Drugs Flashcards
Lidocaine hydrochloride
- Indications
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Ventricular arrhythmias, especially after MI
- IV regional anaesthesia & nerve block
- Pain relief (in anal fissures, haemorrhoids, pruritus ani, pruritus vulvae, herpes zoster, or herpes labialis),
- Lubricant in cystoscopy, Lubricant in proctoscopy
- Anaesthesia before venous cannulation or venepuncture
- Postherpetic neuralgia (vzv reactivation)
- Bronchoscopy, Laryngoscopy, Oesophagoscopy, Endotracheal intubation
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Lidocaine hydrochloride
- Contra-indications for regional and IV administration
- Contra-indications for regional administration
- Side-effects
- atrioventricular block; severe myocardial depression; sino-atrial disorders
- application to the middle ear (can cause ototoxicity);
avoid injection into infected & inflamed tissues;
- Common for IV: dizziness, drowsiness, paraesthesia
Common for IV or RA: bradycardia (may lead to cardiac arrest); confusion; convulsions; hypotension (may lead to cardiac arrest); respiratory depression
Intrathecal administration is?
advantage?
use?
injection into the spinal canal or the subarachnoid space
reaches the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
spinal anaesthesia, chemotherapy, or pain management applications.
Use of bupivicaine
Surgical anaesthesia
a. lumbar epidural block
b. field block
c. thoracic epidural block
d. caudal epidural block
acute pain
a. major nerve block
b. labour
Bupivicaine
- Contra-indications
- Cautions
- Side-effects
- Application to the middle ear (ototoxicity);
Avoid injection into infected & inflamed tissues; (Increased absorption into the blood increases the possibility of systemic side-effects, and the local anaesthetic effect may also be reduced by altered local pH)
complete heart block;
preparations containing preservatives should not be used for caudal, epidural, or spinal block, or for intravenous regional anaesthesia (Bier’s block);
- Cardiovascular disease; cerebral atheroma; debilitated patients (consider dose reduction); elderly (consider dose reduction); epilepsy; hypertension; hypotension; hypovolaemia; impaired cardiac conduction; impaired respiratory function; myasthenia gravis; myocardial depression may be more severe and more resistant to treatment; shock
- Common: Arrhythmias; dizziness; hypertension; hypotension; nausea; paraesthesia; urinary retention; vomiting
Uncommon: Neurotoxicity
Rare or very rare: Arachnoiditis; cardiac arrest; diplopia; nerve disorders; paraplegia; paresis; respiratory depression
Monitor as per local protocol for at least 30 minutes after administration
Paracetomol (NSAID
- Indications & dose
- General side-effects
- Specific side-effects
a. Common
b. Rare or very rare - pregnancy safe?
- Antidote if overdose?
- effects of overdose?
- MOA
Mild to moderate pain
Adult
PO: 0.5–1 g every 4–6 hrs; max 4 g/day
IV: (<50 kg) 15 mg/kg every 4–6 hrs, dose to be administered over 15 minutes; maximum 60 mg/kg per day.
(=>50 kg) 1 g, 4–6 hrs, over 15 mins; maximum 4 g/day.
(HEPATOTOXICITY max 3 g/ day)
Rectum: 0.5–1 g every 4–6 hours; maximum 4 g/day
Prophylaxis of post-immunisation pyrexia following immunisation with meningococcal group B
GBS-EOD are septicemia without apparent location, pneumonia, and less frequently meningitis
GBS: group B streptococcal
- Rare or very rare: Thrombocytopenia
- With rectal use: anorectal erythema
IV: hypersensitivity; hypotension; leucopenia; malaise; neutropenia
angioedema; liver injury; skin reactions
- yes
- ABCDE
IV Acetylcysteine ( within 24 hours of ingesting paracetamol)
Activated charcoal
- Within 24hrs: hepatocellular necrosis, renal tubular necrosis, n + v (settle within 24 hrs)
over 24hrs: right subcostal pain and tenderness (hepatic necrosis). Liver damage is maximal 3–4 days after paracetamol overdose and may lead to encephalopathy, haemorrhage, hypoglycaemia, cerebral oedema, and death.
- unknown
Codeine (opiod)
- Indications & dose
- Important safety information
- Signs or symptoms of toxicity
- a. Mild to moderate pain
PO (For Adult): 30–60 mg every 4 hrs if required; max 240 mg/day (6-4 tablets)
IM (For Adult): 30–60 mg every 4 hrs if required.
b. Dry or painful cough
By mouth using linctus
15–30 mg 3–4 times a day
2.codeine should not be used in breast-feeding mothers because it can pass to the baby through breast milk
life-threatening adverse reactions in children with obstructive sleep apnoea who received codeine after tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy:
12–18 years, the maximum 240 mg
Doses may be taken up to four/day, intervals of no less than 6 hours
duration of treatment should be limited to 3 days
- constipation, RDS, pin point pupils (para)
Codeine continued
- Contraindications For all OPIOIDS
- For CODEINE PHOSPHATE
- MOA
- S/E for codeine phosphate
- breast feeding?
- Acute respiratory depression; comatose patients; head injury (opioid analgesics interfere with pupillary responses vital for neurological assessment); raised intracranial pressure; risk of paralytic ileus)
- Acute ulcerative colitis; antibiotic-associated colitis;
- codeine -> morphine CYP2D6
- Biliary spasm; hypothermia; mood altered; sexual dysfunction; ureteral spasm
- mothers vary considerably in their capacity to metabolise codeine—risk of morphine overdose in infant
Morphine
- Indications
- a. Acute pain
PO, SC, IM: initially 10 mg every 4 hrs (adult)
5 mg every 4 hrs (elderly)
IV: Initially 5 mg every 4 hrs
b. Chronic pain
PO, IM, SC: 5–10 mg every 4 hrs
PR: Initially 15–30 mg every 4 hrs
c. Pain (with modified-release 12-hourly preparations) PO
d. Pain (with modified-release 24-hourly preparations) PO
e. Pain management in palliative care (starting dose for opioid-naïve patients)
PO: 20–30 mg/day, divided doses, immediate-release preparation 4-hourly/ 12-hourly modified-release preparation,
f. Pain management in palliative care (starting dose for patients being switched from a regular weak opioid)
PO: 40–60 mg/day (as above)
g. Pain in palliative care (following initial titration)
h. cough in terminal illness
i. PCA
j. MI
k. Acute PO
l. Dyspnoea
- Contra indications for morphine
- S/e
- Breast feeding?
- MOA
- Bioavailabilty
- Acute abdomen; delayed gastric emptying; heart failure secondary to chronic lung disease; phaeochromocytoma
- arryhtmias, insomnia, constipation,
- safe
- mu-opioid receptors (kappa & delta agonist)
binds to and inhibits GABA inhibitory interneurons
- 30%.

