engines and APU Flashcards
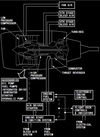
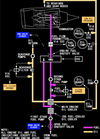
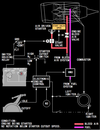
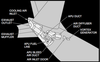
in the picture what is number 1 ?

Total Air Temperature (TAT) indicated in degress C
label - cyan
temperature - white
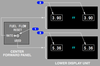
what does number 2 indicate in the picture ?

Displayed (green) – the active N1 limit reference mode.
in the picture below number 2 indicates the active N1 limit reference mode, in what position does the N1 SET Outer Knob need to be ?

in AUTO
page 7.11.2

when the pilot sets the N1 SET Outer Knob on either 1,2 or BOTH the thrust mode annunciation on the Thrust Mode Display will be ?

MAN (manual)
page 7.11.2

what does number 3 indicate on the picture below ?

Displayed (green) – selected assumed temperature (degrees C) for reduced thrust takeoff N1.
Repeats data selected on TAKEOFF REF page.
page 7.11.3
what does the number 4 in the below picture indicate and when does this come up ?

Illuminated (white) – The FMC is not providing the A/T system with N1 limit values.
The A/T is using a degraded N1 thrust limit from the related EEC.
page 7.11.3
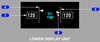
when the N1 SET Outer Knob is on AUTO where are both reference N1 bugs based on and what is displayed ?

both reference N1 bugs are set by FMC based on Limit Page and T/O Page
N1 bugs display A/T N1 limit
page 7.11.3
when the N1 SET Outer Knob is on BOTH where are both reference N1 bugs based on ?

N1 bugs and readouts are manually set by turning N1 SET Inner Knob
(has no effect on A/T ops)
page 7.11.3
when the N1 SET Outer Knob is on 1 or 2, where are both reference N1 bugs based on ?

respective N1 reference bug and readout are manually set by turning N1 SET Inner Knob
(has no effect on A/T ops)
page 7.11.3
what is the N1 SET Inner Knob used for ?

to position reference N1 bug(s) and readouts when N1 SET outer knob is set to BOTH, 1, or 2
page 7.11.4
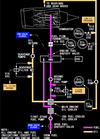
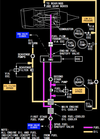
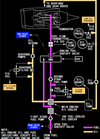
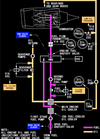
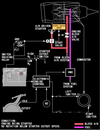
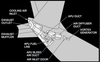
what is the item rappresented by number 3 in the picture ?

Position corresponds to digital value on the Reference N1 Readout.
Displayed (green)
page 7.11.4
what is the item rappresented by number 4 in the picture ?

N1% RPM operating limit
Displayed (red)
page 7.11.4
what does the indicate the item rappresented by number 5 in the picture ?

difference between actual N1 and value commanded by thrust lever position
Displayed (white)
page 7.11.4
what does the item rappresented by number 6 indicate in the picture below ?

N1 RPM Digital Readout
(displayed white for normal operating range)
page 7.11.4
what does it mean when the N1 RPM readout (item number 6 on picture) is red and surrunded by a red box ?

red - operating limits have been exceeded
red box - on the ground after engine shut down it will indicate an exceeded has occured during flight
page 7.11.4
when would the Reference N1 Readout (item number 7 on picture) be displayed ?

when N1 SET outer knob is in BOTH, 1, or 2 position to manually set N1 % RPM
displayed green
page 7.11.4
what does it mean when the Reference N1 Readout (item n7 on picture) displays “- - - -“

N1 SET outer knob is in AUTO position and FMC source invalid.
when is the Reference N1 Readout (item n7 on picture) blank ?

when N1 SET Outer Knob is in AUTO position
page 7.11.4
when is the Thrust Reverser Indication green and when amber ?

Displayed (amber) – thrust reverser is moved from stowed position
Displayed (green) – thrust reverser is deployed
page 7.11.4
when is the Termal Anti-Ice Indication green and when amber ?

