Examination findings Flashcards
(81 cards)
What is the diagnosis?

Sub Conjunctival Haemorrhage
Name 3 factors that increase your risk of this happening

suddenly increase pressure – such as coughing, hypertension or Aspirin (as anti-platelet agent) will make this more likely as will trauma and increasing age.
This 30 year old felt the sensation of something in his eye since yesterday. His eye is watering and is uncomfortable. Why?

Small foriegn body (FB) can be seen when everting the eyelid
The FB is removed and the eye re-examined after insertion of a dye.
- What dye is it? What do you see?
- What is this called?
- Why has it occurred?
- What colour is the lamp used to examine in the above picture?
- What colour lamp is used to specifically look at blood vessels in the retina?

- Fluorescein – note uptake over cornea
- Corneal abrasion
- FB has rubbed epithelial surface of retina
- Blue light – fluorescein is orange therefore if uptake see as green
- Green light used to look at blood vessels.
This 23 year old man was involved in an altercation on Wind Street last night.
- What is the term given to the appearance of the eye above?
- What exactly is it?

a hyphema—a hemorrhage in the bottom of the anterior chamber of the eye.
The bleeding came from disruption of blood vessels at the iris root. It is a sign of severe ocular contusion. There may be other signs of ocular contusion: corneal and retinal swelling, bleeding in the vitreous cavity, dislocation of the lens, rupture of the iris, cornea, retina, or sclera.
This six year old is brought into surgery by his mother.
- What is the name of this sign?
- List 3 potential causes of this sign in THIS patient.

- Ptosis
- Myasthenia, Horner’s, Benign, Congenital, Traumatic (head injury), III nerve palsy
In this case, while Ca lung is a cause of horner’s and ptosis, it wouldn’t be expected in a 6 year old
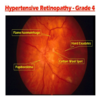
- What part of the body is this a picture of?
- What are the features indicated by the arrows?
- What is the most common underlying disease which results in the features show?

- Retina – NOT eye
- Flame haemorrhages
- Hypertension
- What is indicated by A?
- What are the white areas indicated by the black arrow B?
- What are these white areas caused by?
- What is indicated by the yellow / green arrow C?
- What is the underlying disease?

- Optic Disc
- Hard Exudates
- Leakage of protein from blood vessels
- Flame haemorrhage
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- What is …
A? B? C? D?
2.What is the underlying disease?

A Laser Scars
B Macula
C Retinal Vessel
D Microaneurism
2) Diabetic retinopathy (specifically diabetic macula oedema)
- What problem is visible?
- What symptoms may the patient have presented with?
- Name a very common underlying problem that would make this condition more likely.

- Retinal Detachment
- Deteriorating vision in curtain or flashing lights (remind them of history in year 1)
- Short sightedness
What feature is visible in the disc?
In this particular patient it may be due to:
- Pulmonary embolism?
- Multiple sclerosis?
- chronic coughing?
- Head injury ?
- Malignant hypertension?

Papilloedema
Found in:
MS – (if optic neuritis)
Head injury (if raised ICP)
Malignant hypertension (not controlled)
What is seen in the picture?
What symptoms might this woman present with?
Which women are more likely to have this condition of the cervix?

Cervical ectropion (or cervical eversion)
- central (endocervical) columnar epithelium protrudes out through the external os, undergoes squamous metaplasia, and transforms to stratified squamous epithelium
Symptoms = mucus discharge, post coital bleeding
Normal in younger women, pregnancy and those taking oestrogen OCP
What condition is this?
What virus causes it?
How is this usually transmitted?
What condition does this predispose to?
What should she be advised to do regularly in future?
Name one way of treating this

Genital warts
HPV
Sexual contact / skin to skin
Cancer
Wear a condom
Cream - podophyllotoxin
Cryotherapy
What is the metal object at the bottom?
What is the tube at the top?
What is the name given to this finding?
Name three reasons that might predispose to this?
Name three symptoms that this woman might have presented with.

Simms speculum
Catheter
Prolapse - Cystocoele
Vaginal deliveries, pregnancy, obesity, chronic cough
Dragging sensation, difficulty passing stools, urinary incontance/frequency

IUS - eg. merina coil
Checking threads
What 2 things does this show?

Threads from IUS
Cervical ectropion
What does this show?

Polp extending through the Os
This 36 year old woman has attended for her cervical screening and her cervix is pictured.
Has this woman ever been pregnant?
Explain how you have derived your answer.

Yes
- The os gets damaged/can form more of a slit after a vaginal delivery
At present, how often are women normally and routinely offered cervical screening?
Every 3 years from 25-49
Every 5 years from 50-64
How many times should the brush be rotated as part of the cervical screening process?
5 complete turns
Where exactly should the cells be obtained from in a cervical smear?
The transitional zone
What is the abnormality shown?
Name three factors that predispose to this?
What symptoms may the patient present with?

Anal fissure
Anything that stretches anal skin so straining at stool, diarrhoea, trauma, childbirth, Inflammatory bowel disease (crohn’s and UC), some STI’s (syphilis, chlmaydia, herpes)
Symptoms include – pain, bleeding – usually bright red on paper after wiping, constipation (largely due to pain and contraction of sphincter)
What is the abnormality shown in the picture?
Name three predisposing factors.

Haemorrhoid
Chronic diarrhoea/constipation
Straining on toilet
Anal intercourse
Obesity
Sitting for long periods of time on toilet
Increasing age
Increased intra-abdominal pressure
Pregnancy
Chronic cough
Name a complication of this.
Name three different types of treatment

Complications are rare but include anaemia from chronic blood loss, strangulation (pain and gangrene)
Treatment:
Conservative – laxatives to avoid straining, analgesia
Creams – to shrink - little evidence of benefit
Rubber band ligation
Sclerotherapy
Cautery
Haemorrhoidectomy