Exam 2 Flashcards
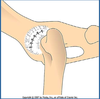
True/False: Negative Ortolani Sign in Mature Dogs means the dog Does NOT have Hip Dysplasia
False
*Ortolani Sign is Typically Absent in Mature Dogs with Hip Dysplasia due to Remodeling
List common Tumors arising from the Penis
TVT
Papilloma
Squamous Cell
Mast Cell Tumor
Lateral Patellar Luxations are a _____ Image to Medial Patellar Luxations
Mirror
*Conformational Abnormalities of Lateral Patellar Luxations and Medial Patellar Luxations are Mirror Images of Each other
In a Partial Tear of the Cranial Cruciate Ligament, there will be a Positive Cranial Drawer or Tibial Thrust ONLY when the Joint is in Partial ______
Flexion
*When the Stifle is in Extension, it will Appear Stable

______ Collateral Ligaments have both a Short and Long Portion
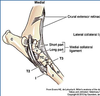
Tarsus

Procedure for Abdominocentesis where False Negatives are Common in Dehydrated Patients
Blind Tap

Two Components in the Etiology of Prostatitis
Ascending Infection from the Urethra- E.Coli Most Common
Pre-Existing Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Required
*What is the Most common Isolate in Prostatic Infections? E. Coli
True/False: Treatment for Cystic Endometrial Hyperplasia is typically an Emergency
False

Complication of Gastric Dilatation Volvulus:
Tissue Blood Flow is Absent, Then Returned when GDV is Corrected
Accumulated Waste Products and Oxygen Radicals (Toxins) Release into General Circulation
Reperfusion Injury

Surgical Procedure Recommended for Recessed Vulva
Episioplasty (aka Vulvoplasty)

When Performing a Physical Exam on a Patient with Cancer, ______ Evaluates:

Size and Location of Masses
Mobility of Masses
Consistency of Masses
Body Mapping
*When you have Masses on the outside of the body, part of your physical exam should be measuring those masses and drawing them on a Body Map
*Body Map-Profile Picture of an Animal where you draw masses and Number them. Next to the Number you should Describe the Mass
*Helps when you evaluate the Patient in the Future- Make sure Masses haven’t Changed. Really helpful in tracking the Development of cancer in these Patients

Review Card: Pathophysiology of Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
Respiratory System: Increased CO2, Respiratory Acidosis
Cardiac System- Decreased Preload and Afterload, Arrhythmias
Gastric System- Mucosal Sloughing, Bacterial Translocation

Corrective Procedure used in the Treatment of Hip Dysplasia Described Below:
Fuses Pubic Symphysis with Cautery
“Tethers” Growth of Pelvis
Only useful in Dogs < 20 Weeks of Age
Low Complication Rate

Juvenile Pubic Symphiodesis (JPS)
*Once the Patient is Older than 5 Months this Procedure is NO longer Indicated

True/False: Prognosis for Dogs with Metastatic Mammary Tumors is Poor
True
*With Metastasis- Mean Survival Time is 5 Months
List the Factors playing a Role in Pathogenesis of Chronic Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease
Degeneration of Cranial Cruciate Ligament Occurs with Age- This Degeneration tends to be worse in Larger Dogs (Over 15 kg/ 30lbs)
Factors that Contribute to Degeneration:
Obesity/Poor Fitness- More Stress/Strain on Ligaments
Conformation- Conformation of Femur, or even Stance/Gait would place Additional Stress on the Ligament
Excessive Plateau Angle- If the Slope is Steeper, the CCL would be under Greater Strain

With Regards to Blood Supply to the Spleen:
Blood Supply Stems from ______ Artery
_____ Artery is a Major Contributor: It Supplies the Pancreas prior to Branching at the Level of the Spleen
Celiac Artery
Splenic Artery- Major Contributor
*Blood Supply comes from Celiac Artery. The Celiac Artery is going to Give off the Splenic Artery which will Supply the Pancreas prior to Branching and Feeding off a Branch to the Spleen

History Typical of _____ Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease:
Significant Hind Limb Lameness that is Aggravated by Activity or After Rest
Intermittent/Progressive Hind Limb Lameness- Slow Degeneration of Ligament leads to Degenerative Joint Disease
Difficulty Rising
“Bunny Hopping”- Bilateral
Chronic
*Highly Variable Presentation- Early in the Disease, signs may be Mild or Episodic with lameness seeming to Resolve between Bouts
*Envision the Diseased Ligament as a Weakened, Braided Fraying Rope- Individual Fibers give way Progressively

Corrective Procedure used in the Treatment of Hip Dysplasia Described Below:
Improve Femoral head Coverage
Rotate Acetabulum Dorsally
Best in Animals 6-8 Months of Age

Triple Pelvic Osteotomy (TPO)
True/False: When Performing a Biopsy, you want to Obtain the Sample from the Junction of Normal and Abnormal Tissue
True

Surgical Technique for Gastric Dilatation Volvulus Described Below:
Incision through Right Abdominal Wall Caudal to Last Rib
Purse String Suture in Stomach
Place Foley or Mushroom Tip Catheter
Suture Stomach to Abdominal Wall
The Tube is Clamped and Bandaged
Tube Prevents Recurrent Dilatation

Tube Gastropexy
Uterine Rupture caused by Pyometra can lead to _____
Septic Peritonitis

True/False: In cases of Canines with Multiple Mammary Tumors, Each mass should be Removed and Tested Histopathically
True

Main Function of the Pancreas
Secretes Digestive Enzymes- Exocrine Function
*Secretes Digestive Enyzmes after the Patient has Eaten to Help break down food Products for metabolism
Grade of Patellar Luxation Described Below:

Grade II
True/False: Metastatic Ovarian Neoplasia is more common in Dogs than Cats
False
*Cats- Metastatic Ovarian Neoplasia is MORE COMMON

Possible Complications of _____ Stabilization Techniques for Cruciate Ligament Disease:
Risk of Infection
Implant Failure- Ex. Screw/Plate Breakage
Incomplete Stabilization
Iatrogenic Angular Limb Deformity
Iatrogenic Patellar Luxation
Osteotomies (TPLO, TTA)

Review of Radiographic Hip Dysplasia

Anatomic Indications for Ventral Approach to the Lower Reproductive Tract
Intrapelvic and Abdominal Lesions
What Diagnostic Modality can be used to Differentiate Congenital Versus Acquired Pyloric Stenosis?
Ultrasound
*Ultrasound for Congenital Pyloric Stenosis- Only see Hypertrophy/Thickening of Muscular Layer
Ultrasound for Acquired Pyloric Stenosis- See Hypertrophy/Thickening of Mucosal AND Muscular Layer
Treatment and Prognosis for a Solitary (Non-Metastatic) Ovarian Tumor
Complete Excision is Curative- Excellent Prognosis
Signalment associated with Ovarian Cysts
Young Adult (Dogs < 3 years, Cats < 5 Years)
Collateral Ligament Carpus Injuries are Frequently associated with Loss of Soft Tissue and Bone known as _____
“Road Rash”
*Animal gets HBC, Limb gets trapped underneath the Car which drags the Soft Tissue off the Limb- “Road Rash”
*Accompanying Shear Injuries are Common
Cardiovascular Effects associated with which Gastric Disease?
Poor Venous Return- Decreased Preload and Cardiac Output
Decreased Perfusion- Hypovolemia/Hypotension
Catecholamine Release- Vasoconstriction
VPC’s/Ventricular Tachycardia (40%)!!
Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
*Compression of Vena Cava- Occluding Blood Supply to Heart
Catecholamine Release = Vasoconstriction = Renal Shutdown

Surgical Procedure Described Below:
Removal of Ovary Alone
Procedure Steps:
Ligate Ovarian Vessels
Ligate Uterine Vessels at Proper Ligament
Excise Ovary
Ovariectomy
*Similar to Ovariohysterectomy, Ovariectomy is another way to achieve Elective Sterilization

Uterine Prolapse is a Complication of _____
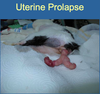
Parturition

Describe the Three Different Stapling Techniques used for Intestinal Anastomosis
Triangular End-End:
Inexpensive
Place Staples 3mm Apart around Circumference of Anastamosis Site
Inverting End-End:
End to End Anastamosis combined with TA Stapler
Place Cartridge in Enterotomy Site 3-4 cm from Transection and Place Anvil in Opposite End
Inverts Tissue
Side to Side Anastomosis:
Uses GIA Stapler
Oppose Antimesenteric Surfaces, Place Stapler in Lumen and Fire
Where should Gastrotomy Incisions for Exploration and Removal of Gastric Foreign Bodies be Made?
Ventral Midline Approach
*Stab Incision in Center of Vessels
*Prior to Gastrotomy, Inspect the ENTIRE Abdomen/GIT- Explore and Lavage Entire Abdomen
*After you have Removed the Foreign Body: Change Gloves and Instruments and Lavage the Abdomen prior to Closing

Two most Common Methods of Screening for Hip Dysplasia
Orthopedic Foundation for Animals (OFA)
University of Pennsylvania Hip Improvement Program (PennHIP)
Osteochondrosis (OCD) of the Tarsus:
Lesion is Most Commonly Located on the _____ Ridge of the Tarsus
Medial (Most Common)
*While Rottweilers are Predisposed to Lateral Lesions, even in Rottweilers, Medial Lesions are more Common

What is Meniscal Release and why might it be Done?
Meniscal Release- Cutting the Caudal Pole of the Medial Meniscus
Why is it Done? Reduce the Likelihood of Having a Patient Develop a Meniscal Injury after Surgery
*Meniscal Release- Has the effect of Letting the Caudal Pole of the Meniscus side out of the way when the Tibia Slides Forward into Thrust

Tumor of the Penis that is NOT Treated Surgically
TVT
*TVT is Commonly Treated Medically

Surgical Technique for Gastric Dilatation Volvulus Described Below:

Circumcostal Gastropexy
Stabilization Technique for Cruciate Ligament Disease Described Below:
Heavy Monofilament Nylon Suture Placed in Orientation Similar to Native Cranial Cruciate Ligament
Placing Heavy Gauge Suture around the Lateral Fabella and Through a Bone Tunnel in the Tibia

Lateral Suture
Orthopedic Test used to Diagnose Cranial Cruciate Ligament Rupture Described Below:

Active Constraint
Generates Tibial Thrust
Tibial Compression Test
*AKA Tibial Thrust Test
*Tibial Compression Test is like Pushing the Wedges Together to see if they Slide Past eachother more than the Ligament should Allow. They they do, that is a Positive Test
Tibial Compression- More Consistent in Large Dogs

True/False: Treatment for a Partial Tear of the Cranial Cruciate Ligament is IDENTICAL to the Treatment of Complete Rupture of Cranial Cruciate Ligament
True
*A Partial Tear still has Instability and Results in Wear and Tear on the Cartilage. Most Importantly a Dog with a Partial Tear has Discomfort. For these Reasons the Surgical Recommendations for a Dog with a Partial Tear are no different from those for a dog with a Complete Tear
*Partial Tears almost Always progess to Complete Tears
List Medical Treatments used for Paraphimosis
Lube
Hyperosmolar Solutions
Cold/Heat

What Suture should be used for Closing Incisions in the Uterus
3-0 or 4-0 Absorbable Monofilament
Name Two Free Radical Scavengers that Help to Chelate Toxic Metabolites within Circulation and Minimizes Reperfusion Injury in Patients with Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
Acetylcysteine
Deferoxamine
*Minimizes Reperfusion Injury- Free Radical Scavengers
Indications and Description for which Type of Splenic Surgery:
Indication:
Splenic Lacerations or Punctures
Procedure:
Horizontal Mattress Sutures placed through the Splenic Capsule in order to Help with Hemostasis
Splenorrhaphy
*Rarely Indicated- Typically used when we cause Splenic Lacerations during Surgery that need to be Repaired

Surgical Treatment for Megacolon
Subtotal Colectomy
*Goal: Remove as much Colong as Possible
Clinical Signs of _____:
Large Discrete Mass in Caudal Abdomen
May be Asymptomatic- Incidental Finding
Double “Bladder” on Ultrasound
Prostatic Cysts
True/False: Canine Mammary Tumors < 3 cm are more likely to be Benign than Masses > 3cm
True

True/False: Crytorchid Testicles are Prone to Neoplastic Formation
True
*Increased Incidence of Testicular Neoplasia in Cryptorchid Testes
Most common Form of Peritonitis in Canine and Feline Patients
Secondary Septic Peritonitis
*Most common Source of Infection: GI Tract

Most Common Cause of Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction
Biliary Mucocele
*Surgical Treatment: Cholecystectomy (Removal of Gallbladder)

Mast Cell Tumors on the _____ are Frequently More Malignant than Mast Cell Tumors on the Penis
Prepuce
*Prepucial Mast Cell Tumors are More Malignant than Mast Cell Tumors of other Sites
Managment for Short Bowel Syndrome
Small Frequent Highly Digestible Meals
Stance seen with Complete Calcanean Tendon Rupture

Plantigrade Stance

When should VPC’s (Arrhythmias) in Patients with Gastric Dilatation Volvulus be Treated?
*If VPC’s are only Intermittent/Irregular we may not Treat them

True/False: Meniscal Disease significantly Accelerates Wear and Tear on the Cartilage. Arthritis will appear Sooner and be more Severe over time in a Stifle with Damage to the Meniscus
True

Looking at the Function of the Cranial Cruciate Ligament, it can be divided into Two Subdivisions: Craniomedial Band and Caudolateral Band. What is the Functional Difference between the Two?
Craniomedial Band: Taut in Flexion and Extension
Caudolateral Band: Taut Only in Extension (Lax in Flexion)
*These Are Divisions in the FUNCTION of the Cruciate Ligament. There is no clear Anatomical Difference between the Two

What type of Tumors can be Most Readily Diagnosed from a Cytologic Sample
Round Cell Tumors- Mast Cell Tumors, Melanoma, Lymphoma

Salvage Procedure used in the Treatment of Hip Dysplagia Described Below:
Ideally Done after Skeletal Maturity
Remove Entire Head and Neck of Femur

Femoral Head Ostectomy (FHO)

Managment of Perianal Gland Adenoma
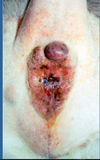
Castration

Review Card: Pancreatic Blood Supply
Duodenum and Pancreas have a very Close/Shared Blood Supply- makes surgery Challenging
Left Lobe is Supplied by Splenic Artery
Right Lobe is Supplied by Cranial and Caudal Pancreaticoduodenal Arteries

Surgical Treatment for Malignant Vaginal Neoplasia
Vulvovaginectomy
*Aggressive Resection is Necessary

The _____ Meniscus is attached to the Tibia. Thus when the Cranial Cruciate is Ruptured and the Tibia Displaces Cranially the Meniscus moves with it, Predisposing it to Crushing Injury when there is Compression between the Femur and Tibia

Medial
*Relationship between the Anatomy and Explanation of why the Medial Meniscus has the Higher Incidence of Injury
Meniscal Injury Accelerates the Wear of Cartilage

Prognosis for Testicular Torsion
Good with Surgery
Diagnosis of ______ is made based on Timing Following Parturition
Metritis
*If an Animal had puppies Recently and Presents Systemically Ill with Vaginal Discharge, Metritis would be at Top of Differential List

