Exam 1 (Fetal Assessment During Labor) Flashcards
Fetoscope & stethoscope
Allow a clear fetal heart auscultation.
What does FHR stand for?
Fetal Heart Rate
What is an Electronic Fetal Monitor (EFM)?
An EFM is a useful tool for visualizing FHR patterns on a monitor screen or printed tracing.
What are the Goals of Fetal Monitoring?
To differentiate reassuring from nonreassuring fetal patterns.
What is FHR a direct link to?
FHR is direct result of fetal oxygenation & wellbeing.
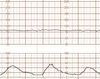
FHR Accelerations
-Increase FHR -Defined as an increase of 15 bpm or greater above baseline lasting at least 15 seconds but less than 2 minutes.
FHR Decelerations
-Decrease FHR -May be benign or non-reassuring.
FHR Baseline
Average FHR
FHR Variability
Variations in FHR
Name 4 ways O2 deprivation occurs by.
- Reduction of blood flow to fetus through maternal vessels (Maternal hypertension, hypotension, hemorrhage) 2. Reduced oxygen in maternal blood (Maternal hemorrhage or anemia) 3. Alterations in fetal circulation (umbilical cord compression, placental separation, head compression) 4. Decreased blood flow to placenta (hypertonic contractions)
What is Normal Uterine Activity (Contractions)?
Contractions q 2-5 minutes.
What is Normal Uterine Activity (Duration)?
Duration - < 90 seconds.
What is Normal Uterine Activity (Intensity)?
Intensity - < 100mmHg by IUPC.
What is Normal Uterine Activity (Resting Time)?
Resting time - 30 seconds or more between contractions.
What is Normal Uterine Activity?
5 or fewer contractions in 10 minutes averaged over 30 min.
What is Tachysystole? [Note: is this the right definition? Please verify!]
5 or more contractions in 10 minutes averaged over a 30 min.
What is a normal Baseline FHR?
110-160 beats/minute
When does acceleration usually occur?
During fetal movement.
How can the mother help recored Fetal monitoring?
The mother records when the fetus moves.
What is nonreasuring FHR Patterns associated with?
Associated with fetal hypoxemia
What does fetal hypoxemia include?
-Baseline FHR < 110 or > 160 bpm -Absent or persistently minimal variability -Recurrent late or variable decelerations -Bradycardia
Do you want variation in FHR?
YES!
What is fetal bradycardia mean?
(baseline FHR < 110 bpm x 10 minutes or longer) Occurs rarely & unrelated to fetal oxygenation. Most often occurs due to fetal cardiac problems, viral infections, maternal hypothermia, maternal hypoglycemia. Bradycardia is a late sign!
Is fetus tachycardia an early or late sign of fetus stress?
Early! Bradycardia is a late and bad sign.