Exam 3 Flashcards
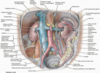
vasc of uterus
uterine A, then ovarian A
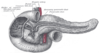
caput medusae
dilated Cutaneous veins in anterior ab wall due to:
- portal htn
- SVC/IVC obstruction

ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine) lies at the level of
sacral promontory
innervations to bladdar
vesical/prostatic plexus
PNS (s2-s4): contract detrusor, relax internal urethral sphincter
SNS: relax detrusor, constrict internal sphincter
Mesentery proper
dbl fold peritoneum
suspends jejunum and ilieum from post ab wall
- The root extends diagonally from the duodenojejunal flexure to the right iliac fossa.
- Its free border encloses the small intestine.
- Contains the superior mesenteric and intestinal (jejunal and ileal) vessels, nerves, and lymphatics.
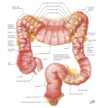
Transverse colon
R hepatic flexure –> L splenic flexure
largest and most mobile
txverse mesocolon attachment to posterior ab wall
N: superior & inferior mesenteric plexus
A: SMA - R, L, middle colic
V: SMV - R, L, middle colic
L: middle colic
lymph of duodenum
follow A
–pancreaticoduodenal, pyloric, superior mesenteric, and celiac lymph nodes
Peri-nephric abscess
spread to pelvis due to fascial attachment
- DOES NOT SPREAD TO ADJ KIDNEY
causes:
- UTI
- staph aureus
- DM
- lsions of urinary tract: stones, cyst
Intraperitoneal Injection
•widely used to administer chemotherapy drugs to treat some cancers, particularly ovarian cancer.
Fluid injected into the peritoneal cavity is absorbed rapidly
functional “left liver” inclues
L lobe, caudate, quadrate lobes
Inguinal ligament

lower free border of external oblique
folds backwards on self
ASIS –> pubic tubercle
direct inguinal hernia
WEAK posterior wall of inguinal canal
No descent into scrotum
medial to inferior epigastric vessels
aquired
Older age
basic celiac trunk pic

Lymphatic drainage of female reproductive organs
- ovary, uterine tube, and fundus follow the ovarian artery and drain into the paraaortic nodes/ lateral/ pre/ lumbar.
- uterine body and cervix drain into the internal and external iliac nodes
2nd part duodenum
descending R of L1–L3
–major duodenal papilla on posteromedial wall = opening of hepatopancreatic ampulla
Thoracic esophagus
superior mediastium, L of median line
- pass behind and R of aortic arch
- desc posterior mediastinum along the right side of the descending aorta
diagphragm @ T10
- distinct dilation before entering diaphragm
front: trachea, aortic arch, R pulm A, L bronchus, pericardium
behind: v-colum, longus colli M, R aortic intercostal, thoracic duct, hemiazygos V
Venous drainage of prostate
prostatic venous plexus b/w true and false capsules
connect to Batson plexus (valve less)
•Veins of most of the pelvic organs are connect to Batson plexus ( except for ovaries and testis)
- how pelvic cancer can spread to the vertebral column
venous drainage of kidney
R & L renal V
- anterior to A
- L receives L suprarenal and L gonadal
drain to IVC
L passes anterior to aorta, posterior to desc SMA
NAVL of liver
N: hepatic N plexus: SNS from celiac plexus, PNS from vagus
A: portal vein (70%), hepatic (30%)
V: 3 formed by union of central veins –> drain to IVC inferior to diaphragm
L: hepatic –> celiac –> cisterna chyli
Subphrenic (Suprahepatic) Recess
pocket b/w diaphragm and anterior/superior part of liver
separated into right and left recesses by the falciform ligament.
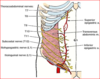
innervation to large intestine
PNS - vagus, pelvic splachnic
SNS: T10-L2
N, A, V, L of scrotum
N:
- anterior 1/3 = ilioinguinal, genitofemoral - genital branch
- posterior 2/3 = pudendal, posterior cut N of thigh
A:
- pudendal –> scrotum
- inferior epigastric –> cremastric
V:
- same as A
L:
- superficial inguinal
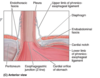
Rectus sheath
•Aponeurosis of int. obl. splits to enclose rectus abdominis to form rectus sheath
anterior
- above arcuate line
- Aponeurosis of external and internal oblique
- Below arcuate line
- Aponeurosis of external oblique, internal oblique and transverse abdominis
posterior
- •Above arcuate line
- •Aponeurosis of internal oblique and transverse abdominis
- •Below arcuate line
- •Deficient, rectus abdominis lie on fascia transversalis
Nerve supply to stomach
PNS
- From anterior and posterior vagal trunks.
- Increase peristalsis and relax pyloric sphincter.
SNS
- From T6–T9 spinal cord segments via great splanchnic nerve to celiac plexus.
- Inhibit peristalsis and contract pyloric sphincter.
Visceral referred pain of stomach
poorly localized –> radiates to dermatome lvl
•Parietal peritoneum pain is severe and localized
innervation to rectum
pns - pelvic splanchnic
Paracolic Recesses (Gutters)
•Lie lateral to the ascending colon (right paracolic gutter) and lateral to the descending colon (left paracolic gutter).
prostate secretes
PSA
PGs
citric acid
acid phosphatase
proteolytic enz
Ascending colon
R posterior ab walll
cecum –> liver: turns @ R colic flexure (hepatic flexure)
secondarily retroperitoneal
N: superior mesenteric plexus
A: ileocolic, R colic
V: ileocolic, R colic
L: epicolic, paracolic nodes
Xiphoid process: located at T____
T9
complications of gastric ulcers
bleeding, perforation
if on posterior wall of stomach: can erod large splenic A
Scrotum
- Cutaneous bag containing testis, epididymis and lower part of spermatic cord
- Has six layers-skin, dartos muscle, Colles fascia, external spermatic fascia, cremasteric fascia and internal spermatic fascia
- Dartos m. is supplied by sympathetic fibers passing through genital branch of genitofemoral nerve
Subhepatic Recess
- Hepatorenal Recess (Morrison’s Pouch)
- ■ Is a deep peritoneal pocket between the liver anteriorly and the kidney and suprar-enal gland posteriorly.
- It communicates with the lesser sac via the epiploic foramen and the right paracolic gutter, thus the pelvic cavity.
Innervation to Adrenal glands
myelinated presynp SNS –> celiac plexus, thoracic splanchnic –> chromaffin cells (SNS postgang)

