Eye Anatomy Flashcards
Label the orbit bones


Label the fissures/ canal/ formina of the orbit


What is contained within the optic canal?
Optic nerve
Ophthalmic artery

where do eyelids meet?
Medial and laterla Canthus

Label this
What is the orbital septum?

orbital septum- connecitve tissue that attaches to orbit- extension of the periosteum

Describe the Muscle which is superficial to the fibrous framework of the orbit ?
what is there function?
Orbicularis oculi muscle——> movements of the eyelid (close)
orbital; part- forcefully
Palpebral part- gently
what Nerve innervated the orbicularis occuli?
CN VII facial nerve
Label this


What is the role of Levator palpebrae?
innervated by
innervated by CNIII- oculomotor

what is the role of the superiro trasal msucle

Label this?


Describe the outer coat of the eye?
cornea
Sclera
limbus

Describe the middle cosat of the eye (uvea/ vascular layer)
iris
ciliary body (ciliary muscles/ciliary processes)
choriod

Describe the inner coat of the eye?
retinal pigment epithelium
retina
light sensitive tissue that lines back of the eye
what is the role of the cornea?

What makes up 85% of the outer (fiborous) coat of the eye and provides attachments for extraocular muscles?
Sclera

What is this?

Keratoconus
non inflamamotry eye condition- cornea thins and progressive becomes cone like bulge

what is the uveal layer
uveal or vascular
Middle coat of the eye
what is the choriod
Most posterior and highly vasuclarised area of the posteriro eye
what are the Ciliary processes
connected to the lens of the eyeball by the zonula fubres (suspensory ligament of the lens)
describe the action and innevration of the ciliary msucle
parasympathetic control and CNIII m(oculomotor)
contracts and pulls the ciliary proccess forward-
suspensory ligament relax
lens fattens , more relaced
label this
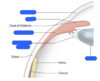

what is the iris?
the iris is an extension of the ciliary body that cotnrols pupil size
this is the coloured area of the eye
what is the role of the spincter pupillae?
Parasympathetic
constrict the pupil
CNIII (oculomotor)
(circular fibres)