Principal Difference between Tightrope and Lateral Suture Stabilization Techniques used for Treatment of Cruciate Ligament Disease
Tightrope - Placed Noninvasively (Stifle Explored Noninvasively with Arthroscopy)
*Recovery is More Rapid with Less Invasive Technique when Tightrope Technique is Used

Surgical Procedure used to Decrease the Recurrence of Intussusception
Enteroplication
Describe the Three Stages of Labor
Stage 1: Restless, Nesting Behavior
Stage 2: Explusion of Fetus
Stage 3: Expulsion of Placenta
Etiology of Pyometra:
Name which Hormone is Necessary
Name the Most common Bacterial Type
Hormonal: Progesterone
Bacterial: Gram Negative (E. Coli)

Best Diagnostic Modality to Confirm Intestinal Foreign Body
Ultrasound
Etiology for which Surgical Disease of the Stomach:
Dogs: Ingestion of Rocks, Toys, Anything
Cats: Ingestion of Needle, String, Trichobezoars (Hair Balls)
Gastric Foreign Bodies
*Cats commonly Play with Needles and Thread- Check under the Tongue for STRING

Prognosis for Patients that have Undergone Surgery for Septic Peritonitis if the Source of Contamination was the GI Tract? (Secondary Septic Peritonitis)
50% Mortality

Most Common Type of Prostatic Neoplasia
Adenocarcinoma

Once Canine Mammary Tumors have Developed, an _____ is Recommened Prior to Mastectomy
Ovariohysterectomy
*Perform Ovariohysterectomy PRIOR to Mastectomy

Most Widely used Stabilization Technique used in Patients with Cruciate Ligament Disease
TPLO (Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy)
*Lateral Suture and TTA (Tibial Tuberosity Advancement) are also commonly Employed
*Tightrope Technique is the Least Employed of the Four Stabilization Techniques
Earliest Radiographic Finding in Patients with Hip Dysplasia Described Below:
Caudal Curvilinear Osteophyte
Well defined Linear Density between the Femoral Head and Greater Trochanter

Morgan’s Line
*Earliest Radiographic Sign of Hip Dysplasia- Caudal Curvilinear Osteophyte
In Cases of Biliary Mucoceles, when performing a Cholecystectomy its important to Check the Patency of the ____ prior to Resection of the Gallbladder
Common Bile Duct
True/False: Lateral Patellar Luxations are more common in Small Breed Dogs
False
*Lateral Patellar Luxations are More common in LARGE Breed Dogs, however, Medial Patellar Luxations are More Common All Around (Small and Large Breeds)

Signalment and History for _____ Cranial Cruciate Ligament Rupture:
Either Gender/ Any Breed
Cats- Rupture Usually Traumatic (Ex. Hit by Car)
Commonly due to Athletic Injury, Traumatic Hyperextension, Excessive internal Rotation
Sudden Onset Non-Weight Bearing Lameness
Acute
*Acute Cranial Cruciate Rupture is Relatively Uncommon in Dogs and Cats

80% of Vaginal Neoplasias are _____
Benign (Leimyoma Most Common)
Two common Tissues of Origin for Ovarian Neoplasia
Epithelial: Adenoma or Adenocarcinoma
Stromal: Granulosa Cell Tumor

D. Recommend Additional Diagnostics
Most common Cause of Hemoabdomen: Splenic Hemangiosarcoma
Surgical Treatment Described Below:
1. Fuse Tibiotarsal Joint at Standing Angle
2. Remove All Articular Cartilage
3. Pack with Bone Graft
4. Rigid Fixation with Plate and Type 2 External Skeletal Fixator

Tarsocrural Arthrodesis
Describe Surgical Managment of a Meniscal Injury
Partial Meniscectomy- Removal of Damaged Portion
*Primary Repair is Not Useful in Treatment of Meniscus Injury
*Recurrence and Propagation of the Meniscal Damage is Common after Partial Meniscectomy. Meniscal Release is done to Reduce the Likelihood of Developing Meniscal Injury after Surgery

Two Suture Patterns and Type of Suture commonly used in Intestinal Surgery
Pattern: Simple Continuous or Simple Interupted
Suture Type: 3.0 Absorbable Monofilament
*We only do a SINGLE Layer Closer in the Intestines- Avoids Decreasing the Size of the Lumen and Damaging Blood Supply
*Double Layer Closure is NOT Recommended- Leads to Avascular Necrosis and Intraluminal Protrusion
*Monofilament Synthetic Absorbable Suture- Less Susceptible to Infection

Prognosis for Cruciate Ligament Disease following Surgery
Good- 85-90% are Improved
DJD is Progressive, but Slowed
*TPLO/TTA: More Rapid Return to Function

Differences in Uterine Neoplasia in Canines versus Felines
Canines:
Leiomyoma 90% (Benign)
Felines:
Likely Malignant, Likely Metastatic
Prognosis Guarded
History and Clinical Signs compatible with ______:
Failure to Conceive!!!
Muco/hydro/hematometra
Most Dogs (67%) are Bright and Alert
Cystic Endometrial Hyperplasia
True/False: Even Single, Small Canine Mammry Tumors should be Removed
True
*Never “Watch and Wait”- Benign Masses can become Malignant
Radiographic Views commonly taken in Patients with Osteochondrosis of Tarsus
Standard Lateral and Craniocaudal Views
Flexed Lateral- Expose Proximal Talus
Flexed Craniocaudal
Type of Gastric Neoplasia Described Below:
Commonly Malignant and Metastatic
Age: Around 7 Years
Smooth Muscle Origin
Common Location: Cardia
Often Ulcerative into Gastric Lumen
Gastric Leiomyosarcoma
*Prognosis: Mean Survival Time is 21 Months (2 Years)
Failure of Either Testicle to Descend
Cryptorchidism
Clinical Signs common in Cases of ______:
Looking/Biting at Abdomen
Praying Posture
Non-Productive Retching
Distended Painful Abdomen
Hypersalivation
Tachycardia/Tachypnea
Gastric Dilatation Volvulus

Surgical Procedure used in the Treatment of Congenital Pyloric Stenosis Described Below:
2cm Incision Through Seromuscular Layers
Advantages:
Quick and Easy
Lumen Not Opened
Disadvantage:
Only for Congenital
_Stenosis my Reoccu_r
Fredet-Ramstedt Pyloromyotomy
*Allows Expansion of the Tissue
*Stenosis may Reoccur- Don’t use in Advanced Cases of Congenital Pyloric Stenosis
In Patients with Septic Peritonitis, _____ Administration of Antibiotics is CONTRAINDICATED
Intraperitoneal

True/False: Risk of Recurrence is Very Low Following Surgical Managment of Medial Patellar Luxations
True

Two Etiologies that lead to Carpus Hyperextension
Trauma (Fall/Jump from a Height)
Immune-Mediated Arthropathy- Disease Process Tends to Damage Joint Stabilizers

Suture Patterns commonly used to Close the Stomach with regards to the Following Cases:
Benign Gastric Outflow Obstruction (Ex. Pyloric Outflow Obstruction)
Reduced Gastric Volume
Thickened Gastric Wall
Simple Continuous
Simple Interrupted
*Do NOT want to use Inverting Patterns in Cases of Benign Gastric Outflow Obstruction (Pyloric Outflow Obstruction)

At which Age should the Testicles Descend?
30-40 Days
*Usually Descend after 1-1.5 Months of Life

List the Imaging Modalities for Diagnosing Liver Shunts
Plain Radiography:
Does NOT Provide Definitive Diagnosis
Microhepatica
Portography:
Injection of Contrast into a Vessel that Drains into Portal System
Allows Visualization of Shunting Vessel
Ultrasound:
Need Operator Experience
Nuclear Scintigraphy
CT Angiography:
Gold Standard
Allows Complete Evaluation of Portal and Hepatic Vasculature

Prognosis for Salvage Procedures for Hip Dysplasia
Total Hip Replacement:
Greater than 90% Success Rate
Near Normal-Normal Function
Femoral Head Ostectomy (FHO):
Smaller Patients- Normal Function
Larger Patients- Improved Comfort/Function
Primary Function of the Menisci is to act as ______

Shock Absorbers
*As Fibrocartilage they are Compressible and thus act as Padding between the Femur and Tibia
Increase the Surface Area of Load Transmission, which Reduces the Stress on the Cartilage

Diagnosis based on this Radiograph

Craniodorsal Coxofemoral Luxation
____ Meniscus is attached ONLY to the Tibia via the Meniscotibial Ligament
_____ Meniscus is Attached to Tibia AND Femur via the Meniscotibial and Meniscofemoral Ligament
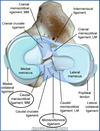
Medial Meniscus- Only Attached to the Tibia
Lateral Meniscus- Attached to Tibia and Femur

Meniscal Release alters the Function of the Meniscus and it can no longer serve the Shock-Absorbing function that it is Intended to. This changes the Way the Weight is Focused on Portions of the Cartilage and Therefore Tends to Increase the Development of _____
Osteoarthritis
*Positive Benefits of Meniscal Release Outweighs the Negative Effects (Osteoarthritis)

When Diagnosing Collateral Ligament Carpus Injuries, which Views should be Taken on Radiographs?
Standard Dorsopalmar and Lateral Views
Dorsopalmar STRESS Views- Valgus Stress and Varus Stress

Diagnostic Tool of Choice for Legg-Perthes Disease
Radiographs
Pathogenesis of Laxity in Patients with ______:
Subluxation occurs with Activity
Abnormal Force Distribution leads to Wear
Wear leads to Osteoarthritis
Hip Dysplasia
*Abnormal Force Distribution leads to Increased Wear and Tear on Cartilage. The Wear and Tear leads to Arthritis over time

Clinical Signs associated with which Condition of the Tarsus:

Osteochondrosis (OCD)
What are the Appropriate Margins for Wide Excision of Potentially Malignant Canine Mammary Tumors
2-3cm Margin Circumference
Four Possible Etiologies leading to ______ in Patients with Gastric Dilatation Volvulus:
Myocardial Hypoxia
Metabolic Acidosis
Myocardial Depressant Factor
Reperfusion Injury
Ventricular Premature Contractions (VPCs)
*Arrhythmias occur Secondary to Decreased Blood Supply to the Heart
True/False: Bacterial Culture of the Lower Reproductive Tract is Rarely Useful because the Caudal Reproductive Tract is Not Sterile
True
*Caudal Reproductive Tract is not Sterile and therefore Bacterial Cultures are of Limited Use
True/False: Surgical Managment for Pyometra is ALWAYS perferred over Medical Managment
True

True/False: Most Patients with Prostatic Neoplasia have Metastatic Disease at the time of Diagnosis
True
*80% have Metastasis on Necropsy
Surgical Technique for Gastric Dilatation Volvulus Described Below:

Belt Loop Gastropexy
*Essentially Creating a Belt Loop in the Abdominal Wall and Feed Portion of Greater Curvature of Stomach through Belt Loop and Suture in Place
Common Surgical Approach when Performing Splenectomies
Ventral Midline Celiotomy

Two Indications for Treatment of Vestibulovaginal Stenosis
Breeding Dogs
Spayed Dogs with Clinical Signs
List Differences between “Standard” Ovariohysterectomy versus Ovariohysterectomy for Pyometra
Pyometra Ovariohysterectomy:
Noncrushing Clamps (Doyen)
Ligate PRIOR to Clamp Placement- Friable
_____ Stabilization Techniques for Cruciate Ligament Disease, Neutralize (Eliminate) Tibial Thrust without Affecting Cranial Drawer
Osteotomy Procedures (TPLO,TTA)
*Osteotomy Procedures (TPLO and TTA)- Eliminate Tibial Thrust but DOES NOT Eliminate Cranial Drawer

Procedure Performed in Patients with Gastric Dilatation Volvulus in order to Prevent Recurrence
Gastropexy
*Creates Permanent Adhesion of the Pyloric Antrum to the Right Body Wall to prevent Gastric Volvulus in the Future

During Surgical Removal of Ovarian Remnant Syndrome, where would you find the Remnant?
Caudal Pole of Kidney

Prognosis Following Treatment for Prostatic Cysts
Good Outcome
*Urinary Incontinence is Reported

Physical Exam FIndings in an Animal with ______ Coxofemoral Luxation:
Affected Leg Held in Relaxed Extension
Foot Beneath Body
Stifle Externally Rotated
Affected Leg Shorter
Loss of Normal Triangular Relationship
Pain/Crepitus on Manipulation

Craniodorsal Luxation

60-70% of Dogs with Cranial Cruciate Rupture will have some amount of ______ Disease
Meniscal

True/False: Metastasis is Rare in Cases of Testicular Neoplasia
True
*Fortunately in Dogs, Testicular Neoplasia is Rarely Metastatic

Prognosis for Gatric Dilatation Volvulus
10-33% Mortality Rate
*Recurrence Rate is High without Gastropexy. Less than 10% Recurrence Rate with Gastropexy

Clinical Signs associated with which Hip Disorder:
Exercise Intolerance
Bunny Hopping Gait
Difficulty Rising/Stiff after Rest
Reluctant to Climb Stairs or Jump
Sits “To the Side”- Avoiding Hip Flexion
Hip Dysplasia

Grade of Patellar Luxation Described Below:

Grade I
*Least Affected Patellar Luxation- Patella Mainly stays in the Groove but by doing Manipulations can move Patella Out of Groove
*Patella is In the Groove, you can Manually Luxate it, but then will Pop right back into the Groove- “In-In”
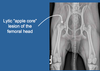
Radiographic Findings common in Legg-Perthes Disease
Focal Bony Lysis: “Motheaten”, “Apple Core”
Radiopacity of Lateral Femoral Head
Flattening/Mottling of the Femoral Head
In Cases of Cryptorchidism, how do we Locate I_nguinal and Abdominal Testicles?_
Abdominal Ultrasound

Contraindication to Closed Reduction of Coxofemoral Luxation
Dysplastic Hip
*Dysplastic Hip- Use Salvage Procedure to Repair. Closed Reduction will NOT work

Inflammation of the Peritoneal Lining
Non Specific Change that can occur secondary to a Variety of Disease Processes
Peritonitis
Three Complications Associated with Which Surgical Procedure for Gastric Adenocarcinoma:
1. Alkaline Gastritis- Bile Flows into Stomach
2. Blind Loop Syndrome- Gastric Contents Move Orally
3. Marginal Ulceration- Ulceration of Jejunal Mucosa
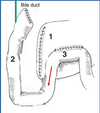
Billroth 2
Gold Standard for Diagonsis of Neoplasia
Biopsies

With Regards to Surgical Managment of Cruciate Ligament Disease, most Surgeons perfer ____ Exploration of the Joint because it provides much Better, Closer View of the Structures in the Joint
Arthroscopy

Common Gastrointestinal Effects Associated with ____:
Vascular Compromise of Stomach Mucosa
Mucosal Sloughing
Mucosal Hemorrhage and Necrosis
Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
Preferred Treatment for Cystic Endometrial Hyperplasia
Ovariohysterectomy

True/False: When Treating Hip Dysplasia, Treat the Dog, not the Radiographs
True
(Frog Fact)
Margin Sizes Recommended during Surgical Excision of Gastric Adenocarcinomas
> 5 cm

