Electrical Activity of the Heart Flashcards
What is contraction of heart muscle stimulated by?
Excitation contracting coupling

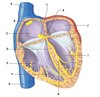
What is A?

T-tubule
What is B?

Actin
What is C?

Myosin
What is D?

Z-line
What is the process of a normal muscle contraction?
1) Action potential reaches cell and causes Na voltage channels to open
2) Cell depolarises and causes calcium to be released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
3) Calcium binds to troponin and starts the muscle contraction
Where is actin anchored?
Z line
What are the deep invaginations in the muscle membrane known as?
T-tubules
What are T-tubules?
Deep invaginations in the muscle membrane that interact with the organelles in the cell, such as the sarcoplasmic reticulum
What allows cardiac cells to act as one big cell?
Gap junctions allowing the cells to communicate to each other by using signalling molecules
Desmosomes preventing the cells from separating during contraction
What do gap junctions allow?
Cardiac cells to communicate with each other using signalling molecules
What do desmosome junctions do?
Prevent cells from separating during a contraction
What are intercalated disks?
Connect cardiac cells to allow them to work as a single functional organ
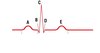
What are the differences between the action potentials of skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle?
Action potential lasts for way longer in cardiac muscle
How long does the action potential last for in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle?
2ms in skeletal muscle
250ms in cardiac muscle
What does the action potential lasting for ages in a cardiac cell allow?
Calcium to enter from outside the cell as well as sodium, allowing regulation of contraction
What does the longer action potential allowing calcium and sodium to enter from outside the cell allow?
Heart contraction to be stronger or weaker
Refractory period is longer
Which is cardiac and skeletal muscle has the longer refractory period?
Cardiac muscle
What differences are there between cardiac and skeletal muscle due to cardiac muscle having a longer refractory period?
Skeletal muscle contractions can add together and accumulate (tetanus) due to many action potentials being added to one another
Cardiac muscle has to fully contract before it can be stimulated again and so they do not add onto each other

Why is it important that the long refractory period of cardiac muscle mean tetanus cannot occur?
Heart needs to fully contract and then relax to pump blood
What is tetanus?
Sustained muscle contraction evoked when the motor nerve that innervates a skeletal muscle emits action potentials at a high rate
What is a sustained muscle contraction evoked when the motor nerve that innervates a skeletal muscle emits action potentials at a very high rate called?
Tetanus
What do cardiac cells that have unstable resting membrane potentials act as?
Pacemakers

What does having pacemakers allow a cell to do?
Depolarise again quicker