Embryology Flashcards
What does the paraxial mesoderm form?
Somites
What does the intermediate plate mesoderm form?
Urogenital system (kidneys + repro)
What does the lateral plate mesoderm form?
Body cavity and coverings
What is below the endoderm?
The yolk sac
What is above the ectoderm?
The amniotic cavity
Take a wee gander at this

What is the allantois?
Allantois is an outpouching of endoderm at the hindgut that extends into the body stalk
(body stalk later forms the umbilical cord)
What is the cloaca?
(noun) The cloaca is the single posterior opening for a bird’s digestive, urinary and reproductive tracts and is used to expel feces and lay eggs.
Wat does the cloaca divide to form?
Rectum and anteriorly the urogenital sinus
What drains into the urogenital sinus?
The mesonephric duct
What does the urogenital sinus later form?
The urinary bladder and its caudal end forms the urethra
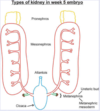
How many sets of kidneys develop during nephrogenesis?
3
Where does the first set of pronephrons form?
Early in the Week 4 the intermediate mesoderm in the neck region of the embryo becomes the pronephros
What makes up pronephros?
•pronephric duct + rudimentary pronephric tubules

Where does the pronephric duct drain?
Drains into the cloaca
When do the pronephros normally degenerate?
•In humans, the pronephros mainly degenerates by Week 5 (except the pronephric duct)
What does the mesonephros form?
•Mesonephros = Intermediate mesoderm in trunk region, late Week 4.
What does the pronephric duct become?
•Pronephric duct now becomes the mesonephric duct
Where do mesonephric tubules drain?
•Mesonephric tubules develop and drain into the mesonephric duct

What does the metonephros develop from?
- A ureteric bud that develops off the mesonephric duct
- Metanephric mesoderm (the most caudal part of the intermediate mesoderm)
What happens to the mesonephros?
Much of the mesonephros will be incorporated into the developing gonad.
(Undifferentiated cells from the yolk sac migrate in to form the spermatogonia/ oogonia)

What forms from the mesonephric tubules and the mesonephric ducts?
The mesonephric tubules become the rete testis
The mesonephric duct becomes the vas deferens
(In females the mesnephros becomes the ovary but the tubules and mesonephric duct degenerate)
What happens to the ureteric bud?
The ureteric bud undergoes repeated branching at its distal end. (Ureteric bud comes from the mesonephric duct)
The stalk becomes the ureter, the expanded cranial end becomes the renal pelvis.
The first 4 generations of branches become confluent to become the major calyces
The next 4 generations form the minor calyces
The remaining generations form the collecting tubules
How are the ureteric bud and the metanephric mesoderm induced?
The ureteric bud and the metanephric mesoderm reciprocally induce each other
What is the definition of a nephron and a uriniferous tubule?
Nephron = Renal corpuscle + PCT + Loop of Henle + DCT
Uriniferous tubule = Nephron + Collecting duct
What do the metanephric mesoderm and the ureteric bud form respectively?
Metanephric mesoderm: Nephron
Ureteric bud: Collecting duct and calyces, pelvis and ureter
Why do the kidneys appear to ascend into the abdomen?
Mainly due to differential growth of lower body inferiorly away from kidneys
Kidneys come to lie in the upper abdomen (T12 - L3)
What direction do the kidneys rotate?
Hilum rotates from ventral to medial (~90degrees)
When does the ascent of kidneys end?
Ascent stops when they come in contact with adrenal glands
During ascent what happens to the vasculature?
Segmental breakdown and reform of vascular supply during ascent