List the Different Pathological Grades of Acquired Pyloric Stenosis
Grade 1: Muscular Hypertrophy (Rare)
Grade 2: Muscular and Mucosal Hypertrophy (Most Common)
Grade 3: Mucosal Hyperplasia + Muscular and Submucosal Inflammation

When Diagnosing Vestibulovaginal Stenosis via Contrast Vaginourethrogram, A Ratio Less than ____ Indicates Severe Stenosis
0.2

Physical Exam Findings typical in Dogs with _____:
Fever
Abdominal Pain
Tachycardia/Tachypnea
Vaginal Discharge- Purulent
Pyometra
True/False: In patients with Medial Patellar Luxations, _Distal Femoral Osteotomy (DFO) i_s typically only used in Large Breed Dogs or Dogs with Very Severe Abnormalities (Grade IV)
True

Surgical Procedures used for Patients with Hip Dysplasia Described Below:
Reverses Laxity
Takes Advantage of Skeletal Immaturity
Corrective Procedures

Two Surgical Treatments for Linear Foreign Bodies
Enterotomy:
Remove Foreign Body
Have to Make Mutiple Enterotomy Incisions
Catheter Technique:
Tie Foreign Body to Catheter and Milk Down Intestines
Foreign Body comes out Anus or Enterotomy Incision

Common Renal Effects associated with _____:
Organs Compromised from Poor Perfusion
Decreased GFR
Oliguria/Anuria
Acute Renal Failure
Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
*Gastric Dilatation Volvulus leads to METABOLIC ACIDOSIS

Cranial Cruciate Ligament _____ occurs when the Cranial Tibial Thrust Exceeds Breaking Strength of the Cranial Cruciate Ligament
Tear
*If the Force of Tibial Thrust is Greater than the Breaking Strength of the Cruciate Ligament, the Ligament will Tear

Open Reduction Procedure for Correcting Coxofemoral Luxation Described Below:
Refers to Closing the Joint Capsule Torn by the Trauma
Heavy Gauge Suture
Usually Insufficient as Sole Repair
Capsulorraphy
Surgical Procedures Indicated for treatment of Small versus Large Prostatic Cysts
Smaller Cysts: Surgical Resection
Large Cysts with Capsular Communication: Partial Resection and Omentalization
ANY CYST: Castration
Indications for _____Reduction of Coxofemoral Luxation:
Pelvic/Acetabular Fracture
Femoral Fractures
Hip Dysplasia
Unstable Closed Reduction
Reccurent Closed Reduction
Open (Surgical)
Medical Treatment Options for Megacolon
Medical Managment:
Increased Fiber Diet
Stool Softeners
Osmotic Laxatives- Lactulose
Prokinetic Agents- Cisapride
*Always Try Medical Managment with them First

Physical Exam FIndings in an Animal with ______ Coxofemoral Luxation:
Non-Weightbearing
Greater Trochanter Difficult to Palpate
Stifle Internally Rotated
Leg is Held Abducted and Flexed
Affected Limb Longer

Caudoventral Luxation
*Femoral Head is Caudal to the Acetabulum

If Medical Managment is used for Treatment of Cruciate Ligament Disease, _____ is Ideal and the Patient’s activity should be Restricted for 6 weeks and Pain should be Managed
Physical Therapy
*Surgery is Perfered over Medical Management in Patients with Cruciate Ligament Disease. Medical Management is NOT Typically Recommended

True/False: Testicular Torsion is a Surgical Emergency
True
True/False: Most Intestinal Neoplasias are Malignant
True
Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Castration
Most Common Cecal Tumors
Leiomyoma
Leiomyosarcoma
*Treatment: Surgical Excision with Wide Margins
Etiology of ______:
Conformational (Acquired) Abnormality
Medium to Large Breed Dogs
AKA “Hooded Vulva”

Recessed Vulva
*Diagnosis: Visual Inspection of the Vulva- Looks like Fold of Skin over the Vulva
Physical Exam and History Findings compatible with _____ Injury:
Increase in Pain Level compared to Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease Alone
Sudden Increase in Lameness
Accelerates Wear of Cartilage
20-30% of Patients have “Meniscal Click”
Meniscal
*Meniscal Click- Popping Sensation as the Stifle is put through Range of Motion (Similar to Cracking a Knuckle)

How can Disparity of Lumen Size be Managed when Performing an Intestinal Anastomosis
Angle Smaller Lumen
Place Sutures Farther Apart on Larger Lumen
*If you cut at a slight Angle it will help compensate for that Decrease in Lumen size during Healing

Pathology of which Gastric Condition:
Infiltrates Submucosa and Muscularis layers of Stomach and Small Intestines
Clinical Signs: Weight Loss, Vomiting, Diarrhea, Hematochezia
Pythiosis

Open Reduction Procedure for Correcting Coxofemoral Luxation Described Below:
Prosthetic Capital Ligament
Toggle- Non Absorbable, Large Diameter Suture attached to Pin or Wire
Toggle Placed through Medial Acetabulum
Suture Material through Femoral Neck and Secured on Lateral Aspect of Femur

Toggle Pin/Rod
What Methods can be used to Decompress the Stomach in Cases of Gastric Dilatation Volvulus and why is this performed prior to surgery?
Performed Prior to Surgery- Improves Cardiovascular and Respiratory Function for Surgery
Best Method: Orogastric Intubation
*Perform Gastric Decompression after Fluid/Volume Support

Ovariohysterectomy in Dogs Prior to ___ years of Age Reduces the Risk for Development of Mammary Tumors
2 years
*Ovariohysterectomy early in life Signifcanty reduces the Risk of Developing Mammary Tumors
*Ovariohysterectomy after 2 Years of Age has no Effect on Development of Mammary Tumors

In a Patient that has had a TPLO or TTA, if you check for ______, they will Test POSITIVE
Cranial Drawer
*They will NOT have a Positive Tibial Compression Test
Patients that have had a TPLO or TTA to Stabilize Cruciate Ligament Disease- will test NEGATIVE for Tibial Compression, and POSITIVE for Cranial Drawer
True/False: Even with Aggressive Surgical Excision and Chemotherapy Gastric Adenocarcinoma is difficulty to completely eliminate and the Animal will most likely Die from the Condition
True
What Three Diagnostic Tests are Recommended for Work up in Cases of Canine Mammary Tumors
Minimum Database (CBC/Chem/UA)
Three-View Thoracic Radiographs- Look for Metastatic Disease
Abdominal Ultrasound/CT/MRI
*Always take Both Lateral Views on Radiographs
With a Partial Tear of the Cranial Cruciate Ligament, It is the _____ Band that Ruptures
Craniomedial
Method for Screening for Hip Dysplasia Described Below:
Distraction Applied Under Anesthesia
Measure Distance of the Femoral Head Center to Acetabulum Center
Distraction Index = Distance: Radius of Femoral Head
PennHIP

Difference between Acute and Chronic Calcanean Tendon Rupture
Acute- Usually Trauma, Complete Rupture
Chronic- Usualy Partial Rupture, Minimal/No Trauma

Radiographic Finding Described Below:
Self-Limiting
Clinically Insignificant
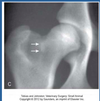
Puppy Line
*Not a Sign of Hip Dysplasia
Osteochondrosis of Tarsus:
Breed Predisposition: _____\_
Frequently Bilateral
Lesion Located on the Ridge of the Talus
Rottweiler
*Rottweiler is Particularly Predisposed to OCD of the Hock
______ Cranial Cruciate Ligament Ruptures usually Result in Dramatic Discomfort, and an Affected Dog will almost instantly be 3-Legged Lame
Acute

What test is the Gold Standard for Diagnosing Septic Peritonitis
Cytology of Abdominal Fluid (Abdominocentesis)
Major Function of the Spleen
Hematopoiesis

Common Respiratory Effects Associated with ____:
Impingement on Diaphragm
Decreased Excursions
Increased CO2- Exacerbates Acidodic State
Respiratory Acidosis
Gastric Dilatation Volvulus

Etiology of Ovarian Remnant Syndrome
Surgical Error
*Ovarian Tissue left Behind on Ovariohysterectomy

Treatment for Tarsal Hyperextension
Partial Tarsal Arthrodesis

True/False: Local Draining Lymph Nodes should be Aspirated prior to Surgery for Cytology if Possible
True
Typical Historical Findings of a Dog with _____:
Recent Heat Cycle
Polyuria/Polydypsia
Systemic Illness- Anorexia, Lethargy, Vomiting
Pyometra
Cecal Intussusception that Causes Obstruction of Ileocolic Junction
Cecal Inversion
Medial Survival Time for Canines with Malignant Mammary Tumors
1-2 Years
*Malignant Mammary Tumors, if small are associated with Longer Survival

Conditions that Predispose to which Surgical Disease of the Stomach:
Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Iron Deficiency
Gastric Foreign Bodies
*PICA- Abnormal Eating Disorder where Animals consume almost everything around them

Radiographic Views used to Diagnose Collateral Ligament Tarsus Injury
Standard Dorsoplantar and Lateral Views
Dorsoplantar STRESS Views- Valgus Stress and Varus Stress

Treatment Options for Rectal Prolapse
Treatment for Viable Tissue:
Manually Reduce- Saline/Lubricants
Place Purse String to Keep Reduced
Treatment for Non-Viable Tissue
Resect 1-2cm from Anus
Reduce Prolapse
What Type of Suture is used in Surgical Treatment for Calcanean Tendon Disease
Monofilament Nonabsorbable Suture
Two Surgical Treatments used for Dystocia
Cesarian Section (C-Section):
Preserves Fertility
En-Bloc Ovariohysterectomy:
Does Not Preserve Fertility
In Patients with Uterine Torsion, when Performing Ovariohysterectomy Do NOT ______
Derotate
*With any sort of Devatilized Tissue you never want to derotate the Tissue before you Remove it
List the Differences between Acute Gastric Dilatation, Chronic Gastric Volvulus, and Acute Gastric Dilation and Volvulus
Acute Gastric Dilatation:
Normal Position
Acute Distended Stomach
Chronic Gastric Volvulus:
Slight Malposition (Pylorus is Slightly out of Position)
Acute Gastric Dilatation with Volvulus:
Distension of Stomach and Rotation around Mesenteric Axis
True/False: Most Cranial Cruciate Ruptures are a Result of Normal Tibial Thrust Forces applied to a Cruciate Ligament that is Abnormally Weak
True
Syndrome Described Below:

Hyperextension, Hyperflexion, Flexural Deformity with Palpable Laxity
Commonly seen in Young Dogs: 5-27 weeks of Age
Carpal Laxity Syndrome
If Cytology is Not Diagnostic for Cancer, always Recommend Pursuing _____
Biopsy
*If your Cytology is not Diagnostic ALWAYS recommend a Biopsy
What is the Incidence of Dehiscence after Intestinal Surgery?
7-16% Incidence
*Dehiscence is caused by Poor Surgical Technique

Etiology for which Congenital Lesion:
Developmental Anomaly
Retained Embryonic Epithelial Tissue- Vertical Septum, Annular Fibrotic Stenosis
Hypoplastic Region
Vestibulovaginal Stenosis
*No Basis for Genetic Transmission

Possible Complications of _____ Stabilization Technique used in Patients with Cruciate Ligament Disease:
Risk of Infection
Implant Failure- Ex. Suture can Break
Incomplete Stabilization
Damage to Peroneal Nerve
Lateral Suture
*Damage to Peroneal Nerve- Unique to this Procedure

Two Orthopedic tests used to Diagnose Cranial Cruciate Ligament Rupture
Cranial Drawer Test (Passive)
Tibial Compression Test (Active)
*A Positive test by either Method Indicates Cruciate Rupture

Two Treatment options for Uterine Prolapse
Manual Reduction
Ovariohysterectomy- If Manual Reduction is not Possible
Surgical Treatment for Paraphimosis
Phallopexy

During the Postoperative Management of Osteotomy Procedures (TPLO,TTA), Activity must be Restricted (Limit Exercise) until Radiographic Healing, which commonly takes _____ weeks
8-12 Weeks

Know the Various Biopsy Techniques for the Pancreas and Associated Risks
Guillotine- Suture Portion then Excise it
Lobar Dissection- Removing Portion of Spleen
Pinch Biopsies (Laproscopic)
Associated Risks- Removing Certain Areas of the Pancreas will be Detrimental to the Flow of Digestive Enzymes into the GIT
*Right Distal Limb- Easiest for Biopsies because there is Decreased Risk for Damage to Blood Supply
Treatment for Vaginal Edema
Ovariohysterectomy- Prevents Recurrence
*Edema Resolves with End of Cycle, but tends to Recur with Subsequent Cycles

_____ Prolapse:
Anal Mucosa Protrudes from Orifice
Incomplete Prolapse
Anal Prolapse
In Cases of Annular Lesions of Vestibulovaginal Stenosis, Resection of Mucosa is Prone to _____
Stricture

_____ Management is Acceptable for Grade I-II Medial Patellar Luxations, So long as they have Minimal Clinical Signs
Conservative
*If Conservative Managment is Chosen, Monitoring is Required due to Progression of Condition

the _____ Portion of the Tarsal Collateral Ligament is only Taut when the Limb is in full Extension
The _____ Portion of the Tarsal Collateral Ligament is Taut in Both Flexion and Extension
Long Portion- ONLY Taut in Extension
Short Portion- Taut in Flexion and Extension
*Long Tarsal Collaterals are Taut when the Joint is Extended (FROG FACT)

Clinical Signs associated with _____:
Patient Stuck in Phase of Estrus Cycle
Estrogen Production Only: Prolonged Proestrus
Estrogen and Progesterone Production: Vulvar Swelling, Vulvar Discharge
Progesterone Production Only: Prolonged Anestrus
Functional Ovarian Cysts

Most common Congenital Deformity in Veterinay Medicine Described Below:
Small and Toy Breed Dogs most Affected
10x’s More Likely in Small breeds
98% are Medial Luxations
Patellar Luxation
*Typically thought of as Small Dog Disease
Benefits of Post-Operative _____ In Cases of Septic Peritonitis:
Pros:
Allows for Continued Evaluation of Fluid Character- Cytology
Allows for Continued Removal of Suppurative Material from Abdomen
Measure the Volume on 24 Hour Basis
Peritoneal Drainage (Abdominal Drainage)
*Check Cytology Daily on Peritoneal Drainage
In Dogs, 50% of Splenic Neoplasias are Malignant. Of those Malignant Masses, 50% will be _____
Hemagiosarcomas
*Most common Type of Malignancy in the Spleen of Canines
60-75% of Hemoabdomen Cases will be Hemangiosarcomas

Treatment Options for Annular Lesions in Cases of Vestibulovaginal Stenosis
Lesion Caudal to Pelvis- Dorsal Approach
Lesion Intrapelvic- Transpelvic or Ventral Abdominal Approach
*Mucosal Resection only leads to Stricture

Ideal Suture Pattern for Gastrotomy Closure
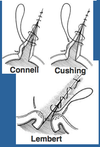
Simple Continuous in Submucosa
Cushing (Inverting) Pattern in Seromuscular Layers
*Other Acceptable Technique: “Traditional” Closure- Cushing Pattern oversewn with Lembert (AKA Double Inverting Pattern)
Three Inverting Patterns used in the Stomach: Cushing, Lembert, and Connell

