Exam 2 (extremities) Flashcards
This is a corticol depression in the posterolateral head of the humerus. It results from a forceful impaction of the humeral head against the anteroinferior glenoid rim when the shoulder is dislocated anteriorly.

Hill-Sachs lesion (Hatchet deformity)
This is an injury of the anterior (inferior) glenoid labrum of the shoulder due to anterior shoulder dislocation.

Bankart Lesion/fracture
Avulsion of the greater tuberosity by retraction of the rotator cuff is what type of fracture?
Flap Fracture
The humerus is dislocated anterior and inferiorly with the arm hyperabducted and locked above the head.
Luxatio Erecta
How much will the acromiohumeral join space narrow in a rotator cuff injury?
to less than 6mm
60% frequency in children

Supracondylar fracture
Adults are 50% likely to fracture what in an elbow injury?
radial head or neck
What’s the diagnosis?

Anterior dislocation of radius
A line paralleling the shaft of the radius should pass through the center of the capitellum.
Radiocapitellar line
What’s the diagnosis?

sail sign(radial head fracture)
What is the MC elbow fracture in adults but very rare in children?
olecranon fracture
What age does nursemaids elbow typically occur in?
2-5 years old
A fracture of the proximal 1/3 of the ulna with dislocation of the head of the radius.
Monteggia fracture
Diagnosis?

Monteggia Fracture
Findings?

anterior dislocation of the radial head with transverse fracture of proximal 1/3 of ulna
Diagnosis?

Galeazzi fracture
Findings?

fracture of the radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint
Diagnosis?

Greenstick radius fracture
These represent what kind of fractures?

Greenstick
Fracture of the radius about an inch and a half above the carpals with posterior displacement of the distal fragment?
Colles Fracture
Diagnosis?

Colles Fracture
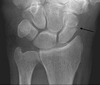
Diagnosis?

Smith’s Farcture
Diagnosis?

Barton’s fracture
Diagnosis?

Barton’s fracture