Displayed (green) – cowl anti–ice valve(s) open.
Displayed (amber) – cowl anti–ice valve is not in position indicated by related engine anti–ice switch.
page 7.11.4
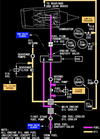
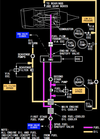
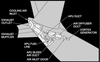
what does the Exhaust Gas Temperature Redline indicate (n1 on picture) ?

maximum T/O EGT limit
page 7.11.6
what does the Exhaust Gas Temperature AMber bands indicate (n2 on picture) ?

lower end of band displays maximum continuous EGT limit.
what does the EGT Start Limit Indicate (n3 on picture) ?

Displayed (red) – until the engine achieves stabilized idle (approximately 59% N2)
page 7.11.6
what does it mean when the EGT Digital Readout is white ?

normal operation range
page 7.11.6
what does it mean when the EGT Digital Readout is amber ?

maximum continuous limit exceeded
page 7.11.6
how many minutes is the color change inhibited from changing from amber to white of the EGT Readout during T/O or G/A ?

5 min
page 7.11.6
when is the color change inhibited to change from amber to white of the EGT Readout during T/O or G/A extended up to 10 min?

during takeoff or go-around when an engine out condition occurs within the first 5 minutes of the inhibit
page 7.11.6
when does the EGT Readout become red ?

- maximum T/O limt exceeded
or
- start limit exceeded
page 7.11.6
after both engines are shut down on the ground what does a red box around the EGT Readout indicate ?

an exceedance has occurred
page 7.11.6
what does it mean when the EGT Readout is white-blinking ?

EEC senses conditions that may lead to hot start or stall during ground starting
page 7.11.6
what does the EGT indication white colour indicate ?

normal operation range
page 7.11.6
when does the EGT indication become amber ?

when maximum continuous limit has been exceeded
page 7.11.6
how many minutes is the color change inhibited from changing from amber to white of the EGT Indication during T/O or G/A ?

5 min
page 7.11.6
when is the color change inhibited to change from amber to white of the EGT Indication during T/O or G/A extended up to 10 min?

during takeoff or go–around when an engine out condition occurs within the first 5 minutes of the inhibit
page 7.11.6
when does the EGT Indication become red ?

- maximum T/O limit exceeded
or
- start limit exceeded
page 7.11.6
when does the ENG FAIL Amber Indication come on ?

- engine operating below sustainable idle (less than 50% N2)
and
- engine start lever in IDLE position.
page 7.11.6
how long does the ENG FAIL Amber Indication alert remains ?

until:
- engine recovers
or
- start lever moved to CUTOFF
or
- engine fire warning switch pulled.
page 7.11.7
when does the START VALVE OPEN Alert illuminate steady amber and when amber-blinking ?

steady – respective engine start valve open and air is supplied to starter
blinking – uncommanded opening of start valve
page 7.11.7
when does the LOW OIL PRESSURE Alert illuminate steady amber and when amber-blinking ?

steady – oil pressure at or below red line
blinking – with a condition of low oil pressure.
page 7.11.8
when does the OIL FILTER BYPASS Alert illuminate steady amber and when amber-blinking ?

steady – indicates an impending bypass of scavenge oil filter
blinking – with an impending bypass.
page 7.11.8
when is the amber-blinking of the START VALVE OPEN, LOW OIL PRESSURE, OIL FILTER BYPASS alerts is inhibited ?

- during takeoff from 80 knots to 400 feet RA, or 30 seconds after reaching 80 knots, whichever occurs first
- during landing below 200 feet RA until 30 seconds after touchdown
- during periods when blinking is inhibited (alerts illuminate steady)
page 7.11.8
when are the Secondary Engine Indications dispalyed ?

- when CDS initially receives power
- when selected by the Multi-Function Display (MFD)
- in flight when an engine start lever moved to CUTOFF
- in flight when an engine fails
- when a secondary engine parameter exceeds normal operating range.
page 7.11.9
what does the N2 redline indicate ?

