Exocrine Images Flashcards
Identify
What kind of glands are sweat glands?

Skin of Finger
Sweat glands: simple coiled tubular glands
Bright red keratin layer in epidermis (skin surface)
Difference between nerves and sweat glands: perineurium encircles nerves

Identify

Skin of finger
Several cross sectioned and longitudinal sectioned sweat glands and their ducts
Pale cells near periphery, dark cells near lumen
Straitfied cuboidal epithelium lines secretory ducts

Identify the cells of sweat glands

Eccrine secretory cells:
- Pale cells: more numerous, larger, clear cytoplasm
- Dark cells: pyramid shaped, darker, near lumen
- Myoepithelial cells by basal lamina

Identify
Sebacious glands with hair follicles
Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium up top
Dense irregular CT of dermis beneath

Identify
Sebaceous gland with centrally located hair follicle
Notice portions of the acini
Cells are large and colorless - filled with fat droplets
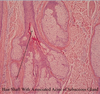
Identify

Close up on sebaceous gland acinus
Stem cells on periphery, proliferate and generate acinar cells
Migrate to center as they mature
Increase in size as fat droplets accumulate

Identify

Low power view of human pancreas

Identify

Medium power of human pancreas
2 islets of Langerhans (endocrine pancreas, contain hormone-producing cells)
Many serous acini - secretory product stained bright pink

Identify

High powered view of serous acini (exopcrine pancreas)
Centriacinar cells: beginnning of the intercalated duct. Cells have clear cytoplasm, found in lumen of acinus

Identify

High power of exocrine pancreas
Intercalated duct with number serous acini
ID centroacinar cells - central nucleus surrounded by clear cytoplasm

Identify

Exocrine pancreas
Drainage pattern: acinus –> intercalated duct (longitudinal section) –> intralobular duct

Identify

High power of exocrine pancreas
Cross section of intralobular duct - surrounded by serous acini
Good examples of centroacinar cells in lumen of acini
Islets of Langerhans at bottom

Identify

Low power of submandibular gland
Septa (connective tissue) divides gland into lobules



