Embryology Questions Flashcards
what is present in the 2nd week of development of the extraembryonic cavity?
exocoelomic cysts
in IVF, what is used to stimulate ovaries?
Gonadotrophins
On which day does the posterior neuropore close?
day 27
which of the following are derived from the endoderm?
none of the following
which embryonic layer is in contact with the parietal hypoblast?
Cytotrophobast
which layer is generated by the epiblast?
epiblast
which layers are the primary villi originated from?
cytotrophoblast
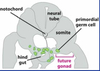
what structure is under the neural tube?
notochord
how long does semen capacitation take?
10 hours
what is the placenta?
haemochoral
what is the percentage of sperm in a sample?
14-90%
on which day does the process of allantosis begin?
day 15-16
when does the second meosis of oogenesis occur?
fertilisation
at the eigth day of development, the hypoblast consists of
small cuboidal cells
The amniotic cavity is formed by cells of the
epiblast
approximately how long after fertilisation does the first cleavage of the zygote occur?
30 hours
the primitive endothelial cells are formed by?
cells lining the yolk sac
in the beginning of the third week, the paraxial mesoderm differentiates into segments known as
somites
which embryonic layer is in direct contact with the parietal hypoblast until the formation of the extraembryonic mesoderm?
cytotrphoblast
monozygous twins may have
common amnion, placenta and chorion
the intraembryonic lateral plate mesoderm generates which of the following?
limb buds
which of the statements regarding the types of spermatogonia is NOT true?
stem cells generating sertolli cells
the number of oogonia at birth is approximately?
700,000-2,000000
the primitive endothelial cells are formed by?
cell linings of the yolk sac
the amniotic and yolk sac cavities are temporarily connected by?
The neurenteric canal
the intraembryonic intermediate mesoderm forms?
gonads
from which germ layer do the adenohypophysis originate?
(anterior pituitary) surface ectoderm
which pharyngeal arch contributes to most of the middle eat ossicles
second
which cells are generated by the secondary spermatocytes?
early spermatids
what effect does prostaglandin have on the semen?
a+c
how does the female tract assist sperm migration?
b+c
which of the following statements is true?
chorionic villi are part of the foetal placenta part
the merging of which structures contributes to development of the face?
maxillary and mandibular processes and frontonasal prominence
from which component of the blastocyst can the stems capable of organ regeneration in humans?
embryoblast
which of the zona pellucida proteins acts as a receptor for spermatozoa binding?
ZP3
what is the name of the outer layer of the blastocyst?
trophoblast
the process of compaction of the pre-embryo leads to formation of an outer and inner cell mass, which differ in their intercellular junctions as follows:
outer cell mass–> tight junctions—> inner cell mass—> gap junctions
from the 3rd month, hemopoiesis is
extravasal
the number of somites at the end of the 5th week of development is?
42-44
which of the following structures originates from the endoderm?
epithelium of vagina and prostate
which of the following stages is not a process of fertilisation?
gastrulation
which of the following phases of the menstrual cycle is under progesterone control?
secretory phase
primary villi result from the proliferation of?
cytotrophoblast
in which cavity are the exocoelomic cysts located during the second week of development?
extraembryonic cavity
how long after ejaculation is the maximum fertile time for most sperm?
48 hours
which of the following originates from the paraxial mesoderm?
dermis
the amniotic cavity is formed by cells of the?
epiblast
gastrulation begins with formation of the?
primitive streak
the following structires are NOT derived from the endoderm
all answers are true
how long does capacitation of the semen normally take>
about 5-7 hours
the primitive endothelial cells are formed by?
cell linings of the yolk sac
trophoblastic overgrowth with lack of embryoblast development may lead to?
molar pregnancy
which pharyngeal arch contributes to the formation of the mandible?
first
what is the rate of occurrence of abnormal blastocysts?
20-30%
what is formed at the cranial end of the embryonic disk?
primitive knot
In the presence of how many cells generated by the zygote is the process of cleavage assumed to begin?
16
the following originate from the endoderm
urinary bladder, urethra, alimentary canal, liver, pancreas, trachea, bronchi, alveoli, throid, thymus, tympanic cavity
the conjoined monozygotic twins connected in the thoracic region are called?
thoracopagus
each somite differentiates into all the following
dermatomes, myotomes, syndetomes, sclerotomes
the bilaminar disk consists of?
epiblast and hypoblast
turner syndrome is
monosomy X(absence of an entire sex chromosome) resulting in 45 chromosomes
which germ layers do the nephrogenic cords originate from?
intermediate mesoderm
outermost layer of the embryonic mesoderm?
ectoderm
outermost layer of the preembryo
trophoblast
what are the two layers of the endometrium?
stratum functionalis and stratum basalis
time period within which the secondary oocyte can be fertilised
12-24 hours
how many cavities characterise the pre embryo at the end of the 2nd week of development
2(chorionic and amniotic)
the first blood cells originate from
yolk sac
what is the normal sperm count of the sperm in 1/ml?