Ibruprofen
- Indications
(dose: initial, max, maintainence)
a. Pain & inflammation in RD & other MSK disorders,
Mild to moderate pain including dysmenorrhoea (early 20s),
Postoperative analgesia,
Migraine,
Dental pain
PO immediate release med: Initially 300–400 mg 3–4/day; increased if necessary up to 600 mg 4 times a day; maintenance 200–400 mg 3/day
PO modified-release med: 1.6 g once daily, dose to be taken in the early evening, increased if necessary to 2.4 g daily in 2 divided doses, dose to be increased only in severe cases.
Contra-indications of ibuprofen
IV: active bleeding (especially intracranial or gastro-intestinal) (in neonates); coagulation defects (in neonates); known or suspected necrotising enterocolitis (in neonates); life-threatening infection (in neonates); marked unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia (in neonates); pulmonary hypertension (in neonates); thrombocytopenia (in neonates)
With systemic use: active gastro-intestinal bleeding; active gastro-intestinal ulceration; Hx of GI bleeding/perf/ recurrent haemorhage related to previous NSAID therapy; history of recurrent gastro-intestinal ulceration (two or more distinct episodes); severe heart failure
- TB drugs and side
- What is tinea pedis
- image
- dermatophyte infection of the soles of the feet and the interdigital spaces
3.

inducers and inhibitors of cyp450
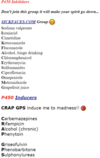
Naproxen
- Indications and dose
- Contra-indications
- s/e
- pregnancy
- caution
- Avoid if
- a. Pain & inflammation in RD
PO: 0.5–1 g daily in 1–2 divided doses
b. Pain & inflammation in MSK disorders, Dysmenorrhoea
PO: initially 500 mg, then 250 mg every 6–8 hours as required, maximum dose after the first day 1.25 g daily
c. Acute gout
PO: Initially 750 mg, then 250 mg every 8 hrs until attack has passed.
- current or Hx of GI bleeding/per/ulcer
- everything e.g. alopecia, agranulocytosis, vertigo
- Avoid unless benefit outweighs the risk.
Avoid during the third trimester (risk of closure of fetal ductus arteriosus in utero and possibly persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn); onset of labour may be delayed and duration may be increased.
- Long-term use of some NSAIDs is associated with reduced female fertility, which is reversible on stopping treatment
- eGFR less than 30 mL/minute/1.73 m2 (90-120)
Senna (low dose initially then increased)/ anthraquinone
- Indications & dose
- Why is it usually taken at bedtime?
- breastfeeding? pregnancy?
- s/e
Constipation
TABLETS 6–17 yo: 7.5–30 mg/day
TABLETS Adult: 7.5–15 mg/day (max. per dose 30 mg daily)
SYRUP 4–17 yo: 3.75–30 mg/day
SYRUP adult: 7.5–15 mg once daily (max. per dose 30 mg daily)
- 8-12hrs to work , greater parasympathetic drive at night = more bowel movements, gastrocolic reflex in the morning
- breastfeeding infant > 1mth
safe in pregnancy
- melanosis/ pseudomelanosis coli: lipofuscin in macrophages (senna causes necrosis of bowel which is taken up by machrophages)
colonoscopy no association with disease
ISPAGHULA HUSK/ fybogel
- Indication
- MOA
- Contra-indications
- Cautions
- Side-effects
- Constipation
PO: 1 sachet twice a day
dose in water >= 150ml
taken after food
morning and evening
- Bulk-forming laxatives relieve constipation by increasing faecal mass which stimulates peristalsis
- Colonic atony; faecal impaction; intestinal obstruction; reduced gut motility
- Adequate fluid intake should be maintained to avoid intestinal obstruction
- Abdominal distension; bronchospasm; conjunctivitis; gastrointestinal disorders; hypersensitivity; rhinitis; skin reactions
Lactulose
- Indications
- pharmacokinetics
- Contra-indications
- Cautions
- S/e
- pregnancy
- a. Constipation
PO Adult: Initially 15 mL twice daily, adjusted according to response
b. Hepatic encephalopathy (portal systemic encephalopathy)
PO adult: Adjusted according to response to 30–50 mL 3 times a day, subsequently adjusted to produce 2–3 soft stools per day.
- may take up to 48 hours to act
- Galactosaemia; intestinal obstruction
- Lactose intolerance
- Common: Abdominal pain; diarrhoea; flatulence; nausea; vomiting
Uncommon: Electrolyte imbalance
- Safe
- Galactosaemia
- can’t metabolize the galactose properly
+ autosomal recessive mode

