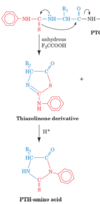
Exam I Flashcards
- proteins are least soluble when the net charge is __________?
- How would you adjust the pH of your solution to accomplish this?
- This is relevant to what purification technique?
- zero
- adjust pH to isoelectric point (pH=pka)
- salting out, to elute the remaining polar group (usually the desired protein)
ion exchange chromatography is best used when the proteins in a mixture for purification ______________
have a big difference in net charge
in ion exchange chromatography, what is the name of the chemical attachment to the matrix which serves as the anion exchanger?
DEAE (diethylaminoethyl - positively charged)
in ion exchange chromatography, what is the name of the chemical attachment to the matrix which serves as the cation exchanger?
CM (carboxymethyl - negatively charged) CH2—COO^-
what is meant by the term “salting in”
the phenomenon of how solubility of a protein at low salt concentrations increases as salt is added because the additional salt shields the protein’s own ionic charges such that the protein doesn’t fold in on itself
what is meant by the term “salting out”
when the salt concentration increases beyond the point of salting in, the salt ions then take up solvating water molecules such that the protein has to group together to get solvated (less surface area of solvation for a precipitated protein than for non precipitated) Essentially, the salt out-competes the protein for solvation.
When doing this technique, the salt concentration is usually adjusted to just below the precipitation point of your desired protein.
why is affinity chromatography the most powerful chromatography purification technique?
because it exploits the target proteins unique biochemical properties rather than smaller differences like size, polarity, charge, etc.
- what do 2-mercaptoethanol or another type of mercaptan do?
- What are they commonly used for?
- The resulting free sulfhydryl groups are then ___1______, usually by treatment with_______2____, to prevent the re-formation of disulfide bonds through ________3____
- they break a disulfide bond to separate subunits of a protein because they themselves contain -SH groups.
- It is used in protein sequencing and SDS-PAGE to separate the subunits of a protein bonded by a disulfide bond. The SDS alone is not going to break this bond.
- alkylated 2. iodoacetate 3. oxidation
In SDS-PAGE, the relative mobilities of proteins vary approximately ________ with the logarithm of their _______ .
linearly with the log of their molecular masses
What does the mathematical graph for the proteins purified in SDS -PAGE look like in shape and what terms denote the X and Y axes?

About half of the 20 amino acids are called essential because
Option A: they are essential for the synthesis of pyrimidines.
Option B: they are essential for nitrogen metabolism.
Option C: they are essential for the synthesis of purines.
Option D: our bodies cannot synthesize them and therefore they need to be present in our diet.
Option E: our bodies need them for protein synthesis.
Option D: our bodies cannot synthesize them and therefore they need to be present in our diet.
IEF refers to
isoelelectric focusing
what is isoelelectric focusing
when proteins in an electric field that has a gradually increasing pH travel to the point on the field corresponding to their pI
it is often used in conjunction with SDS-PAGE in the perpendicular direction
Question NumberQ 1:
Ribosomes use L amino acids to synthesize proteins.These amino acids are called “L” because
Option A: they are all (R)-amino acids.
Option B: they turn polarized light to the left.
Option C: they have a configuration of groups around the Cα that can be related to the configuration of groups around the asymmetric carbon in L-glyceraldehyde.
Option D: they are all (S)-amino acids.
Option E: they are chiral.
Option C: they have a configuration of groups around the Cα that can be related to the configuration of groups around the asymmetric carbon in L-glyceraldehyde.
What is an Isopeptide bond
An amide linkage between an α-carboxylate group of an amino acid and the ε-amino group of Lys,
or between the α-amino group of an amino acid and the β- or γ-carboxylate group of Asp or Glu

An amide bond between a side-chain carboxylate and an α-amino group is also called a(n)
Option A: isopeptide bond.
Option B: disulfide bond.
Option C: ester bond.
Option D: glycosidic bond.
Option E: anhydride bond.
Option A: isopeptide bond.
T/F: Amino acid derivatives play an important role in various biological processes.
True lol duh
T/F:
The pK values of the ionizable groups of amino acids may be altered when the amino acid is part of a polypeptide.
True
How do you convert mL or L to moles?
*(if you have to figure out an equation with A-/HA, then you may need to put those quantities in moles form and this is how you can do that)

T/F: Amino acids may be covalently modified after they have been incorporated into a polypeptide.
True
_____________is the only amino acid of the 20 standard amino acids that lacks a primary amine.
proline
A ________bond is a CO-NH linkage that is formed between amino acids.
peptide
The polymerization of amino acids to form a polypeptide can be represented as a _______ reaction.
condensation

Proteins are molecules that contain one or more __________ chains
polypeptide