How is Cystic Endometrial Hyperplasia Diagnosed?
Ultrasound
*Will be able to see Cysts on Ultrasound
Review Card: Radiographic Findings for Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease
Radiograph Shows Tibial Displacement
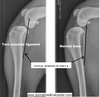

How to Differentiate Metritis from Pyometra
Metritis: Occurs Postpartum
Pyometra: Recent Heat Cycle
Most Common Injury to the Carpus where there is Damage to the Palmar Support Structures

Carpus Hyperextension
True/False: Treatment for Pyometra is considered an Emergency
True

Most Common and Perferred Treatment for Uterine Rupture
Ovariohysterectomy
*Treatment of Choice
True/False: TPLO and TTA (Osteotomy) have more Rapid Return to Function than the Lateral Suture (Extracapsular)
True
*TPLO and TTA can be Considered Largely Equivalent in Outcome

True/False: Glucocorticosteroids are CONTRAINDICATED in Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
True
Most Significant Clinical Sign noted in Patients with Hip Dysplasia during Palpation
Pain on Extension of Hip
Three Key Components of Preoperative Stabilization of Gastric Dilatation Volvulus and the Order you want to Perform the Treatments
1. Fluids- Crystalloids and Colloids

2. Gastric Decompression
3. Pain Managment
Surgical Technique for Gastric Dilatation Volvulus Described Below:

Incisional Gastropexy
True/False: Surgical Treatment is not Typically Pursued for Prostatic Neoplasia
True
*Prognosis is Guarded due to Stage at Diagnosis. Treatment is Not usually Pursued
Clinical Signs for which Congenital Lesion:
Recurrent Vaginitis
Recurrent UTI
Difficulty or Pain with Breeding
Urinary Incontinence
Vestibulovaginal Stenosis
*Urine Secretions are not being Eliminated Properly- Leads to Recurrent Vaginitis and UTI
Urinary Incontinence- This condition is also associated with Ectopic Ureters therefore many of the cases will have Urinary Incontinence. If the Urinary Incontinence is the Dogs Primary Clinical Sign, that is not related to the Vestibulovaginal Stenosis. You can correct the Stenosis and it will NOT correct the Incontinence
Diagnosis for Patellar Luxation is Made via _____
Physical Exam
Vestibulovaginal Stenosis is also associated with _____therefore many of the cases will have Urinary Incontinence
Ectopic Ureters
*If the Urinary Incontinence is the Dogs Primary Clinical Sign, that is not related to the Vestibulovaginal Stenosis. You can correct the Stenosis and it will NOT correct the Incontinence
______ is a Very important Component in the Treatment of Septic Peritonitis that aims to:
Improve Perfusion
Treat Hypotension
Improve Metabolic Disease
Correct Electrolyte Abnormalities
Fluid Therapy
*Typically use Crystalloids as well as Colloids (Hypoalbuminemia)

Best Diagnostic Tool for Pyometra
Ultrasound
*Large Fluid Filled Uterus

Two Most Common Corrective Procedures used in Patients with Hip Dysplasia
Juvenile Pubic Symphiodesis (JPS)
Triple Pelvic Osteotomy (TPO)
Proper Positioning for Episiotomy Approach to Lower Reproductive Tract
Position for Perineal Surgery

Surgical Procedure used in the Treatment of Gastric Adenocarcinoma Described Below:
Gastrectomy with Gastrojejunostomy
Allows Extensive Gastrectomy without Tension on Suture
Indications:
When Resection of Stomach is so Proximal to Limit End to End Astamosis

Billroth 2 (Gastrojejunostomy)
*Removal of Part of the Proximal Duedenum and a significant area of the stomach
Condition caused by Damage to Plantar Stabilizers
Tarsal Hyperextension
Treatment and Prognosis for Ovarian Cysts
Surgical Excision is Curative
*Ovarian Cysts removal will completely resolve the Problems
Typical Presenting History in Patients with ______:
Intermittent Weight-Bearing Lameness
Holds Leg in Flexed Position for Few Steps- “Skipping Gait”
Patellar Luxation
*Non Weight Bearing when Patella is Luxated
Minimal Lamness when Patella is Reduced (In Groove)

True/False: Radiographs are Insensitive to Low Grade Patellar Luxations
True
*Radiographic Luxation Variable with Low Grade Disease
True/False: Adjunctive Therapy (Ex. Radiation) is always recommended in Conjunction with Surgical Treatment in cases of Feline Mammary Tumors
True
*Adjuctive Therapy required for Optimal Outcome
Type of Ovarian Neoplasia that is Usually Functional and Secreting Estrogen, Progesterone, or Both
Granulosa Cell Tumor
There are Two Cruciate Ligaments in the Stifle, A Cranial and a Caudal:
The _____ Cruciate Ligament arises from the Medial Aspect of the Lateral Femoral Condyle
The _____ Cruciate Ligament Arises from the Lateral Aspect of the Medial Femoral Condyle

Cranial- Inserts on the Cranial Aspect between the Condyles
Caudal- Inserts on the Caudal Aspect of the Intercondylar Region
*Most Important Thing to Remember- Cranial Cruciate Ligament is the one that Inserts Cranially on the Tibia

True/False: Medical Managment for Cruciate Ligament Disease can be successful in Patients and is commonly Recommended
False
*Medical Managment for Cruciate Ligament Disease is NOT Recommended. Even Smaller Patients will improve more quickly with Surgery than Without
Given a choice between Surgical and Medical managment of Cruciate Ligament Disease, Surgery would be Perferable

Two Objectives for Open Reduction of Coxofemoral Joint Luxation
Reconstruct Joint Capsule and Adjacent Soft Tissues to Hold Hip in Reduction
OR
Maintain Reduction Temporarily with Implant until Soft Tissue Heals
If Ovariohysterectomy is Performed Prior to First Estrus Cycle, the Risk of Mammary Tumors is ____%
0.5%
*Spaying the Dog before its First Estrus Cycle Virtually Eliminates the Possiblity of Mammary Tumor Development

Diagnostic Modality of Choice for Congenital Pyloric Stenosis
Ultrasound
*You will be able to see the Significant Hypertrophy of of the Muscular Layer of the Pylorus
*If on Ultrasound you see Hypertrophy of the Muscular Layer in conjuction with the Predisposed Breed (Brachiocephalic), and the Clinical Signs in a Young Dog = Congenital Pyloric Stenosis

Review Card: Anatomy of Liver and Gallbladder and Blood Supply
Hepatic Artery- 20% of Blood Supply
Portal Vein- 80% of Blood Supply

_______ is an effective Barrier between the Collagen of the Cruciate Ligament and the Immunoresponsive Mechanisms of the Joint. When the Ligament is Damaged the Barrier is Disrupted, thus a Damaged Cruciate Ligament is a Potent Stimulus for Ongoing inflammation and Degenerative Joint Disease
Synovial Lining
Two Etiologies for Tarsal Hyperextension
Trauma
Chronic Instability/Degeneration: Middle Aged Shelties/Collies are Predisposed, Genetic Weakness Suspected

Most Common Tumor of the Rectum
Adenomatous Polyps

Surgical Treatment Indicated in:
Severe Injury of Tibiotarsal Joint
Failed Calcanean Tendon Repair
End-Stage Tarsal Osteochondrosis
Tarsocrural Arthrodesis
Name the Three Main Goals of Surgery in Cases of Septic Peritonitis
1. Primary Source of Bacteria must be Contained and Corrected
2. Reduce Peritoneal Bacterial Load
3. Remove Foreign Material, Inflammatory Mediators
*Main Goal: You want to Eliminate the Source of Sepsis
Goals Achieved Via: Debridement of Tissues that are Necrotic and Lavage

Three Diagnostic Tests that should be Done when Working up Testicular Neoplasia
CBC/Chemistry/UA
3 View Thoracic Radiographs- Metastasis Check
Abdominal Radiographs/Ultrasound- Metastasis Check
What Changes might you Expect on a Blood Gas Analysis from a Patient with Septic Peritonitis
High pCO2 (Hypoventilation)
High Lactate
Acidosis
*Septic Peritonitis: Metabolic Acidosis/ Lactic Acidosis

True/False: Hip Dypslasia can be Expressed very Differently in Littermates
True

In Patients with Gastric Dilatation Volvulus, they Loose the GIT Protective Barrier leading to _____ Translocation
Bacterial
*Many of these Patients can become Septicemic

Radiographic Signs of ____ Intestinal Foreign Bodies:
Plicated Intestines
Bunched in Central Abdomen
Pleating of Intestines

Linear
List Five Typical Radiographic Findings with Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease
Effusion- Displacement of Fat Pad
Osteophytosis- Patella, Trochlear Ridge
Subchondral Sclerosis- Femoral and Tibial Condyles
Increased Medial Soft Tissue (Medial Buttress)
Tibial Displacement
*Effusion occurs First- May be only Radiographic Sign of Disease, especially Early on

Treatment for Legg-Perthes Disease
Femoral Head Ostectomy
*Medical Therapy Unhelpful
Treatment for Craniodorsal Coxofemoral Luxation
Closed Hip Reduction
*Early Reduction Essential

Pros and Cons of Performng FNA vs. Tru Cut Biopsies vs. Surgical Biopsy of the Liver
FNA:
Pros: Safe, Minimally Invasive
Cons: Poor Diagnostic Yield
Tru-Cut Biopsies:
Pros: Minimally Invasive, High Chance of Definitive Diagnosis
Cons: Increased Risk of Bleeding
The Mainstay of Diagnosis of Cranial Cruciate Ligament Rupture is the Presence of ______ in the Joint (Ex. Drawer Motion, Tibial Thrust)
Instability
*If Instability is Present in the Stifle Joint, Confirms Cranial Cruciate Ligament is Damaged

Radiographic Stress View used to Diagnose Medial Collateral Ligament Carpus Injuries:
Pressure from the Medial Side is Pushing the Distal Limb Laterally
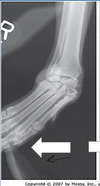
Valgus Stress
*When you have an Injury to the Medial Collateral Ligament, you put the Carpus in Valgus Stress and you have a lot more Valgus motion than you normally would
What are the Three Functions of the Cranial Cruciate Ligament
Prevents Internal Rotation
Prevents Hyperextension
Prevents Cranial Tibial Thrust- Most Important

Techniques for Partial and Complete Liver Lobe Resection
Complete Liver Lobectomy:
Ligature Technique: Should only be Used for Left Lateral and Left Medial Liver Lobectomies in Small Dogs and Cats
Partial Liver Lobectomy:
TA Stapler: Most Common Technique (Best)
Suturing: Technique Results in Greatest Blood Loss
Most Critical Time Period for Postoperative GDV Patients
First Four Days Post Op
*Death due to Hypovolemic Shock

Local Lymph Node Excision is Prognostic for which Three Types of Tumors
Mammary Carcinoma
Mast Cell Tumors
Apocrine Gland Adenocarcinoma of the Anal Sac

Most common Cause of Primary Peritonitis in Veterinary Medicine
Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP)

Name the Procedure used to Surgically Manage Pyometra
Ovariohysterectomy
*Only after Adequate Resuscitation
Treatment for RECURRENT Rectal Prolapse
Non-Incisional Colopexy or Incisional Colopexy
Indications for which Corrective Procedure used in Hip Dysplasia:
Clinical Signs of Hip Dysplasia
6-8 Months of Age
No Radiographic Evidence of Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD)
Distinct “Clunk”- Ortolani Sign
Angle of Rotation < 30 Degrees
Triple Pelvic Osteotomy (TPO)

Pathology of which Condition leading to Gastric Outflow Obstruction described Below:
Hypertrophy of Circular Muscles of Pylorus!!
Young Dogs
Predisposed Breed: Brachiocephalic (Ex. Boston Terrier)
Signs start at Weaning- Dietary Alteration (Changing from Liquid to Solid Diet)

Congenital Pyloric Stenosis

Description and Indications for which Surgical Technique used for Canine Mammary Tumors:
Removal of Solitary Mass < 5-10mm
ONLY Appropriate if No Criteria of Malignancy
Mass Removed with 1cm Margin
Lumpectomy
Detection of _____ by the Tibia in either the Cranial Drawer Test or Tibial Compression Test is Considered a Positive Test
Cranial Translation
Cranial Translation: Movement of the Tibia Cranially. Any Movement of the Tibia Cranially Denotes a Positive Test = Cranial Cruciate Rupture

Preferred Treatment for a Medial Collateral Ligament Carpus Injury
Surgical Managment- Reconstruct/Replace Collateral Ligament
*Splinting and Rest are Unhelpful as Sole Treatment- CONSERVATIVE Managment is Rarely Useful
______ INCREASES the Incidence/Risk for Prostatic Neoplasia and Increases the risk of Metastasis
Castration
How would your approach for Obtaining Biopsies Change with Focal vs. Mulifocal vs. Generalized Pancreatic Lesions
Multifocal Disease: Obtain Multiple Biopsies
Biopsy of Large Lesions- Partial Pacreatectomy
Mainstay of Diagnosis of Vestibulovaginal Stenosis
Contrast Vaginourethrogram (Contrast Radiography)
*Measure Ratio between Narrowest and Widest Point
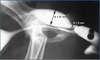
Surgical Procedure used in the Treatment of Congenital Pyloric Stenosis Described Below:
3-5cm Full Thickness Incision (Into Lumen)
Suture Transversely
Advantages:
Reoccurrence Unlikely
Disadvantages:
Lumen Opened
Not Usually Effective with Acquired Stenosis
Heineke-Mikulicz Pyloroplasty
*Widens the Pyloric Area- Works better in More Advanced Cases of Congenital Plyoric Stenosis
Indications and Pros and Cons for which type of Biopsy:
Indications:
Large Superficial Lesion
Lesions in Tissues where Morbidity associated with Definitive Surgery without a Diagnosis would be Unacceptable (Ex. Liver)
Less Invasive Sampling Techniques have not Yielded a Diagnosis
Cons:
Will Require Second Surgical Procedure
May Create Communication between Neoplastic and Normal Tissue (Cell Seeding)
Incisional Biopsy

Which Breed is Predisposed to Malignant Mammary Tumors
German Shepherds
Gastric Condition Described Below:
Causative Agent: Fungal Organism (Pythium Insidiosum)
Organism lives in Aquatic Environment
Signalment: Young Large Breed Working Dogs (Ex. Labradors)
Pythiosis
*Common in Large breed Working Dogs - Ex. HUNTING
List Various Options for Medical Managment for Animals that have Hip Dysplasia or who are Predisposed to Hip Dysplasia
Nutritional Managment- Lower Calcium/Vitamin D Diet in Puppies
Weight Managment in Adult Dog- MOST IMPORTANT
Exercise Modulation
Physical Therapy
NSAID
*Medical Managment of Hip Dysplasia should Precede Surgical Treatment

Description of what Surgical Technique used in the Intestines:

Resection and Anastomosis
*Very Important to Begin Anastomosis at Mesenteric Border!!
*Ligate Blood Supply to all the areas the we Plan to Remove