•Mesosalpinx
•Suspends the uterine tube
NAVL of Large intestines
N: from superior mesenteric plexus: PNS - vagus, SNS - lower thoracic SC seg
A: ileocolic
V: ileocolic
L: ileocolic
Suspensory ligament of the ovary
•connects ovary to the lateral pelvic wall
FIRST PART OF DUODENUM
•Superior
–Neck of gallbladder
–Hepatoduodenal ligament (lesser omentum)
•Inferior
–Neck of pancreas
–Greater omentum
Iliacus
O:Iliac fossa
I: lesser trochanter, femoral shaft, psoas major tendon
N: femoral
A: flex thigh, stab hip
•SMA syndrome
–Compression of the third part of the duodenum by the SMA and AA
Symptoms
- include early satiety, nausea, vomiting,
- extreme “stabbing” postprandial abdominal pain (due to both the duodenal compression and the compensatory reversed peristalsis
- severe malnutrition accompanying spontaneous wasting
- “Food fear” is a common development among patients with the chronic form of SMA syndrome
Coverings of spermatic cord
Ensheathed in three layers of tissue:
- External spermatic fascia, an extension of the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle
- Cremasteric muscle and fascia, formed from a continuation of the internal oblique muscle and its fascia
- Internal spermatic fascia, continuous with the transversalis fascia

•Vermiform appendix
–Arises from the posteromedial side of cecum
–Usually retrocecal
–Has a short mesentery from cecum: mesoappendix
–Supplied by appendicular artery from ileocolic artery
Hesselbach’s triangle
Boundaries:
•Medially
- •Rectus abdominis
•Laterally
- •Inferior epigastric artery
•Inferiorly
- •Inguinal ligament
•Direct inguinal hernia occur through this

Intraperitoneal organs are…
enclosed by peritoneum on all sides
Uterine and vaginal plexus
-drains into the uterine vein
Iliac crest @ what lvl of vert?
L4
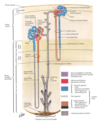
portosystemic anatomoses

