Nasolabial
- Medial Cheek
- Middle Cheek
- Lateraltemporoparietal (cheek)
- Inferior orbital
- Superficial musculoaponeurotic System
- = superficial fascia and mimetic muscle
- continuous w plastysma (superficial cervical) fascia, TPF, galea
- Fixed over the parotid, mobile medial to parotid and fuses again medially at NLF
- Parotidomasseteric fascia - Deep facial fascia
- continuous w superficial leaflet of DTF, into neck as deep cervical fascia
- Neurovascular structures are in and deep to PM fascia
- Bone/periosteum

Name the muscles in the face (4 layers)
- Zm, Oo, DAO
- Risorius, Plastysma, DLI
- ZM, LLSAN, LLS, Ooris
- Mentalis, LAO, Buccinator * innervated on superficial surface
+ procerus
+ depressor supercilli
LLSAN, LLS, Zn, ZM (from medial to lateral)
Mentalis, DLI, DAO (from medial to lateral)
What is the blood supply to the face and main branches
- central
- middle
- outer/lateral
- scalp/forehead
External carotid
Internal carotid (ophthalmic artery ->eyebrow, lid, forehead, scalp)
- Central: angular, Nasal, S&I labial,
- Middle: facial, M&P jugular, submental, infraorbital
- Lateral: S&I masseteric, transverse facial, Zygomatico-orbital
- Scalp forehead: STA, SO, post auric, occipital
Describe the course of the facial branches
-
Frontal
- Course; 0.5cm below tragus to 1.5cm above lat brow (pitangays line). AT midpoint b/w tragus and lat canthus, nerve crosses arch
- Inf to arch: deep to PM
- At arch, on periosteum+sup.leaf of DTF
- Sup to arch, deep to TPF
-
Zygomatic
- deep to PM, above masseter
- VULNERABLE at anterosuperior parotid, deep to orgin of Z.M at 3cm anterior to tragus
-
Buccal
- vulnerable at anterior parotid, deep to PM
-
Marginal Mandibular
- exits anteroinferior parotid - deep to PM, deep cervical fascia
- always deep to plastysma, protected by deep cervical fascia
- posterior to facial vessels, nerve lies inferior to mandible
- anterior to facial vessels, nerve lies superior to mandible
-
Cervical
- penetrates deep cervical fascia, runs deep to plastyma at a pint 1/2 b/w mastoid/mentum at angle of manidble

Describe the course of CN11
- exits jugular foramen
- runs along posterior deep surface of SCM
- leaves posterior SCM 7-9cm above clavicle to travel on deep surface of trapezius
What si the anaotmic landmark for he Greater auricular nerve and what is the consequence of its injury
- 6.5cm below EAC, ont he superficial surface of SCM, traveling form posterior to anteriro to course with the EJV
- injury results in numbness of loule, inferior auricular region
What provides the sensory innervation to the face
- external nasal
- infratrochlear
- supratrocheal
- supraorbital
- infraorbital
- zygomaticofacial
- zygomaticotemporal
- mental
- buccal
- auriculotemrpoal
- GAN
- LON
- GON