Two Associated Complications of Cholecystectomy
Bile Peritonitis
Bleeding

Treatment for Intestinal Foreign Body when the Intestines are Healthy versus Necrotic
Healthy: Enterotomy
Necrotic: Resection and Anastomosis
*Enterotomy- Simple Incision in Intestinal Wall and Removal of Foreign Body

Review Card: Normal Anatomy of Portal Vasculature and Effect of Portosystemic Shunt
Portosystemic Shunt- Aborization from the Portal Vein into the Liver doesn’t Happen
*Instead there is a Vessel that comes from the Portal Vein that Bypasses the Liver and dumps directly into the Caudal Vena Cava
Most common Type of Tumor that affects the Stomach
Adenocarcinoma
*Extremely Malignant and Aggressive
Two Joints that are at Risk for Tarsal Hyperextension
Proximal Intertarsal
Tarsometatarsal
*Tibiotarsal Joint- Almost all Motion occurs here, but is Rarely effected by Tarsal Hyperextension

History and Signalment compatible with ______:
Young Dogs
One of First Few Proestrus/Estrus Cycles
Mucosa Becomes Edematous
Edematous Mucosa Protrudes from Vulva
Vaginal Edema/Hyperplasia
Two Indications for Medical Managment of Pyometra
NOT Systemically Ill
Open Pyometra ONLY

Three Procedures used in the Treatment of Gastric Adenocarcinoma
Gastrectomy- Rarely Done
Billroth 1
Billroth 2- Most Common
Differences between Younger and Older Patients with Hip Dysplasia during Palpation
Young Patient:
Palpable Laxity- Subluxate Femoral Head
Ortolani Test/Sign
Mature/Older Patient:
Decreased Range of Motion in Extension
NO PALPABLE LAXITY due to Remodeling
Two most Common Surgical Options for Treatment of Portosystemic Shunt
Ameroid Constrictors
Cellophane Banding

Indications for _____Treatment of Metritis:
Valuable Breeding Animal
Good Response to Initial Therapy
No Devatalized Tissue/Retained Placenta or Fetus
Medical
*Surgical Exploration is Indicated Otherwise
Physical Exam Findings with ______:
Effusion- Palpable behind Patellar Tendon
Stifle More Rounded- Due to Large Volume Effusions
Muscle Atrophy- Limb Disuse
Medial Buttress- Firm Medial Collateral Fibrosis
Crepitus- Degenerative Changes/ Osteophyte Formation

Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease
*Effusion: Infill of Parapatellar “Divot”
*All of the Above Findings only Indicate the Presence of Joint Disease. They Do not Provide a Specific Diagnosis

Indications for which Type of Splenic Surgery:

Complete Splenectomy
*Most Common type of Splenectomy Performed!
Etiology of Chronic Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease
Chronically Weakened Cruciate Ligament- Progressive Degeneration of Cranial Cruciate Ligament
Lower Breaking Strength Results in Rupture with Normal Weightbearing- Ligament cannot withstand the Normal Forces Associated with Weightbearing
*Degenerative Process that is Frequently in place long before there are any Clinical or Radiographic Findings
Stabilization Technique for Cruciate Ligament Disease Described Below:
Longitudinal Cut in Tibial Tuberosity
Advancement of Tuberosity makes Patellar Tendon Perpendicular to Plateau

Tibial Tuberosity Advancement (TTA)

True/False: In Patients with Medial Patellar Luxation, Soft Tissue Reconstruction is ONLY effective when Combined with Bone Reconstruction
True
Most Common Neoplasm in Intact Female Dogs
Mammary Tumor

Radiographic Stress View used to Diagnose Medial Collateral Ligament Carpus Injuries:
Pressure from the Lateral Side is Pushing the Distal Limb Medially

Varus Stress
*When you have an Injury to the Medial Collateral Ligament, you put the Carpus in Varus Stress, you end up with Subluxation of the Joint toward the Medial Side (Subluxation goes towards the Side of the Injury)
True/False: Whenever you do Surgery to Remove a Foreign Body in the GIT you are going to do a Full Exploratory Laparotomy
True
*Must Inspect every and all aspects of the Gastrointestinal Tract
____% of Feline Mammary Tumors are Malignant
85-90%

Four Main Techniques used for Intestinal Biospy
Logitudinal Intestinal Biopsy- Most Common
Logitudinal Biopsy with Longitudinal Closure- Disadvantage: Narrows Lumen of the Intestine
Logitudinal Biopsy with Transverse Closure- Advantage: Widens Lumen of the Intestine

Common Signalment for ____ Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease:
Large/Giant Breed Dogs
Female > Male
Breed Disposition: Rottweiler, Newfie, Staffordshire Terrier, Labrador, Mastiff, St. Bernard
Chronic
*Large Breed Dog Disease
Maneuvers Required Following Closed Reduction of Caudoventral Coxofemoral Luxation
Put Joint through Range of Motion to Clear Debris
Apply Hobbles at Level of Stifle for 10-14 Days
*Once you get the Hip back in, you want to put the Joint through Aggresive Range of Motion because you want to make sure that you cleared all the Blood Clots and Fibrosis out of the Joint
Apply Hobbles- Prevent the Limbs from Sliding Laterally
Limitation to using OFA Screening Method for Hip Dysplasia
Cannot Certify Hips Before 24 Months (2 years old)
*Positioning Underestimates Subluxation
*If animal is 2 Years old and has No Radiographic Signs of Hip Dysplasia, then the Animal will Not Develop Hip Dysplasia. If the Animal is Under 2 Years Old than the OFA will Not Certify
List the Differences between Extracapsular versus Osteotomy Stabilization Techniques for Cruciate Ligament Disease
Extracapsular:
Rely on an Implant to Stabilize the Joint- Placed on the Outside of the Joint Capsule
Ex. Lateral Suture and Tightrope Techniques
Tibial Osteotomies:
Rely on Change in the Forces on the Joint to Neutralize Tibial Thrust
Cut in the TIbia to Induce a change in the Way that Weight is Transferred through the Joint
Ex. Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy (TPLO) and Tibial Tuberosity Advancement (TTA)

Definition of _____ Surgery:
Will Improve Quality of Life but Not Extend Life
Ex. Splenectomy or Liver Lobectomy for Hemangiosarcoma
Ex. Amputation for Osteosarcoma
Palliative Surgery
*No Curative Intent
Most Common Type of Malignant Vaginal Neoplasia
Leiomyosarcoma
*Relatively Low Risk of Metastasis

98% of Patellar Luxations are on the _____ Side
Medial
*Larger Breed Dogs: Higher % of Lateral Patellar Luxations (MPL Still > LPL)

Three Tests that are Recommended for Workup of Feline Mammary Tumors
CBC/Chem/UA
Radiographs- For Metastasis
Ultrasound- Diagnose Risk of Malignancy
Typical Clinical Signs associated with _____:
Multiple Episodes of Vomiting
Painful Distended Abdomen
Lethargy
May be Asymptomatic
Gastric Outflow Obstruction
*Ex. Gastric Foreign Bodies

Grade of Patellar Luxation Described Below:

Grade III
*Patella is outside the Groove the Majority of the time
Most common Types of Splenic Neoplasia in Felines
Lymphosarcoma
Mast Cell Tumors

Invagination of One Portion of the GIT into the Lumen of an Adjacent Segment
Intussuseption
Damage to the _____ Nerve is a Possible Complication of Lateral Suture Stabilization of Cruciate Ligament Damage. Generally the Suture is passed around the Fabella but if the Fabella is not Visualized Properly the Suture can Entrap the Nerve
Peroneal

Peritoneal Fluid Biochemical Analysis Results that Support ______ Diagnosis:
Total Protein > 3.0 (Very High Total Protein)
Cell Count > 5000 (Very High Cell Count)
Blood Glucose will be 20mg/dL Higher than Fluid Glucose
Fluid Lactate will be 2.0 mmol/L Higher than Blood Lactate
Septic Peritonitis
*Blood Glucose will be > 20 mg/dL Higher than Fluid Glucose (Dogs and Cats)
*Fluid Lactate will be 2.0 mmol/L Higher than Blood Lactate- DOGS ONLY

Most common Intestinal Tumors of Dogs and Cats
Dog: Adenocarcinoma
Cat: Lymphosarcoma (Most Common) and Adenocarcinoma
Dogs: Adenocarcinoma (Most Common Intestinal Tumor), Adenonmatous Polyp (Most Common Rectal Tumor)

Radiographic Views Taken in Patients with Carpal Hyperextension
Standard Dorospalmar and Lateral View
Stress Views_: Simulate Weightbearing_

True/False: In patients with Cruciate Ligament Disease, TPLO Outcomes are Better than for Lateral Suture, Particularly for Larger Dogs
True
*TPLO is Superior in Outcome to Lateral Suture- This Evidence makes it much More Reasonable to Recommend TPLO for the Typical Cruciate Rupture Case
*Small Dogs/Cats: Lateral Suture and TPLO have Good Outcome
Large Dogs: TPLO Better Outcome than Lateral Suture

Predisposing Factors for _____:

Rectal Prolapse
*Seen with Conditions that Cause Straining
Most Common Hepatic Neoplasias and their Associated Prognosis
Dogs: (Mainly Hepatocellular)
Adenocarcinoma: Most Common Primary Malignant
Massive Form has Good Prognosis with Complete Excision
Diffuse and Nodular Form- Poor Prognosis
Adenoma: 30% of Hepatocellular Tumors
Cats: (Mainly Cholangiocellular)
Carcinoma: #1 Malignant Primary Tumor
50% are Benign Adenomas

Treatment for Vaginal Prolapse
Manual Reduction + Ovariohysterectomy
Grade of Patellar Luxation Described Below:

Grade IV

Best Diagnostic Tool for Rectal Tumors
Biopsy

Surgical Goals with Portosystemic Shunt
AVOID PORTAL HYPERTENSION

Prognosis for Treatment of Recessed Vulva
Recurrent Signs almost Always Resolve- Good Prognosis
What Abnormalities of the Spleen may occur in Patients with Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
Splenic Torsion- Splenectomy
Venous Congestion
Vessel Thrombosis- Splenectomy

Definition of _______:
Force that Causes the Tibia to Slide Cranially Relative to the Femur
Naturally Occurs during Weightbearing- Weighbearing Creates Compression across Joint
Angle between Compression and Tibial Plateau Results in Shear
Shear Results in Cranial Force on Tibia
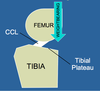
Cranial Tibial Thrust
*Cranial Cruciate Ligament Opposes Shear and Prevents the Tibia from Sliding Cranially

Procedure Described Below used in Treatment of Medial Collateral Ligament Carpus Injury:
1. Screw or Bone Tunnel in Styloid Process
2. Screw or Bone Tunnel in Radial Carpal
3. Heave Suture Placed in Figure 8 between the Two
Medial Collateral Replacement

Surgical Procedure for Medial Patellar Luxations Described Below:
Medial Release:
Chronic Fibrosis of Medial Joint Capsule- Free up Contracted Tissues
Allows Reduction of Patella
Lateral Imbrication:
Prevents Reluxation
Soft Tissue Reconstruction
Breed and Disease Associations with Gallbladder Mucocele
Breed: Shelties, Cocker Spaniel
Disease Associations: Hypothyroidism, Hyperadrenocorticism

Most Common Type of Meniscal Injury associated with Cruciate Ligament Disease
Buckethandle Tear
*Longitudinal Tear in a Portion of the Meniscus
*It is So-Named because the Damaged Portion of Meniscus Remains Attached to the Meniscal Body at its Periphery, thus the Damaged Meniscus can Fold back and Forth, like the Handle on a Bucket

Type of Gastric Neoplasia Described Below:
Common Benign Gastric Tumor
Very Slow Growing- Commonly Incidental Finding
Age: > 15 Years
Gastric Leiomyoma
Description and Indications for which Surgical Technique used for Canine Mammary Tumors:
For MULTIPLE Tumors in Adjacent Glands
60% of Dogs have Recurrence on Same Side (Rarely Used)
Regional Mastectomy
*Regional Mastectomy is RARELY Used due to 60% Recurrence Rate
Four Treatment Options and their Indications for Removal of Gastric Foreign Bodies
Conservative:
Monitoring Patient
Indicated: If Patient consumes a Small/Benign Object that will Most Likely Pass through
Endoscopy:
Grab Foreign Body if Amenable to Removal
Contraindication: Foreign Bodies with Sharp Edges (Ex. Bone)
Gastrotomy:
Surgical Exploratory Procedure
Induce Emesis:
Indicated: TOXINS
List Five signs of Malignancy when Evaluating Canine Mammary Tumors

Inflammatory Carcinoma is Rapidly Progressive, Highly _____ and Effects Multiple Mammary Glands
Metastatic
*Inflammatory Carcinoma is essentially a very aggresive Version of Canine Mammary Tumors
Describe Postoperative Care for Patellar Luxations
Controlled Activity- Leash Walking for 6 Weeks
Physical Therapy
Differentiate Primary versus Secondary Peritonitis
Primary Peritonitis: Source of Inflammation is Outside of Abdomen (Very Rare)
Secondary Peritonitis: Souce of Inflammation is Within Abdomen
*Secondary Septic Peritonitis is seen most Commonly

Goal of Subtotal Colectomy in the Managment of Idiopathic Megacolon
Remove as much Colon as Possible
Surgical Procedure used in the Treatment of Gastric Adenocarcinoma Described Below:

Gastrectomy
*Removing Affected Piece of the Stomach Wall
*Know the Indications for this Procedure!