Secondary retroperitoneal organs are
start intraperitoneal
fold
end up pressed against posterior body wall
lose mesentery –> become retroperitoneal
Neuromuscular plane is located…
•Between internal oblique and transverse abdominis
Pudendal block
- sacrospinous ligament attaches from sacrum to ischial spine
- Pudendal n. crosses the sacrospinous ligament on its lateral aspect near its attachment to the ischial spine
- Locate the spine, find location of the nerve for injection
-
-

internal oblique
O: thoracolumbar fascia, anterior 2/3 of iliac crest, lateral 1/2 inguinal ligament
I: ribs 10-12, linea alba, conjoint tendon to pubis
N: thoracoabdominal anterior rami of inferior 6 thoracic N, L1
A: compress, support ab viscera, flex and rotate trunk

•3 superficial artery from femoral artery for cutaneous anterior abdominal wall
- Superficial epigastric
- Superficial external pudendal
- Superficial circumflex iliac
Intestine in Omental Bursa
uncommon
omental foramen –> omental bursa: may become strangulated
boundaries of foramen cannot by incised due to bv
MUST decompress intestines –> return
3 main branches of celiac trunk
- common hepatic
- gastroduodenal
- supraduodenal
- superior pancreaticoduodenal
- R gastro-omental
- R gastric
- con’t as proper hepatic
- R hepatic
- cystic
- L hepatic
- R hepatic
- L gastric
* esophageal - splenic
- short gastrics
- L gastro-omental
general parts duodenum
4 parts: 2-4 are retroperitoneal, anterolateral to L1
•Lateral or Transverse Cervical (Cardinal or Mackenrodt) Ligaments of the Uterus
extend from cervix and the vagina to the pelvic walls
extend laterally below the base of the broad ligament
support the uterus
•Main ligament that prevents the prolapse

hepatorenal recess
subhepatic recess
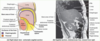
potential space b/w liver and R kidney
Rectal venous plexus
drains into any rectal vein
Abdominal Paracentesis
anterolateral ab wall: superior to empty bladder
avoids inferior epigastric A
Vesical venous plexus
-drains the bladder, prostate (m), deep and dorsal veins of the penis/clitoris and will drain into the inferior vesical vein
Sacral Plexus

Lesser omentum
dbl layer
porta hepatis –> lesser curv of stomach and 1st part of duodenum
- Hepato gastric and hepatoduodenal ligaments.
- Right free margin contains the portal triad.

Need to be careful during hysterectomy
Ureter and uterine artery relationship

Lesser Sac (Omental Bursa)
- ■ Is an irregular space that lies behind the liver, lesser omentum, stomach, and upper anterior part of the greater omentum.
- ■ Is a closed sac, except for its communication with the greater sac through the epiploic (omental) foramen.
•
indirect inguinal hernia
deep inguinal ring –> scrotum
- lateral to inferior epigastric vessels
Congenital: incomplete closing of (embryonic) process vaginalis
Younger age
•Prostatectomy may lead to….
erectile dysfunction
•Sacrocervical Ligaments
•Extend from the lower end of the sacrum to the cervix and the upper end of the vagina
NAVL of ureters
N:
- abdominal, aortic and superior hypogastric plexuses
- pain fibers follow SNS T11-L2: referred pain to lower quad of anterior ab wall
A: branches of renal, gonadal, aorta, common iliac
V: renal, gonadal
L:
- follow renal V –> lumbar lymph nodes (caval &aortic)
- middle –> common iliac nodes
- inferior –> common, external, iliac nodes
vasc supply to adrenal glands
A:
- superior suprarenal A (6-8) from inferior phrenic
- middle suprarenal artery from the aorta
- inferior suprarenal artery from the renal artery
V: suprarenal vein –>
- R: IVC
- L: L renal
lymph drainage to rectum
upper rectum: superior rectal –> inferior mesenteric –> aortic
lower: internal iliac
Epiploic or Omental (Winslow’s) Foramen
and boundaries
- natural opening between the lesser and greater sacs.
- ■ Is bounded superiorly by peritoneum on the caudate lobe of the liver, inferiorly by peritoneum on the first part of the duodenum, anteriorly by the free edge of the lesser omentum, and posteriorly by peritoneum covering the IVC.

