Eczema Flashcards
Describe the clinical features of eczema?
Itchy, erythematous and dry.
In the acute phase there may be vesicles or blisters which may weep or bleed.
Chronically fissures and lichenification (skin thickenning) develop
What is the childhood prevalence of atopic eczema?
10-20% of children
Usually presents before 2 years of age and the severity decreases with age.
Describe the aetiology of atopic eczema?
Mutation of a gene causing a primary skin barrier defect.
Endogenous.
Note commonly effects the face in young children and as they get older often moves to the flexor regions.
Which factors can commonly exacerbate atopic eczema?
Irritants (soap, nylon sheets)
Allergies
Weather
Stress
Illness
Which group is sebhorraeic eczema most common in and what organism is it associated with?
It is most common in middle aged adults.
It is associated with the Pityosporum yeats species and may be due to an immune reaction to these micro-organisms.
It is exacerbated by alcohol.
It is an endogenous form of eczema.
How does discoid eczema present and in which age groups?
Any age.
Disc like well demarkated lesions.
Often infected, and thougt to potentially be a manifestation of atopic eczema.
It is an endogenous form of eczema.
What is irritant contact eczema/dermatitis and who does it usually effect?
Direct effect of irritant substances affecting the skin integrity usually the hands. It is a type 4 immune response.
It usually effects the following occupations:
Hairdressers
Chefs
Cleaners
Housewives
Nurses
This is an exogenous form of eczema.
List some common irritants in allergic contact dermatitis?
Nickle in jewlerry and belt buckles
Hair Dye
Plants
Topical meds
Frangrances
Occupation
Diagnosis is confirmed by patch testing.
Describe the management of eczema?
Avois irritants.
Emollients for dry skin, should be used as a soap substitute.
Treat active eczema with topical steroids or second line treatments if the patient cannot tolerate the side effects of steroids.
The lowest strength sterois which will treat the eczema should be used.
What are the different strengths of steroid?
Mild: Hydrocortisone 1%
Moderate: Eumovate
Potent: Elocon, Betnovate
Very Potent: Dermovate
Emollients should be used preferntially to creams and she be applied 1-2 time a day in short courses.
What are the risks of applying potent steroids long term on the face?
Telangeictasia
Perio-orbital dermatitis
Glaucoma and cataracts
+ skin thinning
What are the second line treatment options?
Immunomodulators
Bandaging and wet wraps
Photodynamic therapy
Oral steroids
What type of eczema is shown?

Discoid eczema
What type of eczema is shown?

Atopic eczema
Often on face in young children and flexure regions as the child gets older
What type of eczema is shown?

Severe eczema + secondary infection
What type of eczema is shown?
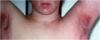
Irritant contact dermatitis
What type of eczema is shown?

Seborrhaeic Eczema
Most commonly seen in middle aged adults on the face
What type of eczema is shown?
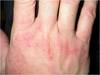
Irritant contact dermatitis
Most commonly effects the hands
What type of eczema is shown?

Pompholytic eczema also known as dyshydrotic eczema
It is an eczema of unknown aeitiology and presents as an itchy vesicular rash on the hands, fingers and soles of the feet.