What are the 7 facial danger zones
- GAN : 6.5 cm below EAC
- posterior to SMAS
- =>numbness inferior 2/3 rd of ear, cheek, neck
- Temporal: 0.5cm below tragus to 1.5cm above lat brown
- deep to SMAS
- =>paralysis of frontalis
- Marginal mandibular: 2cm posterior to oral comissure, midmanidble
- deep to SMAS (platysma)
- =>paralysis lower lip
- Zygomatic+Buccal : triangle formed by points on malar, oral commisure, posterior angle mandible
- deep to SMAS
- =>paralysis upper lip cheek
- Supraorb/supratroch: SOR at midpupil
- anterior to SMAS
- =>numbness forehead, nose, scalp, upper eyelid
- Infraorbital: 1cm below IOR at midpupil
- anterior to SMAS
- =>numbness side of nose, upper lip, lower eyelid
- Mental: midmandible bwlow 2nd premolar
- anterior to SMAS
- =>numbness to half lower lip/chin
Name the facial retaining ligaments of the face (furnas,stuzin)
Osteocutaneous (Direct)
-
Zygomatic RL*
- along arch/body, posterior to Zm, 4.5cm ant to tragus
- suspends malar fat pad
- deep to ZRL is zyg/buccal branches, parotid duct, trasnverse facial artery
-
Mandibular RL*
- along parasymphysys and anterior 1/3 of body
- posterior limit of MRL defines anterior border of jowl
Indirect cutaneous (between deep and superficial fascia)
- Parotid-preauricular CL (Lore’s fascia)
- Parotid-Masseteric CL*
- Superior temporal line CL
- Platysma CL
- orbicularis RL (orbitomalar ligament)
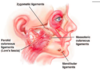
WHat is contained in the buccal fat pad
- Zygomatic, buccal branches superficial
- parotid duct
What is macgregors patch?
Malar fat pad
= 3 superficial fat compartments
= Nasolabial, medial cheek, inferior orbital
- descends with age and deflates
= deepened NFL and jowls
Describe facial aging by decade and by structure
30s - eyelid, crow feet
40s - NLF, glabella, forehead
50s - neck, jaw, jowls, nasal tip
60s- deepened wrinkles and sagging
Skin: thining epidermis, atrophic dermis, less collagen 1
Soft Tissue - deflation, descend, deterioration
- Middle 1/3 NL and mrionette groove
- Lower 1/3 jowl, witchs chin
Bone - retrusion of IOR and maxilla anteriorly and height
What are rhytids and examples of each type
Creases in the skin due to intrinsic changes in skin structure and perpendicular to muscle movement
- Dynamic - animation creease
- Static fine - disrupted elastin network
- Static coarse - deep caused by solar elastosis
What changes occurs histologically to skin with aging
- Loss of cells
- melanocytes
- langerhans
- Loss of structure
- DE papillae
- reticular dermis
- Loss of substances
- ground substance
- elastin
- collagen type 1 (more t3:t1)
- increase size of sebaceous glands
What changes occur with photoaging
- telangiectasia
- dyschromias:hypo/hyperpigment
- atrophy
- erythema
- static rhytids: fine and deep
What genetic syndromes predispose to facial aging and who are good and poor surgical candidates?
POOR CANDIDATES FOR SURGERY
-
Ehlers -Danlos
- abnormal production of lysyl oxidase -> required for collagen crosslinking
- = capillary friability, poor wound healing
- Progeria
- Adult Progeria (Werner’s)
-
Cutis Laxa (AR or Xlinked only)
- deficiency of lysyl oxidase
Good or select
- Cutis Laxa (AD)
-
Meretoga syndrome
- amyloidosis of facial skin and facial nerve
- Pseudoxanthoma elasticum
- Idiopathic skin laxity
Describe your Pre-operative Facial Analysis
HISTORY
- Desires and Expectations
- Full PMHx, previous treatments
- Effect on skin aging: Sun>Smoking>Weight change
PHYSICAL
- Skin: quality, photoaging
-
Facial Proportions
- Midface width (line thorugh infraorb rim)
- Facial Length (height from malar projection to inferior jowl)
- Facial Fullness (distribution)
UPPER 1/3
PERIORBITAL ZONE (FOREHEAD, BROW, MIDFACE)
- Brow position
- Glabella rhytids
- Forehead rhytids and height
-
Temporal
- crows feet
- atrophy
- Lateral canthus position
- Upper lid ptosis, pseudoptosis, skin, fat
-
Lower lid laxity, position, lid-cheek jx
- Tear trough
- Festoon
-
Malar projection, fat pad descent
- negative/positive vector
MIDDLE 1/3
PERIORAL ZONE
- NLF
- Angle of mouth
-
Upper lip
- height
- volume loss & periooral rhytids
- Lower lip
-
Chin
- labiomental crease
- ptosis (witchs chin)
- jowls
- Nasal tip
- Ear lobule
LOWER 1/3
NECK
- Platysmal banding, transverse cervical bands
- Jawline
- Submandibular ptosis
Describe your surgical goals of facial rejuvenation
- Correction of Ptosis and Laxity
- general skin laxity
- malar
- Jowls
- Labiomental crease
- NLF
- Neck definition
- Jowls
- Alter face shape form rectuangular to conical
- Bidirectional advancement of skin and SMAS
What are options for non-surgical facial rejuvenation
Sunscreen (prevention)
- Anti-UVA (titanium dioxide, Zn oxide)
- Anti- UVB (‘, PABA, salicylate)
- Retin-A (vitamin A and derivative)
- stimulates collagen synthesis, inhibits MMP
- 0.025% topical nightly
- Exfoliants
- alpha hydroxyl acids
- Bleaching agents
- hydroquinone
- HRT (estradiol retards loss of collagen)
- (probably should include):
- filler: synthetic, autogenous
- laser
- chemical peel
Describe the incision options for a cervicofacial rhytidectomy
- Temporal - want normal hairline relation to ear
- Hairline (if >4cm b/w lateral orbit and hairline)
- In Hair (3cm in temporal scalp extending superirly from root of ear (if <4cm =>hairline will be posteriorly positioned postop)
- **look at amount of hair sitting in front of ear as it will be back 2-3cm depending on laxity
- Preauricular - want normal camouflage of color/texture, prevent tragal distortion
- Anterior to tragus - if preauric rhytid, male
- Tragal edge - if no preauric rhytid
- posterior margin
- Perilobular
- incision 2-3mm below crease (lob-cheek jx)
- Post-auricular
- inciion directly in auriculomastoid groove then turn posterior at upper level of EAC
- Occipital
- along hairline within inferior incison turned back into hairline at jx of thin/thick nair
- Submental incision
- plan w posterosuperior traction on cheeks - placed parallel and posterior tosubmental crease
List the techniques for cervicofacial rhytidectomy
- Skin only
- Skoog (skin+SMAS as a single unit)
- Subperiosteal
- Endoscopic (Byrd)
- SMAS + Subcutaneous
- SubSMAS + Subcutaneous
List the variations for the SMAS techniques
SMAS (5 variations)
- Plication (no elevation)
- Imbrication (advanced and overlapped)
- MACS (minimal access cranial suspension)
- subcut separation, SMAS suspension to DTF
- Lateral SMASectomy
- strip excised along anterior parotid
- SMAS stacking
- SMAS incised and two edges stacked
List the variations for the SubSMAS techniques
SubSMAS = deep plane, deep SMAS (5)
- Low SMAS - below arch, treats only lower face
- High SMAS *BARTON
- above arch, treats midface and lower face
- Extended SMAS (Stuzin)
- into upper mid cheek to release ORL and superior malar fat pad. Risk o.o branches
- Composite SMAS (Hamra)
- Skin +SMAS raised as single unit
- Lamellar SMAS
- bidirectional elevaiton and adv.
List and describe minilift procedures
- Webster lift
- short ant and post scar w only SMAS plication
- S-Lift (Ansari)
- temporal + preauric incision w SMAS plastysma plication
- Short scar lift (Baker)
- S-lift variation w lateral SMASectomy