Pathophysiology leading up to______:
Distension of Stomach from Gas/Fluid
Distension Alters Pyloric/Esophageal Sphincter Position
Limited Eructation causes Further Distension
Further Distension causes body of the Stomach to Rotate Clockwise along the Long Axis of the Esophagus
This Creates a Soft Tissue Fold between the Two Gas Filled Structures
Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus
Review Card: Pathophysiology of Peritonitis
*Common Eletrolyte Imbalances found in Patients with Peritonitis: Hyperkalemia and Hyponatremia
Inflammation→Vasodilation→Hyopvolemia→SIRS/DIC
Surgical Procedure used in the Treatment of Acquired Pyloric Stenosis Described Below:
2-3 cm Pyloric Incision
Resect Mucosa
Transpose Antral Wall to Pyloric Region: Suture Antral Flap to Pyloric Base
Advantages:
Creates Wider Pylorus and Pyloric Antrum
Shortens Gastric Emptying Time
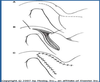
Y-U Pyloroplasty

Method for Screening for Hip Dysplasia Described Below:
Single Ventrodorsal Pelvis View
Hip Extended
Stifles Internally Rotated
7-Point Ordinal Scale- Excellent to Severe

OFA
List Six Important Principles of Oncologic Surgery
Minimize Handling of Tumor- Do Not Penetrate Tumor Capsule
Ligate Blood Supply as Early as Possible
Excise Biopsy Tract
Excise Lymph Nodes if Indicated
Lavage Tissues, Change Gloves and Instruments, and Lavage again before Closing
AVOID USE OF DRAINS
Collateral Ligament Tarsus Injuries usually occur due to Trauma (Hit by Car) and _____ Injury is the Most Common

Medial

Major Benefit of PennHIP Method
Does Not Change after 16 weeks (4 Months)
*Early on you can test Animals and determine their Distraction Index Accurately
In Patients with Gastric Dilatation Volvulus, what Area of the Stomach is most comon affected by Vascular Compromise?
Greature Curvature

Two Treatment Options for a Simple Septal Lesion in Cases of Vestibulovaginal Stenosis
Episiotomy- Mucosal Resection at Lesion Attachments
Endoscopic Treatment- Laser Ablation

Review Card: Common Causes of Splenomegaly

What is the Most common Splenic Neoplasia in Dogs and what is the Prognosis?
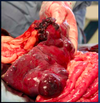
Hemangiosarcoma
Prognosis with Surgery ONLY- 86 Days
Prognosis with Surgery and Chemo- 140-202 Days
*Widespread Metastases Common

True/False: For Anything other than a Round Cell Tumor (Ex. Mast Cell Tumors, Melanoma) you want to Interpret Cytology Cautiously because Inflammation from other Tumor Types can sometimes Mimic Malignancy
True

Preferred Treatment for Carpal Hyperextension
Surgical Managment- Arthrodesis
*Splinting and Rest are Not Helpful- Conservative Managment is Rarely Useful

____% of Canine Mammary Tumors are Malignant
50%
Inability to Retract Penis Into Prepuce

Paraphimosis
*There are Congenital (Narrowed Orifice) and Acquired (Trauma) Causes
Collateral Ligament Carpus Injuries Typically arise from Major Trauma such as _____ and are commonly on the Medial Side of the Joint

Hit by Car
*Make sure the Animal is Stabilized before you address the Collateral Ligament Injury- Treat Life Threatening Trauma FIRST

Radiographic View that is Considered Diagnostic for Hip Dyspasia
Hip Extended View
*Internal Rotation of Distal Limbs
Know how to Judge Proper Positioning: Slight Overlap of Ischial Tuberosity, ALIEN EYES

Treatment for Benign Vaginal Neoplasia
Excisional Biopsy via Episiotomy
Orthopedic Test used to Diagnose Cranial Cruciate Ligament Rupture Described Below:

Passive Constraint
Cranial Drawer Test
*Cranial Drawer Test is a bit like trying to Pull the Wedges Apart. If the Wedges Separate, then there is Positive Cranial Drawer

Treatment for Mesenteric Torsion
Aggresive Fluid Therapy- Crystalloids and Colloids
Immediate Surgery to Untwist Torsion
Typical Signalment associated with ______:
INTACT Female Dogs
Older than 10 Years of Age
Vaginal Neoplasia
What Two Patient Factors Increase Complication Rates of the Lateral Suture Technique?
Higher Body Weight
Younger Age
*Larger Dogs and Younger Dogs are more prone to complications with the Lateral Suture Stabilization Technique

______ Syndrome Spontaneously Recovers in 1-4 Weeks with:
Energy Restricted Diet
Controlled Exercise
Flooring with Good Traction
Carpal Laxity Syndrome
*Self Corrects within 1-4 weeks- Prognosis is EXCELLENT
Treatment for Intestinal Tumors
Adenocarcinoma: Resect with 4-8cm Borders
Lymphosarcoma: Chemotherapy
Palmar Ligament described Below:
Encloses the Deep Digital Flexor (DDF) Tendon

Flexor Retinaculum
Procedure Described Below to Treat Tarsal Hyperextension:
Lag Screw or Pin/Tension Band at Calcaneoquartal Joint
Laterally Applied Plate to the Tarsometatarsal Joint
Good to Excellent Function Expected
Partial Tarsal Arthrodesis
*Giant Screw placed through Calcaneoquartal Joint

Name the Signalments associated with Intrahepatic vs. Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts
Extrahepatic:
66-75% of Shunts are Congenital, Single and Extrahepatic
Small Dogs and Cats
Yorkies, Shih Tzues, Maltese ec.
Intrahepatic:
Large Breed Dogs- Labradors, Australian Shepherds
Poorer Prognosis
Uterine Disease/Complication more common in Cats
Uterine Prolapse
Contraindications for _____ Treatment of Dystocia:

Medical
*60-65% of Dystocia Cases will be Treated Surgically
Treatment for Mild versus Severe Cases of Prostatitis
Mild Prostatitis:
Castration, Systemic Antibiotics
Severe Prostatitis:
Resuscitation, Systemic Antibiotics
Exploratory Laparotmy and Omentalization
Castration
Prognosis for Osteochondrosis of the Hock (Tarsus)
Guarded to Poor

Treatment for Collateral Ligament Tarsus Injury
Surgical Managment- Reconstruct/Replace Collateral Ligament
*Splinting and Rest are unhelpful as Sole Treatment
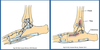
Description and Indications for which Surgical Technique used for Canine Mammary Tumors:
Removal of Entire Chain of Mammary Glands
Indications:
Multiple Masses throughout the Chain
Tumors in Gland 3 with any Criteria of Malignancy
Solitary Masses Anywhere with Multiple Criteria of Malignancy
Chain Mastectomy
What is the Holding Layer for Suturing the Stomach?
Submucosa
*QUESTION ON EXAM
*Apposition of Subumosa Results in Stronger Closure

Only way to Differentiate Benign vs. Malignant Canine Mammary Tumors
Biopsy
Etiology of Acute Cranial Cruciate Ligament Ruptures
Usually Traumatic
*Catastrophic Overload on Cranial Cruciate Ligament
*Result from Excessive Torsion or Extension on a Normal, Healthy Cranial Cruciate Ligament

Prognosis for Mesenteric Torsion
Almost 100% Mortality Rate
*Early Surgery leads to Higher Survival Rate
Manifestations of Hip Dysplasia in Young versus Older Patients
Young- Subluxation
Older- Remodeling and Osteoarthritis
*Young Patients are going to Present to you for signs of Laxity and Pain Related to Subluxation of the Joint
*Older Patients have gone through the Regenerative Process and will present with signs of Osteoarthritis


C. Perform a Splenectomy and Biopsy one of the Liver Lobes as Changes are Diffuse
*Benign and Malignant Processes can look the Same
List the Most Common Types of Pancreatic Neoplasia
Exocrine Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma:
Most Common Pancreatic Tumor of Dogs and Cats
Extremely Poor Prognosis
Insulinoma:
Adenocarcinoma of Beta Islet Cells
Cause Severe Hypoglycemia
____ Prolapse:
Complete/All Layers of Rectum Prodtrude through Anal Orifice

Rectal Prolapse
When Treating Medial Collateral Ligament Carpal Injuries, there is a Straight and _____ Component to the Collateral Ligament
Oblique
*Medial Carpus- Straight and Oblique Ligament Components
Lateral Carpus- Only Straight Ligament Component

Surgery Technique for Septic Peritonitis described Below:
Allows for Continuous Removal of Suppurative Material From Abdomen
Consider in cases of Moderate to Severe Peritonitis
Allows for Continued Evaluation of Fluid Character and Cytologic Changes

Abdominal Drainage
*Continued Evaluation of Fluid Character: Are we seeing Less Cells? Are the Neutrophils Gradually looking Better? Is our fluid Volume Decreasing?
Type of Gastric Neoplasia Described Below:
60-70% of all Gastric Neoplasia
Average Age: 7-10 Years
Common Locations: Pyloric Antrum, Lesser Curvature
Highly Malignant and Likely to Metastasize- Regional Lymph Nodes and Liver
Gastric Adenocarcinoma
*ALMOST ALWAYS Affects the Pyloric Antrum
*Common Mestastasis Location: Liver, Regional LNs
Prognosis: Mean Survival Time- 7-8 Months
Postoperative Recommendations following Femoral Head Ostectomy
Immediate Postop Limb Use Essential
Range of Motion and Physical Therapy Exercises Encouraged
Treatment of Choice for Uterine Torsion
Ovariohysterectomy

How does the Stomach most Commonly Move with Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
Clockwise Rotation (180 Degrees)- MOST COMMON
*Greater Omentum covers Stomach
*The Greater the Rotation, the More Severe the Clinical Signs

Surgical Procedure recommended for Feline Mammary Tumors
Chain Mastectomy on Affected Side
*In Cases of Feline Mammary Tumors we are will be Removing the Entire Mammary Chain every time

Nongenetic Etiologies leading to ______:
Smaller Pelvic Muscle Mass- Higher Incidence
Body Weight- Rapid Weight Gain Predisposes to Disease
High Calcium/Vitamin D Diets
Hip Dysplasia
*Pelvic Muscle Mass- Ex. Greyhounds have no Incidence of Hip Dysplasia and a large Pelvic Muscle Mass Relative to Bone Mass. German Shepards have Higher Incidence of Hip Dysplasia and Small Pelvic Muscle Mass

Clinical Signs associated with _____ Peritonitis:

Septic Peritonitis
*Any of these Signs, especially in Conjunction with Recent Abdominal Surgery or Abdominal Trauma shoud raise a Red Flag!!

Prognosis for Legg-Perthes Disease
Good
*Warn Owners of Risk for Contralateral Disease- Can be a Bilateral Disease

Treatment for Carpal Hyperextension Described Below:
Antebrachiocarpal Joint is Normal
Middle and Carpometacarpal Joints are Fused using a T-Plate or Pins
Function of Carpus is Almost Unaffected- Almost all motion at Antebrachiocarpal Joint
Partial Carpal Arthrodesis
*Injury is at the Level of either the Middle or Carpometacarpal Joints

Three Joints that are at Risk for Carpal Hyperextention
Antebrachiocarpal Joint- Between Radius/Ulna and Proximal Row
Middle Carpal Joint- Between First and Second Row
Carpometacarpal Joint- Between Second Row and Metacarpal Bones
*Almost all Motion occurs at the Level of the Antebrachiocarpal Joint (Hinge Action)
Major Limitation of PennHIP Method
Estimate of Risk for Osteoarthritis ONLY
*NOT Clinical Signs
*Distraction Index determines the chance of the animal developing Osteoarthritis of the Hips. Has Nothing to do with Clinical Signs associated with Hip Dysplasia
The Cranial Drawer Test is Testing the Cranial Cruciate Ligament _____ (without any Effort from the Patient). The Tibial Compression Test is testing the Cranial Cruciate _____, by Stimulating Weightbearing
Passively- Cranial Drawer Test
Actively- Tibial Compression Test

What is Serosal Patching and when is it used?

Securing a Antimesenteric Border of Small Intestine Over a Suture Line or Defect
Indications:
When Omentum is Not Available
Closure Integrity is Questionable
Non Resectable Duodenal Defects

Advantages of Suturing the Stomach using _____Patterns:
Advantages:
Fibrin Seal that Aids in a Water-Tight Closure
Provides a Better/More Secure Closure
Water Tight Closure is MANDATORY
Inverting

Surgical Procedure used for Treatment of Fibroadenomatous Hyperplasia
Ovariohysterectomy (Spay)- Flank Approach Recommended
Using the PennHIP Method, The Lower the Distraction Index, the ____ Laxity
Less
*Lower Distraction Index is BETTER
*Distraction Index = Distance : Radius of Femoral Head

Typical Radiographic Findings in Patients with Hip Dysplasia
Subluxation- Increased Joint Space
Femoral Neck: Thickening, Coxa Valga
Femoral Head: Flattening/Sclerosis
Osteophytosis
*Poor Acetabular Coverage: Greater than 50% Coverage is Considered Normal

Treatment for a Caudoventral Coxofemoral Luxation
Reduce Hip- Closed Reduction usually Successful
*Reduction = Putting Femoral Head back into its socket
Closed = Surgery Not Required vs. Open = Surgery Required

Ideal Distraction Index for Animals using the PennHIP Method
LESS than 0.3
*Greater than 50% Acetabulum Coverage and a Distraction Index LESS than 0.3 is Considered Ideal for an Animal
*Every Animal with a Distraction Index less than 0.3 has below a 10% Chance of Developing Osteoarthritis

Physical Exam Findings associated with _____:
Stance- Rear Base-Wide/Forward Weight Shifting
Gait- “Hip Sway”
Difficulty Rising/Sitting
Sits Frequently in Exam Room
Muscle Atrophy- Quadriceps/Biceps

Hip Dysplasia

Treatment of Osteochondrosis of Tarsus
Surgical Treatment - Fragment Excision/Debridement and Tarsocrural Arthrodesis (Ideal in Young Dogs with No Osteoarthritis)
Medical Therapy- Older Dogs, Established Osteoarthritis
*Surgery Improves Function Somewhat but does not Eliminate Lameness. Surgery Does NOT prevent the development of Osteoarthritis

True/False: Patients with GDV, should be taken to Surgery As soon as they are Cardiovascularly Stable
True
Biochemical Changes that would be Consistent with Diagnose of ______:
Hyperbilirubinemia
Hypoalbuminemia
Hyponatremia
Hyperkalemia
Hypoglycemia
Septic Peritonitis

Clinical Signs of what type of Intestinal Foreign Bodies:
Vomiting, Anorexia, Depression
Pain on Abdominal Palpation
Clumping and Pleating of Intestine
Linear Foreign Body
Preferred Test for Diagnosis of Gastric Adenocarcinomas
Endoscopy
*Very Diagnostic

Holding Layer for Closing Incisions in the Uterus
Submucosa

Best Diagnostic Test for Diagnosing Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
Right Lateral Radiograph

What are the Various Techniques for Obtaining a Liver Biopsy? Which Techniques are the Best for Generalized vs. Multifocal vs. Focal Disease
Guillotine Technique:
Lesions at Periphery of the Lobes
Generalized Hepatic Disease
Punch Biopsy:
Generalized Hepatic Disease- Multiple Biopsies Needed
Superficial Lesions that are Centrally Located
Laparoscopy:
Small Sample Sizes- Multiple Samples

Four Treatment Options for Acquired Pyloric Stenosis
Transverse Pyloroplasty- ONLY Grade 1
Y-U Pyloroplasty- Very Common
Billroth 1- Removing Entire Pylorus (Mainly Grade 3)
Biopsy
Indications for which type of Spenic Surgery:
Focal Benign Disease Processes
Abscess
Laceration
Partial Infarction
Biopsy
Partial Splenectomy
*Not Performed Often: Associated with Significantly Prolonged Surgery Time compared to Complete Splenectomy with Increased Risk of Complications

In Cases of Septic Peritonitis, the Patients need Early Intervention with _____, considering High Metabolic Demands due to Massive Protein Losses (Hypoalbuminemic)
Nutrition
*Septic Peritonitis- These Patients NEED Nutrition Early. We want to give them Nutrients as early as we Possibly Can

Etiology of a Dog with ______:

Metritis
Name Five Biochemical Tests that can be Performed on the Peritoneal Fluid to Confirm a Diagnosis of Septic Peritonitis
Lactate
Glucose
Bile
Creatinine
Potassium (K)
*These Tests can be Done on a Sample of Abdominal Effusion to Help Confirm Diagnosis of Septic Peritonitis
Surgical Technique for Gastric Dilatation Volvulus Described Below:

Incorporating Gastropexy
*NOT RECOMMENDED- Only used in Patients with CV Compromise who need abrupt discontinuation of Anesthesia
True/False: In Cases of Inflammatory Carcinomas the Prognosis is Poor and Surgical Treatment is NOT usually Recommended
True
*Mean Survival Time- 1 Month

