Epithelial Tissues Flashcards
List four major tissue types
- Epithelium 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous
List characteristics of epithelial tissues
- Highly cellular: densely packed cells 2. Intercellular contacts: tight junctions, desmosomes, &a gap junctions 3. Basement membrane and support anchors to connective tissue 4. Polarity: apical (free edge) and basal (fixed edge) 5. Avascular: no blood supply; nutrient and oxygen thru diffusion 6. Highly mitotic: regenerate fast
Subcategories of epithelial tissues
- Simple -squamous -cuboidal -columnar 2. Stratified -squamous -cuboidal -columnar 3. Special -pseudostratified columnar -transitional
Epithelia: Simple squamous description and fxn
Description: single layer of flatted cell with disc-like nuclei Fxn: allows diffusion/filtration in areas where protection is not highly important; secretes lubricating substance into serosae
Epithelia: Simple squamous locations
Kidney glomeruli; air sacs (alveolar) of lungs; lining of heart; blood vessels, lymphatic vessels; lining of ventral body cavity (serosae)
What tissue:

Simple squamous epithelia
Epithelia: Simple cuboidal description and fxn
Description: single layer of cube-like or round cells with large, spherical nuclei
Fxn: secretion and absorption
Epithelia: simple cuboidal location
Kidney tubules; ducts and secretory portion of small glands; ovary surface
What tissue:

Simple cuboidal epithelia
Epithelia: Simple columnar description and fxn
Description: single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei; some cells have cilia; layer may contain muscus-secreting unicellular glands (globlet cells)
Fx: absorption; secretion of muscus, enzymes, and other substances; ciliated type propels muscus or reproductive cells by ciliary action
Epithelia: Simple columnar locations
Nonciliated type lines the digestive tracts (stomach and rectum), gallbladder, excretory ducts of some glands
Ciliated type lines the small bronchi, uterine tube, and some regions of the uterus
What tissue:

Simple columnar
Epithelia: Pseudostratified columnar description and fxn
Description: single layer of cell, differing in heights, some don’t reach the apical, nuclei seen at different levels, some contains globet cells (muscus-secreting glands), attached to basement membrane
Fxn: secretion of substance (primary muscus), proplusion of muscus by ciliary action
Epithelia: Pseudostratified columnar location
Nonciliated are found in male’s sperm-carrying ducts and ducts of large glands
Ciliated type lies in the trachea, mostly in upper respiratory tract
What tissue:
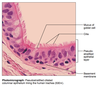
Pseudostratified columnar epithelial
Epithelia: Stratified squamous description and fxn
Description: 2-20 layers resting ontop of each other, only the deepest layer range from cuboidal to columnar, which pushes the older layer to flatten (squamous), only the deepest layer is attached to the basement membrane and contains active stem cells
Two different variation: Keratinized vs Nonkeratinized
Fxn: protects underlining tissues in areas subjected to abrasions
Epithelia: Stratified squamous locations
Nonkeratinized forms moist lining of the esophagus, mouth, vagina, tongue
Keratinized forms the epidermis of the skin, a dry membrane
What tissue:

Stratified squamous epithelial
Epithelia: Stratified cuboidal description and fxn
Description: generally two layers of cubelike cells
Fxn: protection
Epithelia: Stratified cuboidal location
Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands
What tissue:
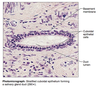
Stratified cuboidal epithelial
Epithelia: Stratified columnar description and fxn
Description: several cell layers, basal cells are generally cuboid and superficial cell are generally elongated and columnar
Fxn: protection and secretion
Epithelia: Stratified columnar location
Rare in the body, small amounts in male urethra and in large duct glands
What tissue:

Stratified columnar epithelial
Epithelia: Transitional description and fxn
Description: resemble stratified squamous/cuboidal, basal membrane are cuboidal/columnar, surface are generally dome shape or squamouslike, depends on degree of organ stretches
Fxn: stretches readily and prevents distension of urinary organ by contained urine
Epithelia: Transitional location
Lines the uterus, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra
What tissue:

Transitional epithelial


