External Eye Disorders Flashcards
Objectives
1
Q
PANCE External Eye Conditions
A
- Hordeolum
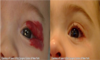
- Hyphema
- Blepharitis
- Chalazion
- Conjunctivitis
- Orbital cellulitis
- Pterygium/Pinguecula
- Cataracts
- Corneal abrasion
- Dacryocystitis
- Ectropion
- Entropion
- Foreign bodies
2
Q
Differentiate between
A
- Benign eyelid vs. conjunctival conditions
- Sight threatening vs malignant eyelid/conjunctival conditions
3
Q
Benign Eyelid Lesions
A
- HIDROCYSTOMA
- HORDEOLUM
- CHALAZION
- BLEPHARITIS
- XANTHALASMA
- KERATOACANTHOMA
- CAPILLARY HEMANGIOMA
- BENIGN EYELID NEVUS
4
Q
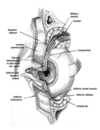
Meibomian Glands
A
- Modified sebaceous glands located within tarsal plates of eyelids
- responsible for secretion of oily layer of tear film
- critical for normal ocular surface lubrication
- Preventing tear evaporation, facilitating spread of tears over ocular surface
5
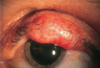
Q
HORDEOLUM
A
- Acute, purulent,inflammation of eyelid
- External
- infection of lash follicle/glands of Zeis /Moll – points to skin
- Internal
- infection of meibomian gland- large swelling on conjunctival surface of lid
- External
- S/S
- Red, swollen, tender nodule with central core of pus-upper/lower eyelid
- Tearing, photophobia, foreign body sensation
- Etiology
- s. aureus
- TX
- Warm compresses
- I&D
- topical abx

6
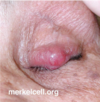
Q
CHALAZION
A
- Obstruction of meibomian glands within tarsal plates
- Internal hordeola may develop into chalazion
- Results in formation of granulomas
- Noninfectious
- S/S
- begin as localized eyelid swelling/erythema, then develops into a painless rubbery nodule
- Heaviness of eyelid; vision distortion
- Common in patients with blepharitis and rosacea
7
Q
Treatment of Chalazion
A
- Warm compresses/massage to soften/drain them
- Antibacterial ointment
- Steroid injections
- Surgical incision and removal
- DDX if persistent
- carcinoma
- BCC
8
Q
BLEPHARITIS
A
- Chronic inflammation of eyelids with intermittent acute exacerbations
- 2 types
- anterior
- posterior
- Typical patient
- female and younger
9
Q
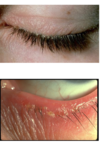
Anterior BLEPHARITIS
A
- infection at base of eyelashes
- staphylococcal: colonization leads to scales/crust around lashes
- •Aka:”collarette”/scurf

10
Q
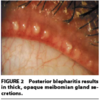
Posterior BLEPHARITIS
A
- More Common than anterior blepharitis
- inflammation of the inner eyelid, at level of meibomian glands
- Meibomian gland dysfunction causing plugging/hypertrophy of sebaceous glands
- Associated w/ rosacea/seborrheic dermatitis
11
Q
Clinical manifestations if blepharitis
A
- burning, gritty sensation
- Itching
- epiphora
- an overflow of tears onto the face
- sign that constitutes insufficient tear film drainage
- crusting of lashes in am
- flaking skin
- red rimming
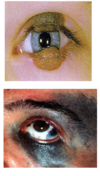
- Phlyctenulosis
- a characteristic nodular growth occurring as an allergic response of the conjunctival and corneal epithelium
- in image

12
Q
blepharitis PE
A
- punctate epithelial erosions on cornea
- From hypersensitivity reaction to staph antigens and toxins
- Diffuse conjunctival injection.
- Foamy appearance of tear film
13
Q
BLEPHARITIS TREATMENT
A
- Lid Hygiene
- warm compresses
- lid massage
- lid washing – baby shampoo
- Treat with Antibiotic ointments
- erythromycin, bacitracin, or sulfacetamide
- Steroid/Antibiotic ointments
- Patient education and counseling.
- Maintaining a regimen to prevent future exacerbations.
14
Q
XANTHALASMA
A
- Cholesterol filled soft yellow plaques
- medial aspects of eyelids bilaterally
- nontender
- ETIOLOGY
- conditions that cause elevated blood lipids; deposition of cholesterol laden histiocytes
- Hyperlipidemia (50%), primary biliary cirrhosis
- Appear with elevated triglycerides
- *May have normal levels of cholesterol
- conditions that cause elevated blood lipids; deposition of cholesterol laden histiocytes
- TX
- Surgical Removal-cosmetic
- Correction of underlying cause

15
Q
HIDROCYSTOMA
A
- Benign fluid filled tumor
- S/S
- Solitary, dome shaped translucent nodule on eyelid –bluish gray
- Not confined to lid margins
- asymptomatic
- Etiology
- produced by the cystic proliferation of apocrine/eccrine glands
- High-frequency U/S confirms dx
- TX
- Excision to r/o BCC
- Removing all ectopic epithelium to prevent recurrence