inguinal ring: superficial and deep
- Superficial inguinal ring
- Triangular gap in external oblique aponeurosis situated superomedial to pubic tubercle
- Deep inguinal ring
- Lies in fascia transversalis just lateral to inferior epigastric vessels
Peritonitis
- Bacterial contamination of the peritoneum.
- Causes: Trauma, infection, appendicitis, perforation an ulcer.
- Generalized peritonitis is dangerous.
Parietal peritoneum
internal surface of the abdominal and pelvic wall.
same NAVL as region of the wall it lines
pain, heat, cold and laceration.
Pain = well localized
0Anterior abdominal wall
- Part of trunk below diaphragm
- Divided by plane of pelvic inlet
- •Larger upper part abdomen proper
- •Smaller lower part true pelvis
•Contents
- •Large part of the digestive and urogenital system
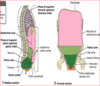
celiac A supply


recesses of lesser sac
- Presents three recesses:
- (1) superior recess, which lies behind the stomach, lesser omen-tum, and left lobe of the liver;
- (2) inferior recess, which lies behind the stomach, extending into the layers of the greater omentum.
- (3) splenic recess, which extends to the left at the hilus of the spleen.
recesses of liver
subphrenic: split yb falciform ligament, sep liver from diaphragm
hepatorenal: R side, sep anterior from kidney, post by adrenal gland
Hiatal hernia
stomach to mediastinum via esophageal hiatus
•More common in middle aged people.from weak muscles.
- paraesophageal
* cardia remains in normal position, only esophagus moves - sliding
- clamping of R crus of diaphragm = weak
- ab esophagus, cardia, parts of fundus of stomach
- esp when person lying down, bends over

Constituents of spermatic cord
- Ductus deferens
- Testicular, cremasteric, and artery to ductus deferens
- Pampiniform plexus of veins
- Lymph vessels from testis
- Genital branch of genitofemoral nerve and sympathetic plexus
- Remains of processus vaginalis

Cryptorchidism
•Undescended testis
ligaments of liver
•Falciform ligament
–Peritoneal reflection from upper anterior abdominal wall from umbilicus to liver
–Has ligamentum teres hepatis (round ligament) in free edge
•Ligamentum teres hepatis (round ligament of liver)
–Fibrous remnant of umbilical vein
–Extended from umbilicus to liver
•Ligamentum venosum
–Remnant of the ductus venosus
–Extended in fetus between the umbilical vein and inferior vena cava (IVC)
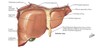
LIVER general characteristics
covered by peritoneum except @ porta hepatis and bed of gall bladder
related to:
–Right side of anterior stomach
–First part of duodenum
–Gall bladder
–Right colic flexure and transverse colon
–Right kidney and suprarenal glands
•Round Ligament of the Uterus
•Attached to the uterus in front of and below the attachment of the uterine tube
•Remnant of Gubernaculum!
- Holds the fundus of the uterus forward, keeping the uterus anteverted and anteflexed
- Enters the inguinal canal at the deep inguinal ring, emerges from the superficial inguinal ring, and becomes lost in the subcutaneous tissue of the labia majora
Esophagus in general
extends what on vertebrae
C6 –> T11/12
most narrow @ start and when it passes through diaphragm
Vagina fornix
forms the recess between the cervix and the wall of the vagina
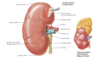
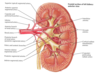
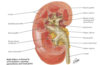
INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF KIDNEYS
Cortex
- Outer layer
- Contains: glomerulus, renal corpuscle, proximal and distal convoluted tubules, proximal collecting ducts
Medulla
- Inner layer
- Divided into medullary pyramids
- Contains: thick and thin limbs of loops of Henle, distal parts of proximal and distal convoluted tubules, distal collecting ducts
lobes of prostate
- Anterior lobe (or isthmus): front of the urethra, no glandular substance
- Middle (median) lobe: between the urethra & ejaculatory ducts, prone to BPH = block internal urethral orifice
- Posterior lobe: behind the urethra & below ejaculatory ducts, prone to carcinomatous transformation
- Right and left lateral lobes: either side of the urethra = main mass of the gland

where is the Site for portocaval anastomoses
Hemorrhoids
hemorrhoids
Posterior Branch of internal iliac

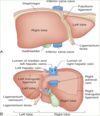
Porta hepatis
txverse fissure on visc surf b/w caudate and quadrate lobes

•Provides entrance/exit for:
–Portal vein
–Hepatic artery
–Hepatic ducts (left and right converge to form the common hepatic duct)
–Hepatic nerve plexus
–Lymphatic vessels
Ureters
retroperitoneal
surface marking: 5cm lateral to L1 SP and PSIS
constricted @ 3 sites:
- jxn ureter and renal pelvis
- cross pelvic brim, external iliac A
- wall of urinary bladdar

Pelvic Inlet vs. Pelvic Outlet