15-40 million
which of the cells produce testosterone in the testis?
interstitial cells
which of the blastocyst poles is directed to the endometrium at implantation?
embryonic plate
the endoderm is crated by?
epiblast
during which stage of prophase of the first mitotic division in gametes does crossing over take place?
pachytene
what is the optimal window for people wishing to conceive a child?
3 days before ovulation and less than a day after
which structure is formed at the dorsal border of the neural tube?
spinal cord
the cells generated by the spermatogonia are?
primary spermatocytes
the cephalic end of the primitive streak is?
primitive node
which layer does the chorion originate from?
extraembryonic mesoderm
amniocentesis is used to investigate and detect?
prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and fetal genetic abnormalities
what is the name of the cells forming the morula?
blastomeres
when does implantation after fertilisation start?
6-7 days
how many chromosomes do fertilised eggs have?
46
what are the risks for pregnant women during a tubal pregnancy?
rupture, bleeding, internal haemorrhage
during the second week of development, the embryoblast differentiates into?
bilaminar germ disc composed of epiblast and hypoblast
what compartment of the blastocyst contributes to the formation of the placenta?
trophoblast
how long does it normally take the sperm to migrate in the female reproductive tract and to each the egg?
18-24 hours
which of the following lists are steps in in vitro fertilisation?
Ovarian hyperstimulation—(last) adjunctive medication
which of the following structures refer to embryonic membranes?
anmion, chorion, yolk sac, atlantosis
what is the average composition of seminal fluid?
2-5% sperm, 65-75% amino acids and citrate, 25-30% acid phosphatase, citric acid, 1% galactose and mucus
what is the average age of menopause in humans?
40 years
the somatopleure and splanchnopleure originate from
lateral mesoderm
which of the which germ layer do the heart and spleen originate from?
mesoderm
what is the name of the inner layer of the blastocyst?
hypoblast
what is the mechanism of the clonal expansion of the progenitors of the gametes?
mitosis
which of the listed options form the corona radiata?
granulosa cells
what is the main factor of sperm migration in the female reproductive tract?
sperm chemotaxis- progesterone
in which phase of the menstrual cycle does the endometrium achieve its maximum thickness?
luteal phase
the myotomes consist of?
epithelial somites
after its penetration in the oocyte, the spermatozoa head is transformed into?
pronucleus of zygote
the initial haemopoesis is
intravasal
the umbilical vein
carries oxygenated blood from placenta to foetus
which of the enumerated characteristics of given semen analysis are normal?
20 and 40 million sperm per mm
which of the following tissues originates from the endoderm?
lung, thyroid or pancreatic cells
cumulus oophorus is characteristic or which follicle?
antral follicles
the embryonic disk gradually becomes elongated with?
primitive streak
the process of cleavage represents a series of
mitotic cell divisions
gastrulation establishes
the trilaminar disc
which component of the preembryo aborts its development in a molar pregnancy?
hydatiform mole
the hypoblast belongs to
trophoblast
the formation of the fingers in the limb buds takes place via
apical ectodermal ridge
what is the correct sequence of the extended first meiotic division?
leptotene—(last)–synchronous processes
at which developmental stage does the segmentation of the paraxialmesoderm begin?
beginning of third week
which germ layer structure do the neurons of the peripheral nervous system originate from?
neural crest of ectoderm
how many pharyngeal arches contribute to the formation of the thymus?
3
the formation of the primitive streak occurs on the surface of
hypoblast
the connecting stalk originates from
extraembryonic medoderm
conjoined monozygotic twins by the head are called
craniophagus
which of the following phases of the menstrual cycle is under oestrogen control
follicular phase
ejaculation is identical to which process?
ovulation
the intervillus space of the placenta contains
blood(from the maternal arteries and veins
which compartment of the blastocyst contributes to the formation of the foetus?
embryoblast(inner cell mass)
the exocoelomic membrane lines the inner surface of?
cytotrophoblast
the secretion of FSH by the pituitary gland is suppressed by a factor secreted by the Sertoli cells called
inhibins
where must sperm normally encounter the egg in order to fertilise it?
ampulla of uterine/fallopian tube
how many pairs of chromosomes contain the primodial germ cells?