List Five Factors used to Access the Gastric Wall Viability in Patients with Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
Peristalsis
Serosal Color- Black or Green is Bad
Palpate for Thinning/Friability
Pulsation of Vessels
Bleeding Cut Surfaces
Which types of Antibiotics are NOT a good First Choice for Patients with Septic Peritonitis
Fluoroquinolones

Indications for which Intestinal Surgery:

Resection and Anastomosis
*Removal of Affected Tissue
*Indicated in Neoplastic Disease, Foreign Body with Necrotic Intestine and Intussusceptions
Description of _____ Coxofemoral Luxation:
Animal Falls or “Splits”- Excessive Abduction of Limb
Femoral Head Traped Ventral to Ischium
Caudoventral
*Uncommon
Surgical Procedure for Medial Patellar Luxations Described Below:
Trochleoplasties:
Deepen Femoral Trochlear Groove
Tibial Tuberosity Transposition (T3):
Realigns Quadriceps
Distal Femoral Osteotomy (DFO)
Especially in Large Breed Dogs
Grade IV Luxation
Bone Reconstruction
*99% of the Time only performing Trochleoplasties or Tibial Tuberosity Transposition. DFO is only Performed in Very Severe Cases
Trochleoplasty- Deepens Trochlear Groove
Tibial Tuberosity Transposition- Realigns Quadriceps

Two Pathogenesis of Laxity in Patients with Hip Dysplasia
Capital Ligament Edema/Stretching
Increased Joint Fluid Volume- Decreases Stability

In Partial Calcanean Tendon Rupture, the _____ is usually Preserved Leading to Partial Hyperflexion

Superficial Digital Flexor
*Partial Calcanean Rupture: Partially Dropped Hock and Flexed Digits due to Preserved SDF

Four Surgical Techniques for Removal of Canine Mammary Tumors
Lumpectomy
Simple Mastectomy
Regional Mastectomy
Chain Mastectomy
Prognosis for Medial Patellar Luxations following Surgical Managment
Grade I-III: Excellent Return to Function
Grade IV: Guarded to Poor, Recurrence Common
Best Diagnostic Tool for Differentiating Pancreatic Cysts vs. Pancreatic Abscesses
Cytology
*Abscess- Expect Neutrophilic Inflammation

How is Testicular Torsion Diagnosed?
Ultrasound and Palpation
Most Common Malignant Rectal Tumor in the Dog and what Breed?
Adenocarcinoma
German Shepherds
How is Ovarian Remnant Syndrome Diagnosed in Dogs?
Vaginal Cytology

Clinical Signs and Physical Exam Findings of _____:
Dystechezia- Trouble Defecating
Palpation Reveals a Symmetrically Enlarged, Pain Free Prostate
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Diagnosis based on Radiograph

Osteochondrosis of Medial Talus
_____Test used in Patients with Hip Dysplasia to Detect Laxity:
Requires Sedation
Hand Position: Stifle, Dorsal to Pelvis
Push Stifle Proximally to Subluxate Femoral Head
Slowly Abduct Stifle
Palpable/Audible Clunk = Positive Test

Ortolani Test
*Ortolani Test- Testing for Laxity in Patients with Hip Dysplasia
Clinical Signs of which Large Intestinal Disease:

Cecal Inversion
Salvage Procedure used in the Treatment of Hip Dysplasia Described Below:
Degenerative Joint Replaced with Prostheses
Skeletal Maturity- Adequate Bone Stock
Ideal Treatment for Large, Active Dogs

Total Hip Replacement
*Removing Acetabulum and Femoral Head and replacing them with Artificial Pieces
List the Five Criteria used to Assess the Viability of the Intestine and name the Most Reliable Physical Criterion
Peristalsis Pinch Test- Most Reliable Physical Criterion!
Color (Black = Dead)
Pulsation of Mesenteric Vessels
Bleeding of Cut Surface
Wall Texture/Thickness
*Peristalsis Pinch Test- Pinch the Intestine and it will Stimulate Intestinal Contraction
Incomplete Formation of the Penile Urethra, that is the Most common Developmental Anomaly of the External Male Genitalia

Hypospadias
Indications for which Surgical Procedure:

Typhlectomy
*Removal of Portion/All of Cecum
Goals of Surgical Managment of ______:
Stabalize Joint
Explore the Joint- Debride Remnants of the Cruciate
Evaluate/Treat Meniscus
Cruciate Ligament Disease
*Direct Examination of the Meniscus is the only way to tell for sure whether it is Injured or not- If Injured it is IMPERATIVE that the Meniscus be Treated

Name the Palliative Treatments available for Prostatic Neoplasia
Tube Cystotomy or Urethral Stent
Maneuvers Required Following Closed Reduction of Craniodorsal Coxofemoral Luxation
Put Joint Through Range of Motion to Clear Debris
Test Stability- If Unstable, Perform Open Reduction
Ehmer Sling 4-14 Days
*Ehmer Sling was CONTRAINDICATED Post-Reduction for Caudoventral Luxations

What are the Risk Factors for Dehiscence in Intestinal Surgery
Technical/Surgical Errors- MAIN CAUSE
Multiple Intestinal Procedures
Pre-Existing Peritonitis
Lack of Omentum
*Poor Surgical Technique- Main cause of Dehiscence

True/False: Neoplastic Testicles are Never Functional
False
*Neoplastic Testicles may be Functional
*Ex. Sertoli Cell Tumors can Produce Estrogen

Treatment for Carpal Hyperextension Described Below:
Antebrachiocarpal Joint is Abnormal
All 3 Carpal Joints are Fused
Dynamic Compression Plate (DCP) Applied
Pancarpal Arthrodesis
*Injury at the Level of the Antebrachiocarpal Joint

Prognosis for Feline Mammary Tumors
Tumors < 2cm: Mean Survival Time is 3 Years
Tumors > 3cm: Mean Survival Time is 6 Months
Treatment for Calcanean Tendon Rupture
Surgically Debride Tendon Ends
Primary Tendon Repair: 3-Loop Pulley
Immobilize Tarsus in Extension- Large Lag Screw
*Always want to use Monofilament Nonabsorbable suture

Indications for _____ in Cases of Recessed Vulva:
Recurrent UTI
Siginificant Skin Fold Dermatitis
Urine Pooling/Leakage
Surgery

Medical Managment for ____ Pyometra is CONTRAINDICATED because Prostaglandin can Predispose the Uterus to Rupture
Closed

Three Main Complications of Anal Sac Surgery
Infection
Draining Tracts
Fecal Incontinence

When Performing Surgery anywhere in the Gastrointestinal Tract, the ______ is the Holding Layer that Must be engaged with Suture to help Minimize the chance of Dehisence
Submucosa
Review Card: Blood Flow to Stomach
Right and Left Gastric Arteries: Supply the Lesser Curvature
Right and Left Gastroepiploic Arteries: Supply the Greater Curvature

True/False: Treatment of Metritis with Ovariohysterectomy does NOT affect Milk Production
True
*Spaying the Dog has no affect on Milk Production
You can Differentiate Prostatitis from other Prostatic Diseases based on ____and Palpation Findings
Ultrasound

Disadvantages of Ileocolostomy and Coloncolostomy when Performing Subtotal Colectomy
Ileocolostomy: Increased Incidence of Severe Diarrhea
Colocolostomy: Tension Free Apposition more Difficult
*Colocolostomy- Remove Entire Colon and Reattach it. More Perferred because we leave the Ileocolic Valve Intact
Ileocolostomy- Remove more of the Colon including Ileocolic Valve

The Cruciate Ligaments have a Thin Lining of _____ over them
Synovium
*Cruciate Ligaments are Described as Intra-articular but Extrasynovial- The Ligaments lie Inside the Joint Capsule but are Actually outside the Synovial Lining of the Joint

Describe Omenatlization of the Prostate
Bringing Omentum Into or Through Abscess Cavity
*Omentalization is Consistently Successful

Abnormal Development of the Coxofemoral Joint resulting in Hip Laxity. Laxity Results in Remodeling and Remodeling Results in Degeneration

Hip Dysplasia
*Abnormal Development of the Hip Joint
*Laxity is the Major Inciting Event

Which Meniscus is most commonly Damaged?
Medial
*Commonly the Caudal Pole of the Medial Meniscus
Give the Definition of Incisional Biopsies and Excisional Biopsies
Incisional Biopsy- Removing a Piece from the Mass
Excisional Biopsy- Removing the Entire Visible Mass
*Excisional Biopsies are Only Performed for very small masses where Definitive Removal can be Guaranteed
List Four Post Operative Complications associated with Splenectomy
Hemorrhage
Vascular Compromise of the Pancreas
Ventricular Arrhythmias- MOST COMMON
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy (DIC)

Description and Indications for which Surgical Technique used for Canine Mammary Tumors:
Removal of Single, Entire Mammary Gland
Single Mass > 1cm
Mass Located within Gland
Ensure 2-3cm Margin around Mass
Simple Mastectomy
What Information is Important to Receive on Histopathology to Help Further Guide Treatment and Provide Prognosis in Oncologic Cases
Benign vs. Malignant
Histologic Type
Grade
Margins
Which Hormone Induces Fibroadenomatous Hyperplasia in Cats?
Progesterone

Three Most Common Open Reduction Procedures for Correcting Coxofemoral Luxation
Capsulorraphy
Prosthetic Capsule
Toggle Pin/Rod
Typical Presenting Signalment for _____:
Large Breed Dogs
Equal Sex Distribution (M:F)
Classic Biphasic Presentation
Young Dogs: Laxity
Mature Dogs: Degenerative Changes/Osteoarthritis
Hip Dysplasia

List the Recommended Treatment and Associated Prognosis for the common Pancreatic Neoplasias
Exocrine Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma:
Extremely Poor Prognosis- No Treatment
Insulinoma:
Medical Managment: Small Frequent Meals, Streptozocin
Surgical Managment: Surgical Resection of All Abnormal Tissue
Prognosis: Good
Anatomic Indications for Episiotomy Approach
Vestibular and Vaginal Lesions

Clinical Signs associated with ______:
Skin Fold Dermatitis or Vaginitis
Urine Pooling- Recurrent UTI
Recessed Vulva
*Skin Fold can cause Retention of Urine leading to Vaginitis

Single Most Important Element in the Treatment of Hip Dysplasia
Weight Managment
(Frog Fact)
*Diet Composition and Weight Managment are Highly Significant in the Medical Managment of Hip Dysplasia
Clinical Signs of which Condition leading to Gastric Outflow Obstruction described Below:
Intermittent Vomiting
Dietary Modification Alters Signs
Normal to Decreased Body Condition
Abdominal Distension but No Pain
Congenital Pyloric Stenosis
Prognosis when using _Corrective Surgery f_or Hip Dysplasia
Juvenile Pubic Symphiodesis:
Benefit UNLIKELY after 20 Weeks of Age
Reduces Incidence of Osteoarthritis
Less Effective for Severe Laxity (High DI)
Triple Pelvic Osteotomy:
Long Term Function Good to Excellent
DJD usually continues to Progress
Two Components Necessary for Reconstruction of Prepuce
Epithelial Surface
Mucosal Surface

Common Signalment and Etiology of Which Intestinal Disease:
Signalment: Male German Shepherd Dogs!!
Etiology: Unknown but Probably Inflammatory
Mesenteric Torsion
*Intestinal Twisting on Mesenteric Axis that causes Devitalization of all of the Intestines
Best Diagnostic Modality for Gastric Foriegn Bodies
Radiographs

Normal Finding in Puppies Under the Age of 6 Months:
4-5mm Drawer/Tibial Thurst
Abrupt Limit
No Joint Effusion
Normal Finding in Puppies < 6 Months Old
Puppy Drawer
Puppy Drawer- Very Young Dogs (< 6 Months) sometimes will have a Little Instability in their Joints as a Normal Finding
*After Age of 6 Months, Significant Puppy Drawer becomes much Less Likely

Criteria for Diagnosing _____:
Prolonged Gestation ( > 68 Days)
Signs of Toxemia During Gestation
Stage 1 lasting > 24 Hours
No Puppies > 36 Hours after Temperature Drop
Active Stage 2 Contraction for > 30 Minutes
> 4 Hours between Puppies
Dystocia
Two Specific Complications associated with Osteotomy Procedures (TPLO, TTA) used in the Treatment of Cruciate Ligament Disease
Iatrogenic Angular Limb Deformity- TPLO
Iatrogenic Patellar Luxation- TTA

Match the Following Congenital Abormalities:
Atresia Ani
Rectovaginal Fistula
Anogenital Cleft
1. Stenosis or Persistent Membrane of Anus or Rectum
2. Passage of Urine through Rectum or Feces through Vulva
3. Common Opening for Anus and Genital Tract Cloaca
1. Atresia Ani (Most Common)
2. Rectovaginal Fistula
3. Anogenital Cleft
*All Conditions carry Guarded to Poor Prognosis
Open Reduction Procedure for Correcting Coxofemoral Luxation Described Below:
Dill Hole Transversely across Femoral Neck
Bone Screws and Washers Placed in Dorsal Acetabulum
Nonabsorbable, Large Diameter Suture Through Femoral Bone Tunnel and Around Screws in Figure 8 Pattern

Prosthetic Capsule
Complication of Intestinal Surgery Described Below:
Malabsorption and Malnutrition that occurs after Extensive Intestinal Resection
Pathophysiology: Decreased Mucosal Surface Area, Decreased Intestinal Transit Time
Clinical Signs: Persistent Watery Diarrhea and Weight Loss
Short Bowel Syndrome

Palmar Ligament Described Below:
Extends from the Distal Aspect of the Proximal Carpal Bones (Radial, Ulnar) to the Proximal Aspect of the Metacarpals

Palmar Fibrocartilage
*One Wide Ligament that sits on Palmar aspect of the Joint and keeps everything Stable
*Carpal Hyperextension Injuries = Breakdown of the Palmar Fibrocartilage
Common Clinical Signs of Which Intestinal Disease:
Abdominal Distension
Hematochezia
Collapse and Death
Mesenteric Torsion
*Have to Intervene Immediately or else these Patients will Die
List the Three Approaches to Surgical Removal of a Mass and when Each is Indicated
Marginal:
Indicated: Lipomas and Benign Masses
Wide:
Removal of 2-3 cm Normal Tissue Laterally around the Mass and 1 Fascial Plane Deep
Indicated: Mast Cell Tumors, Sarcomas
Radical:
Removal of Entire Compartment- Ex. Amputation

Risk Factors for Developing _____:
Large/Giant Breed Dogs!!! (Ex. Great Dane, St. Bernard)
Deep Chested Dogs
First Degree Relative -If Parent had it, more Likely in Offspring
Faster Eating (Consuming more Air)
Larger Volumes of Food Daily
Gastric Dilatation Volvulus

Coaptation Applied for Post Op Managment of Caudoventral versus. Craniodorsal Coxofemoral Luxations
Craniodorsal Luxation- Ehmer Sling
Caudoventral- Hobbles
*Ehmers Sling is Contraindicated in Caudoventral Luxations
Surgical Procedures Recommended for Treatment of Non-Metastasized Testicular Tumors
Bilateral Castration with Scrotal Ablation
*If No Metastasis, Surgery can be Curative- Great Prognosis

