Embryology Flashcards
(53 cards)
Oxygen tension in 1st trimester?
Low - 3% to prevent production of free radicals
Summarise Embryology in 1st trimester 3-8 weeks?

Embryological timings v,s gestational timings?
- Embryological timings are usually about 2 weeks less than the gestational time frames.
- E.G. 12 weeks GA is 10 weeks embryologically.
- GA time frames – starts after the beginning of the last menstrual period.
What is development measured in?
Carnegie stages.
Define Blastocyst, Embryo, Foetus, Conceptus?
- Blastocyst – epiblast and hypoblast present at ~9 days
- Embryo – small developing conceptus present at ~5-6 weeks
- Foetus – developing conceptus present at ~3 months for rest of prgenancy.
- Conceptus – anything derived from a fertilised egg
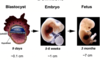
What is the red part in the image?

the red part is the liver developing and is where the RBCs are made before the spleen kicks into action.
The body repeats what 4 simple processes to achieve embryology.
- Cells must – proliferate, move, differentiate & be able to undergo cell loss.
Regulation of Cells in development - signalling methods and concentration signalling?
- Signalling methods:
- Paracrine – to adjacent cells.
- Autocrine – to oneself.
- Endocrine – over long distances via vasculature**.
- During embryo development, there isn’t much vasculature made so this doesn’t occur much.
- Concentration signalling – the strongest signals are received by cells located closest to the source of the signalling molecules.
Concentration signalling – the strongest signals are received by cells located closest to the source of the signalling molecules.
So what happens if the source cells are at the tip?
- If the source cells are at the tip, the highest levels of proliferation will remain at the tip and thus a “bud” will form towards the apex – e.g. a limb bud.

Asymmetrical development can occur how?
- With +ve stimuli and –ve stimuli, asymmetrical development can also occur…
Embryology depends on what?
gradients of factors, combinations of factors, temporal changes in factors or responses to them.
Name a gene important in the regulation of development?
- what it does, how is it activated
- Genes regulate development heavily:
- HOX genes – establish A-P (Anterior-Posterior) axis, differences in the vertebrae, CNS divisions, patterns in the limbs.
- Activation of HOX is controlled by retinoic acid, a derivative of vitamin A.
Embryology Timeline: The conceptus starts as?
- The conceptus starts as a bilaminar disc inside a blastocyst – comprised of an epiblast and a hypoblast layer.

What process forms a 3-layer conceptus?
- Gastrulation forms a 3-layer conceptus – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
What structures do the 3 layers formed in gastrulation form?
- Endoderm = gut, liver and lungs.
- Mesoderm = skeleton, muscles, kidneys, the heart and blood.
- Ectoderm = skin and the CNS.
Describe how gastrulation = 3 layers?
- Epiblast proliferates = a group of cells that infiltrate the space between epiblast and hypoblast (primitive streak)
- mesoderm cells cause hypoblast cells to apoptose and differntiate = endoderm cells.
- so thought that epiblast forms all 3 germ layers
After gastrulation has formed 3 layers what happens?
- After gastrulation has formed 3 layers, the ectoderm proliferates to form the neural plate (with NO proliferation at the neural groove – negative stimulation of notochord) and the neural fold’s fold over and form the neural canal.
The body cavity then closes by day 28 and pinches off the yolk sac into the umbilical cord

How does the neural fold = canal and explain closure of - the neural tube closes by week 4?
- The tissues will fuse down the midline leaving just 2 openings at the anterior neuropore and the posterior neuropore.
- During days 25-28, the neuropores SHOULD close.

Types of Spina bifida – TOP = bad prognosis to good prognosis (bottom)
- Myelomeningocele – neural tissue in bulge.
- Meningocele – no neural tissue in bulge.
- Spina bifida occulta – hair growth over area affected, no growth.
- Note: The fact that there is no formation of vertebrae at the bulge suggests that bone growth is dependent on neural tissue growth.
What can be interpreted from the fact that
Myelomeningocele – neural tissue in bulge.
Meningocele- no neurl tissue in bulge?
- The fact that there is no formation of vertebrae at the bulge suggests that bone growth is dependent on neural tissue growth.

Heart begins to develop at week 4 explain heart development?
- The two endocardial tubes fuse into a primitive heart tube that pumps blood.
- Endocardial tubes develop in the mesoderm and come together as the body cavity closes (pinching off of yolk sack = umbilical chord)
- Note: primary and secondary heart field form into the primitive heart tube by fusing and then breaking the arch at the apex - to allow blood to go through.
- The heart then undergoes a turning action (anti-clockwise) to form the primitive heart and the 4 chambers form.

describe - The heart turning action?
- What aids the heart movement?
- The primitive heart tube undergoes an anti-clockwise turning motion which results in the ventricles being at the bottom with the atria at the apex.
- The atria rotate BEHIND the arteries.
- The head-tail folding is also occurring which aids rotation of the heart and the movement of the heart more internally.

Role of the ductus arteriosus and patent foramen ovale?
- At birth, the ductus arteriosus and foramen ovale close to shift the heart from a single cycle flow in the foetus to a figure of eight loop flow.
- The ductus arteriosus and patent foramen ovale act as shunts to the blood supply (so that the blood avoids the pulmonary system).
How to limbs develop and when?
Limb Development [aprox 4 weeks]
- The forelimb bud appears at day 27/28, hind limb bud at day 29.
- Budding is growth from the lateral plate mesoderm which is done rapidly under control of special signalling regions.