23
placental villi are best developed in the region of
syncytiotrophoblast
the rate of dizygotic twins is
70%
down syndrome is known as
trisomy 21
which germ layer do the serous membrane of the body originate from?
mesoderm(lateral plate?
which type of trophoblastic villi are formed in the 2nd week of development?
primary villi
name the most medially located components of the intraembryonic mesoderm
intermediate mesoderm
the inner layer of the embryoblast adjacent to the amniotic cavity is
epiblast
insemination is a process of passage of spermatozoa through the female genital tract as follows
deposition of sperm into —> migration to the uterus—>uterine tube
which component of the preembryo continues to develop thus forming molar pregnancy?
trophoblast
the definitive umbilical cord contains
2 arteries and 1 vein
what is the normal sperm motility?
3mm/min
the cardiogenic primordium is formed by?
epiblast lateral to primitive streak
what is the sequence of appearance of the limb buds
flatten buds===>radial grooves on distal portion of buds–> digits
which requirements of the semen must be met for sperm motility?
increased flagellum motility, high no of mitochondria
The second meiotic division during oogenesis begins..
at the time of ovulation
From which germ layer develop the smooth muscle cells of internal organs?
Splanchnopleuric lateral plate mesoderm
Which layer of the preembryo is in direct contact with the endometrium?
Amnion
Which of the following tissues is derived from the ectoderm?
Adenohypophysis
Insemination is a process of passage of spermatozoa through the female genital tract as follows:
Vagina- cervix uteri- cavum uteri-uterine tubes
The heart and blood vessels are derivative of
lateral plate mesoderm
Which germ layer forms lacunae?
Syntiotrophoblast (cytotrophoblast + layer of syntiotrophoblast grow into lacunae)
The olfactory placode is located on the surface of which structure?
Frontonasal prominence
What is the inner mucus layer of the uterus called?
Endometrium
From which germ layer, originate the nephrogenic cords?
Intermediate germ layer
Which of the listed structures penetrate deepest into the endometrium?
Tertiary Villi
The formation of the notochord occurs during?
3rd Week
Teratogens are agents that?
cause congenital malfunction
Which of the following do not originate from the endoderm?
heart and blood vessels
gastrulation is established…
Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm( single layered blastula is reorganised into a multi-layered structure known as the gastrula)
Which structures originate from the lateral plate and mesoderm?
Epithelium of the peritoneal, pleural and pericardial cavities
Which components of the seminal fluid contribute to the raising of the pH from 3.5-7.5 and activating the sperm?
Seminal vesicle fluid
During the process of cleavage..
The cells do not change size
Sclerotomes differentiate into..
Bone and cartilage which surround the notochord
Which cells of the spermatogonic population have bivalent chromosomes?
spermatids
In which cells are the cortical granules located?
Oocyte(peripheral cytoplasm)
The preimplantation genetic diagnosis represents analysis of?
blastomeres
Name the medially located compartment of the intraembryonic mesoderm
Paraxial mesoderm
Which Structures originate from the lateral plate mesoderm?
Epithelium of the renal tubes and renal calices
What is the volume of seminal fluid in a healthy individual?
0.5-1ml
which of the listed options is associated with the acrosomal reaction of the spermatozoa?
all answers are true
Which techniques of artificial insemination are available to the public?
a and c
each somite differentiates into the following except..
Nephrotome
At which embryonic stage are the endocardial heart tubes formed?
day 19
Chromosomal aberations(trisomy/monosomy) are most frequently due to..
Non disjunction of homologous chromosomes during first meiotic division
The notochord serves as a basis for
The axial skeleton
The definitive umbilical cord contains
mucous connective tissue( warton’s jelly)
Which structures do the exocoelomic cavities(cysts) arise from in the 2nd week of development?
secondary yolk sac
Which of the following are functions of the yolk sac?
takes part in early blood circulation
The process of cleavage(segmentation) is?
mitosis
gastrulation occurs in the beginning of the….
third week
The umbilical arteries…
surround the urinary bladder
Which of the following tissues is derived from the ectoderm?
Epidermis skin cells, neurons of brain and pigment cells
When does implantation after fertilization еnd?
13-14 days
Which layer is in contact with the cytotrophoblast after the formation of the extraembryonic cavity
Extraembryonic somatopleuric mesoderm