True/False: There is NO Relationship between Age at Ovariohysterectomy and Development of Recessed Vulva
True

Indications and Pros and Cons for which type of Biopsy:
Pros:
Removes Tumor Along with Surrounding Normal Tissue
Allows Removal of Smaller, Non Invasive Masses in Single Procedure
Indications:
Treatment would not be Altered by Tumor Type
Re-Excision Possible without Great Morbidity

Excisional Biopsy

Surgical Technique Described Below:
Used for Most Scrotal or Testicular Disease: Neoplasia, Torsion
Paired Incisions at Base of Scrotum
Scrotal Ablation
*Scrotal Ablation Requires Castration

______ Improves the Outcome with the Extracapsular Procedures (Lateral Suture, Tightrope). If you are Performing either the Lateral Suture or the Tightrope, you should be offering _____ as well.
Physical Therapy

Clinical Signs of _____:
Dyschezia
Pain on Urination/Defecation
Purulent Penile Discharge
Signs of Illness- Anorexia, Lethargy, Fever
Prostatitis
True/False: Both Genetic (Polygenic) and Non Genetic (Environmental) Factors are Necessary for an Animal to develop Hip Dysplasia
True
*Animal will NOT develop Hip Dysplasia unless you have both of these factors- Genetic and Environmental
*Ex. Labrador that does NOT have Genetic Background to develop Hip Dysplasia. Labrador is overfed and exposed to other Environmental Etiologies for Hip Dysplasia. Labrador will still NOT develop Hip Dysplasia
Treatment for Splenic Neoplasia
Complete Splenectomy
*Remove Entire Spleen and explore Abdomen for Evidence of Metastasis
Know the Difference between Pancreatic Cysts and Pancreatic Abscesses
Pancreatic Cysts:
Collection of Pancreatic Secretions and Debris in a Non Epithelialized Sac
Middle Aged-Older Animals
Pancreatic Abscesses
Occurs as Sequela to Pancreatitis
Clinical Signs of ______:
Recurrence of Estrus Cycle
Vulvar Swelling
Behavioral Estrus
Ovarian Remnant Syndrome
*Surgical Error left behind Functional Ovarian Tissue and therefore you will see clinical Signs related to Estrus Cycle
*Commonly during Estrus the Animal will develop Vaginal Bleeding. However, in Cases of Ovarian Remnant Syndrome since the Lining of the Uterus has been Removed, Vaginal Bleeding is UNCOMMON

Clinical Signs compatible with _____:

Prostatic Neoplasia
Surgical Procedure Typically used for a Case of Metritis
Ovariohysterectomy

Indications for _____ Managment of Medial Patellar Luxations:
Significant Lameness Regardless of Grade- Episodes Lasting 2-3 Weeks or Longer
Higher Grade (III and IV) Medial Patellar Luxations
Larger Breed Dogs
Surgical

Typical Signalment associated with Which Prostatic Disease:
Older, Intact Male Dogs
Prostatic Cysts
Roughly _____% of dogs that blow one Cranial Cruciate Ligament as a Result of Chronic Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease, will blow the other within 1-2 years
50%

Signalment and Etiology of which Anal Disease:
Middle Aged German Shepherds
Chronic Suppurative Ulcerative Tracts
Perianal Fistula
Hip Disease Described Below:
Ischemia to Femoral Head Causing Necrosis
Fragmentation of Femoral Articular Surface
Malunion of Fractured Femoral Head
Degenerative Joint Disease results from Incongruent Joint
Legg-Perthes Disease

In Cases of Feline Mammary Tumors, Surgery is Recommended if no _____.
Metastasis

How is Intussusception Managed?
Surgical Management:
Healthy Tissue: Attempt Manual Reduction
Necrotic Tissue: Peform Resection and Anastomosis

Stabilization Technique for Cruciate Ligament Disease Described Below:
Radial Cut made in Proximal Tibia
Rotate Proximal Tibial Fragment

TPLO
Prognosis for a Benign Mammary Mass
Good with Complete Resection
Signalment associated with ______:
Cats and Small/Toy Breed Dogs
Skeletally Immature (4-11 Months Old)
Breed Predisposition- Miniature Poodle, Westie
Legg-Perthes Disease

Short Term and Long Term Sequelae of _____:

Portal Hypertension
Five Surgical Approaches to Rectal Tumors
Transanal- Small, Non Invasive Pedunculated Polyps
Dorsal- Tumors in the Mid-Rectum
Rectal Pull Through
Lateral- Used for Rectal Diverticulum or Laceration
Ventral- Lesions at Colorectal Junction

Treatment for Ovarian Remnant Syndrome
Surgical Removal of Remnant
Similarities and Differences between the Treatments for Pancreatic Cysts vs. Pancreatic Abscesses
Pancreatic Cysts:
Ultrasound Guided Percutaneous Aspiration
Surgical Resection
Debridement and Drainage (Omentalization)
Prognosis: 75% Success Regardless of Treatment
Pancreatic Abscesses:
Emergency Debridement and Omentalization
Prognosis: 50-86% Mortality Rate
Two Surgical Procedures Required in Patients with Grade III or IV Medial Patellar Luxations
Soft Tissue Reconstruction
Bone Reconstruction
True/False: In Cases of Septic Perititonitis, No Treatment will be Effective without SURGERY
True
*These patients will NOT get better without Surgery
Differentiate Aseptic versus Septic Peritonitis
Aseptic Peritonitis: Absence of Infectious Organisms within Peritoneal Fluid
Septic Peritonitis: Presence of Infectious Organisms within Peritoneal Fluid
True/False: Uterine Torsion is Considered an Emergency
True
*Uterine Torsion is considered a Surgical Emergency
Surgery is the Most Important Component of Treatment for Small Animals with _____ Tumors
SOLID
*We only do surgery to treat cancer when it is a Solid Tumor

Prognosis for Dogs and Puppies undergoing Surgery for Dystocia
Dogs: 99% Survival
Puppies: 87% Survival

Surgical Procedure Indicated for Tumors of the Penis
Penile Amputation
*Indicated in most Cases of Trauma or Neoplasia of the Penis
Approximating Suture Pattern that is used when Performing Intestinal Anastamosis that Creates a Stronger Closure
Modified Gambee

Ovarian ____ may be Functional or Nonfunctional, on the Basis of whether they are Producing Hormones or Not
Cysts
*Nonfunctional Ovarian Cysts: Incidental Findings
Functional Ovarian Cysts: Estrus-Producing

Signalment and Pathology of which Large Intestinal Condition:
Predisposed Breed: Manx Cat (5-7 y.o)

Megacolon

Clinical Signs of a Dog with ______:
Occurs POSTPARTUM (12 Hours - 1 Week after Giving Birth)
Signs of Systemic Illness- Fever, Anorexia
Foul-Smelling Reddish-Brown Vaginal Discharge
Metritis
*Major Differentiator- Metritis occurs after the Dog has Given Birth (About 1 Week Post Partum)

True/False: In Patients with Coxofemoral Luxation, Radiographs are ESSENTIAL before Reduction to rule out Fractures
True
Signalment of which Mammary Disease:
Young (< 2 year Old) Cats
Progesterone Dependent

Fibroadenomatous Hyperplasia (Benign)
Whenever we Perform Intestinal Surgery we always perform a Procedure called ______ described Below:
Omentum from the Abdomen is wrapped around the Surgical Site and Sutured in Place
Omentum helps to Promote Blood Supply to the Surgical Site to Promote Healing
Omentalization
*If you don’t have Perfect Closure/Compromise in Closure of the Intestine, the Omentum acts like Glue and Helps to seal the Surgical Site

Most Common Malignant Tumor of the Anal Sacs
Apocrine Gland Adenocarcinoma
*Highly Malignant
Treatment for Pythiosis
Surgical Excision: 3-4cm Borders
Medical Treatment: Itraconazole
Pythium Insidiosium Vaccine
*Monitor for Recurrence within 2-3 Months

Granulosa Cell Tumor Ovarian Neoplasias are commonly Functional and Producing Estrogen, Progesterone or Both. If the Granulosa cell Tumor is Producing Persistent Progesterone, the Patient is Predisposed to ______
Pyometra
*If the Animal has an Ovarian Tumor or Cyst that is Producing just PROGESTERONE, the animal is likely to Develop Pyometra

Surgical Procedures used for Patients with Hip Dysplasia Described Below:
Preserves Function
Generally Reserved for when Medical Treatment Fails
Salvage Procedures
*Skeleton is Matured- Aimed at Preserving Function

As soon as you have a Diagnosis of Septic Peritonitis, you should begin Administering ______
Antibiotics- Broad Spectrum, Bactericidal
Best Options: Cephalosporins or Penicillin
*Early Treatment is associated with Improved Prognosis- The sooner you start Antibiotics, the better the Prognosis

Surgical Procedure used in the Treatment of Acquired Pyloric Stenosis Described Below:
Indication: Severe Outflow Obstruction with Grade 3 Pathology
Excise Pylorus
End-End Anastomosis
Advantages:
Abnormal Tissue Completely Removed
Larger Increase in Gastric Outflow
Disadvantages:
Longer Procedure- Increased Risk of Leakage and Infection
Billroth 1
*AKA Pylorectomy with Gastroduedenostomy
*Essentially resecting Entire pylorus
___% Chance of Medical Managment preserving the Fertility in Animals with Pyometra
50%

True/False: Cryptorchidism is Genetically Transmitted
True

Rotation of Uterine Horn on Long Axis that is Most commonly associated with Dystocia
Uterine Torsion
*Commonly Results from DYSTOCIA- Obstructed Labor
Two Forms of Vestibulovaginal Stenosis
Septal Lesion
Annular Fibrotic Stenosis
Description of _____ Coxofemoral Luxation:
Most Common (>90%)
Pull of Gluteal Muscles
Greater Trochanter Displaced Dorsally
Craniodorsal Luxation
Main Complications that can Occur after Intestinal Surgery?
Septic Peritonitis
Adhesions
Dehiscence
Intestinal Ileus
Short Bowel Syndrome
True/False: The Likelihood of Metastatic Disease with Ovarian Neoplasia is Uncommon
True

Pathology of which Condition leading to Gastric Outflow Obstruction described Below:
Chronic Hypertrophic Pyloric Gastropathy
Mucosal AND Muscular Hypertrophy
Small Breeds: Lhaso Apso, Shih Tzu
Middle Aged Dogs
Acquired Pyloric Stenosis
**Congenital Pyloric Stenosis- ONLY Muscular Hypertrophy*
Acquired Pyloric Stenosis- Mucosal AND Muscular Hypertrophy
Prognosis for Closed versus Open Reduction of Coxofemoral Luxations
Closed Reduction Prognosis:
50% Success (50% Recurrence)
Higher Success if More Recent Injury (< 24 Hours)
Open Reduction Prognosis:
80-90% Success
Good to Excellent Limb Function
Most Common Etiology for Coxofemoral Luxation
Trauma (Ex. Hit by Car)
*Treat Life-Threatening Injuries FIRST

Common Causes of ______:

Gastric Outflow Obstruction
True/False: Chronic Cranial Cruciate Disease is more Common than Acute Cranial Cruciate Rupture
True

Treatment for Cecal Inversion
Surgical Treatment- Manual Reduction and Typhylectomy

Signalment and Pathophysiology of what type of Intestinal Foreign Bodies:
More Common in CATS
Foreign Body anchors around Base of Tongue or Pylorus
Peristalsis Carries FB down GIT to Form Accordian Like Pleats
Foreign Body Embeds in Mesenteric Border and can Perforate Intestines
Linear Foreign Bodies
*Ex. Thread, Nylon Stocking, Rope, String

Etiology of which Large Intestinal Disease:
Usually Idiopathic (62%)
Pelvic Obstruction (23%)
Neurologic (6%)

Megacolon
*Accumulation of Dried Fecal Material in the Colon associated with Chronic Constipation
Fecal Material Retained in Colon becoems Dehydrated and Solidifies
*Most Common in CATS

In Felines, 75% of Spenic Diseases are _____
Malignant

Various Cytologic changes you would see in a Sample of _____Effusion:

Intracellular Bacteria within Hypersegmented Vacuolated Neutrophils
Abdominal Effusion with Intracellular Bacteria and Toxic/Degenerative Neutrophils
Septic Peritonitis

True/False: When Treating Splenic Torsions, DO NOT Untorse the Spleen
True

Multiple Tumors occur in ____% of Canine Mammary Tumor Cases
> 60%
*Multiple Tumors are Very Common
Three Common Findings on Right Lateral Radiographs in Patients with Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
Gastric Dilatation
Malposition of Pylorus
Double Bubble
Etiology/Pathogenesis of ______:
Medial Malalignment of Quadriceps
Results in:
Medial Displacement of Tibial Tuberosity
Abnormal (Shallow) Trochlear Groove
Hypoplasia of Medial Condylar Ridge
Medial Patellar Luxation

In _____ Cranial Cruciate Disease, at some point the Remaining Ligament finally gives out resulting in a severe Non-Weighbearing Lameness. For this Reason the Lameness may present as an Acute problem, however the Presence of Crepitus and Degenerative Joint Disease on Physical Exam proves the Problem has been going on for Some Time
Chronic
*Can see Acute Signs of Rupture with Chronic Cruciate Disease
Medical and Surgical Treatment for Anal Saculitis
Medical:
Express Gland
Infuse Antibiotics and Steroids
Surgical:
Anal Sacculectomy
Indicated when Medical Managment Fails
Describe Open versus Closed Pyometra
Open Pyometra: Cervix is Open and Purulent Material is Draining (You will see a Purulent Vaginal Discharge)
Closed Pyometra: Cervic is Closed and Purulent Material is Not Draining Out (Worse Prognosis)
*Closed Pyometra results in Increased Severity in Systemic Signs
Drug of choice to treat VPC’s associated with Gastric Dilatation Volvulus
Lidocaine
Two Most Common Salvage Procedures used in the Treatment of Hip Dysplasia
Femoral Head Ostectomy (FHO)
Total Hip Replacement (THR)
True/False: Life Threatening Injuries occuring with Collateral Injury to the Carpus should take Precedence over Treating the Trauma to the Joint
True
Prognosis for a Case of Metritis following Ovariohysterectomy
Prognosis with Ovariohysterectomy is Good
Distension of the Stomach and Rotation of the Stomach on its Mesenteric Axis
Surgical Disease
Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus
All Carpal Ligaments are _____ Ligaments:
Connect to Adjacent Bones Only
Do Not Bridge more than One Joint
Short

Vaginal _____ Tends to happen Secondary to Dystocia, Constipation, or Forced Separation
Prolapse
*How to Differentiate Vaginal Prolapse from Vaginal Edema: With Vaginal Prolapse the entire Vagina will be Prolapsed leading to “Donut Shaped” Ring of Tissue
____ is used in Cancer Managment by:
Obtaining a Diagnosis via BIOPSY
Curative/Long Term Tumor Control
Palliation of Clinical Signs
Debulking Surgery prior to Adjunctive Therapy
Prevention/Reduction of Risk of Recurrence
Surgery
*Palliation of Clinical Signs- Ex. Dog with Osterosarcoma and we Amputate the Limb