N2% operating limit
page 7.11.10
what does it mean when the N2 RPM Indications (n2 on picture) is white or red ?

white - normal ops range
red - operating limit exceeded
page 7.11.10
what does it mean when the N1 Digital Readout is white, red or with red box around ?

white - normal ops range
red - operting limit exceeded
red box around on the ground after engine shut down - indicates a inflight exceedance has occurred
page 7.11.10
when does the X-BLEED Indication come on and what is it for?

cross bleed air raccomended for inflight start
displayed when airspeed is less than required for a windmilling start
page 7.11.10
what does RATE indicate on the Fuel Flow Switch ?
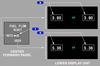
fuel flow to engine
page 7.11.11
what will be displayed when you elect USED on the Fuel Flow switch ?

fuel used since last reset
(after 10 sec reverts to RATE automatically)
page 7.11.11
what does the RESET do on the Fuel Flow switch ?
resets fuel used to ZERO
page 7.11.11
is the fuel flow displayed a KG figure or a LTR figure ?

KG x 1000
page 7.11.11
regarding the OIl PRESS Readout and Pointer explain the white, amber and red colour ?

white - normal ops range
amber - caution range
red - operating limit reached
page 7.11.12
the pointer will fall into the Low Oil Pressure Amber Band when a low oil pressure situation is detected, what is the minim N2 % RPM for it to be dislayed ?

65% N2
page 7.11.12
regarding the OIL TEMP Readout and Pointer explain the white, amber and red colour ?
white - normal ops range
amber - caution range reached
red - operating limit reached
page 7.11.13
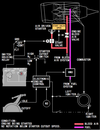
what happens when you turn the ENGINE START switch to GRD ?

- opens start valve
- closes engine bleed valve
- arms igniters
- releases to OFF at start valve cut out
page 7.15.1
is there any difference between igniters selection when the Engine Start switch in on GRD is selected on ground or in flight ?

yes
ground start - selected igniter/igniters (engine start lever IDLE)
inflight start - selectes BOTH igniters (engine start lever IDLE)
page 7.15.1
what happens when you turn the ENGINE START Switch to OFF ?

ignition OFF - this is the normal position
page 7.15.1
with the ENGINE START Switch OFF the ignition is OFF, is there a case when the igniters are activated ?

Engine Start Lever on IDLE igniters are activated when:
- uncommanded rapid N2 RPM decrease
- N2 between 57% - 50%
- in flight N2 between idle and 5%
page 7.15.1
what does the CONT option of the Engine Start Switch do, on the ground and in flight ?

ground - provides ignition to selected igniters (start lever has to be on IDLE)
in flight - provides ignition of both igniters when N2 is below IDLE (start lever has to be on IDLE)
page 7.15.1
what does the FLT option do of the Engine Start Switch ?

provides ignition to BOTH igniters (engine start lever has to be on IDLE)
page 7.15.1
what happens when selecting AUTO on the Speed Reference Selector ?

the reference airspeeds and Gross Weight are provided from the FMC
page 10.16.7
what is the V1 option on the Speed Reference Selector used for ? can it be used on flight

to manually set Decision Speed on the ground
it can’t be used on flight
page 10.16.7
what is the VR option on the Speed Reference Selector used for ? can it be used on flight ?

to manually set the Rotation Speed on the ground
can’t be used on flight
what is the WT option on the Speed Reference Selector used for ?

allows manual entry of reference gross weight
page 10.16.7
what is the VREF option on the Speed Reference Selector used for ? can it be used on the ground ?

to manually set Landing Reference Speed in flight
can’t be set on the ground
page 10.16.7
what is the BUG 5 (little sideway triangle) option on the Speed Reference Selector used for ?

to manually set the white BUG 5 desired value
page 10.16.7
what happens when you select the SET option on the Speed Reference Selector ?

removes the speed reference display
page 10.16.7
what causes the REVERSER Amber Light to illuminate ?

one or more of the following:
- Isolation Valve or Thrust Reverser Valve in not in right position
- one or more of Reverser Sleeves are not in right position
- auto-restow circuit has been activated
- failure in synchronization shaft lock ciruit
page 7.15.3
what causes the ENGINE CONTROL Amber Light to illuminate ?

fault in engine control system
when the ENGINE CONTROL Amber Light to illuminate ?

