Exam 4 Wed.3.30.Kidneys Flashcards
What is the Renal capsule?
- surrounds each kidney
- embedded in a mass of fat; protection from trauma

What is Renal fascia?
- surrounds kidney and fat
- attaches kidney to posterior abdominal wall; protection from trauma
*Dr.T emphasized how much it hold kidneys in place and how it may best be appreciated when watching a kidney being taken out of a body

What is Hilum?
- central indentation where blood vessels, nerves, lymphatics and ureter enter and exit

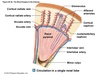
What is the cortex?
- outer region of kidney
- contains glomeruli, most of proximal tubule and some distal tubule
- not the salty region of the kidneys

What is the Medulla?
- inner region of kidney
- contains primarily pyramids, Loop of Henle, and collecting ducts

What are the Pyramids?
contain loop of Henle and collecting ducts

What is the Calyx?
- calices- plural form
- chambers that receive urine from collecting ducts, forming entry into renal pelvis

What is the Lobe?
- structural unit of the kidney
- contains pyramid and overlying cortex ~ 14/kidney
Something to do if you’re mega stressed out or maybe just need a mental break
What is the nephron?
- functional unit of kidney
- 1.2 million per kidney

Tubular structures- What do they do (general)? List the structures (5)
Together function to form urine (end product) via secretion and absorption
–Renal corpuscle- glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule
–Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
–Loop of Henle (important in electrolyte and water balance)
–Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
–Collecting duct (for urine)

What is a Glomerulus?
tuft of capillaries
What is Bowman’s capsule?
surrounds glomerular capillaries
Disadvantage to the “out hole”
- entry point for bacteria
- Women have a shorter urethra than men making them more prone to bladder infections
- 1/3 women get a UTI
Name two (sorta 3) chronic illnesses are highly dependent on kidney function
- Diabetes and hypertension
- Should include metabolic syndrome since it is teh precursor to diabetes
- rely on glucose and electrolyte regulation and balance
Number 1 function of the kidneys
maintain a stable internal environment- homeostasis
What happens to the old kidney with a kidney transplant?
- Docs leave it where they found it. It’s hooked into the aorta and inf. vena cava.
- Won’t remove unless infected
- The new kidney is hooked into inferior vessels near the ilium
Where are the kidneys?
- Tucked under rib cage and musculature for protection
- If kidneys are aggravated, may send pain signals if tapped/palpated over costovertebral angle.
Descriptive word for kidney pain
Colicky (cramping and wave like pain)
List kidney blood vessles in Dr. T’s PP (10)
- Renal arteries
- Interlobar arteries
- Arcuate arteries
- Interlobular
- Afferent arteriole
- Glomerular capillaries
- Efferent arteriole
- Peritubular capillaries
- Vasa recta
- Renal veins
*Bold were vessels emphasized in lecture. She was not as concerned about teh other vessels

Where do Renal arteries branch off from?
abdominal aorta
Where are Interlobar arteries located?
travel down renal columns and between pyramids

*Not emphasized by Dr. T
Where are Arcuate arteries located?
arch over pyramids in cortical medullary junction

*Not emphasized by Dr. T
What are Interlobular vessels connected to?
afferent arteriole

*Not emphasized by Dr. T
