- engine is operating
- airplane on the ground :
below 80kt prior T/O
or
30sec after touch down
page 7.15.3
when does the EEC Switch ON light indicate ?

- normal control mode selected
- engine rating calculated by EEC
(EEC senses atmospheric conditions and bleed air demands)
what does it mean when the EEC ON white light is not in view ?

EEC has been manually selected to Alternate Mode
page 7.15.4
what does the EEC ALTN Amber Light indicate ?

EEC has switched to Alternate Control Mode
( EEC will provide rated thrust or higher )
page 7.15.4
is there any occasion where both ON and ALTN light will be in view on the EEC Engine Panel ?

if EEC has automatically switched to Soft Alternate Mode
page 7.15.4
above what percentage of deployment of the Thrust Reverser do the reverse thrust levers unlock to go above idle position ?

more then 60%
page 7.15.5
when using Reverse Thrust what prevents the Thrust Levers to be moved forward ?

Movement of reverse thrust lever into reverse thrust engages Locking Pawl preventing thrust lever from moving forward
page 7.15.5
what happens when the Engine Start levers are move to IDLE ?

- energizes ignition system through EEC
- electrically opens spar fuel shutoff valve in the wing leading edge outboard of the pylon
- electrically opens engine–mounted fuel shutoff valve via the EEC
page 7.15.5
what happens when the Engine Start Levers are moved to CUT OFF ?

- closes both spar and engine fuel shutoff valves
- de–energizes ignition system
page 7.15.5
what does it mean when the APU Maintenance Light illuminate ?
APU maintenance problem exist
page 7.15.6
is it possible to operated the APU when the Blue MAINT Light illuminates ?

YES
page 7.15.6
how do you disarm the MAINT Blue light ?

APU switch to OFF
page 7.15.6
how long does the APU EGT indicator remain powered after APU shutdown ?

5 min
page 7.15.6
when does the APU OVER SPEED Amber Light illuminate ?

- APU RPM limit has been exceeded (resulting in an automatic shutdown)
- overspeed shutdown protection feature has failed a self–test (during a normal APU shutdown)
page 7.15.6
when the APU OVERSPEED Amber Light illuminate APU RPM limit has been exceeded, what would be a automatic reaction of the APU ?

APU will shutdown automatically
page 7.15.6
how can you disarm the APU OVER SPEED Amber Light ?

APU switch to OFF
(light takes 5 min to exstinguish)
page 7.15.6
what causes the APU FAULT Light to illuminate ?

APU malfunction
page 7.15.7
when the APU FAULT Amber Light illuminate a APU Malfunction has been detected, what would be a automatic reaction of the APU ?

APU will shut down automatically
page 7.15.6
how can you exstinguish the APU FAULT Amber Light ?

turn APU switch to OFF
(light takes 5 min to exstinguish)
page 7.15.6
when does the APU LOW OIL PRESSURE Amber Light to illuminate ?

- during start until the APU oil pressure is normal
or
- oil pressure is low
page 7.15.6
one of the causes for the APU LOW OIL PRESSURE Amber Light to Illuminate is a Low Oil Pressure situation, how would the APU react ?

APU will shutdown automatically
page 7.15.6
how do you exstingush the APU LOW OIL PRESSURE Amber Light ?

APU switch to OFF
(light takes 5 min to exstinguish)
page 7.15.6
what happens when the APU switch is set on START ?

initiates start sequence
page 7.15.7
what happens when switching APU to OFF when APU running ?

- trips APU GEN OFF Busses
- closes APU Bleed Air Valve
- APU Air Inlet door closes after shutdown
page 7.15.7