Augmentin/ co-amoxicillin (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid)
- Indications
- Contraindications
- what is chronic lymphocytic leukaemia
- Describe haematopoesis
- Cautions:
- general S/e
- Specific side-effects, Frequency not known, With oral use
- a. beta-lactamase-producing strains (where amoxicillin alone not appropriate): RTI, bone & joint infections, GU & abdominal infections, cellulitis & animal bites
TABLETS Child 12–17 yo: 250/125 mg every 8 hrs; increased to 500/125 mg every 8 hrs, increased dose used for severe infection.
TABLETS Adult: 250/125 mg every 8 hrs; increased to 500/125 mg every 8 hrs, increased dose used for severe infection.
IV injection/IV infusion: Adult 1.2 g every 8 hours.
b. Severe dental infection with spreading cellulitis,
Dental infection not responding to first-line antibacterial
TABLETS adult: 250/125 mg every 8 hrs for 5 days
c. Surgical prophylaxis
IV injection/ IV infusion adult: 1.2 g, to be administered up to 30 minutes before the procedure, then 1.2 g every 8 hours for up to 2–3 further doses in high risk procedures.
d. _Acute sinusitis PO a_dult: 500/125 mg 3x day for 5 days.
2. hx of co amox associated jaundice or hepatic dysfunction
3. most common type of leukaemia: breathlessness(anaemia), splenomegaly, night sweats, inc no of infections, bruising
5. CLL & CMV infection inc risk of erythematous rash
Cholestatic jaundice
- Common: inc risk of infection
Uncommon: Dizziness; dyspepsia; headache
Frequency unknown: Colitis haemorrhagic; crystalluria; hypersensitivity vasculitis; meningitis aseptic
- akathisia (inner restlessness brought on as a s/e of meds more common in dopaminergic meds); black hairy tongue

co amoxiclav
- Breast feeding? pregancy?
- What is black hairy tongue?
- Effect on kidneys ?
- MOA
- safe
- proliferations of squamous epithelium and micro
RF: smoking, xerostomia (dry mouth), soft diet, poor oral hygiene and certain medications
- inc risk of crystalluria (crystals in urine/cloudy urine) -> inc risk of urolithiasis
if poor eGFR need to adjust dose
- cluvanate:
inhibitor of β-lactamases produced by Gram-negative bacteria including Haemophilus ducreyi, H. influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Bacteroides fragilis, and some Enterobacteriaceae. It also inhibits β-lactamases produced by S. aureus

Teicoplanin
- Targets what microorganisms?
- Teicoplanin is similar to?
- family of drug?
- MOA
- Gram positive (aerobes and anaerobes)
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis
- vancomycin, but has a significantly longer duration of action, allowing once daily administration after the loading dose.
- glycopeptide
- bind to the aa within the cell wall preventing the addition of new units to the peptidoglycan
Teicoplanin
- Indications & dose:
Clostridium difficile infection (bacilli gram. gram positive, blood agar, spores)
PO Adult: 100–200 mg, 2x daily for 7–14 days
Serious infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria (e.g. complicated skin & soft-tissue infections, pneumonia, complicated UTI)
IV injection/infusion/ IM injection for adult: Initially 6 mg/kg every 12 hrs for 3 doses, then 6 mg/kg/day
Streptococcal or enterococcal endocarditis (+ another antibacterial), Bone & joint infections
IV injection/ IV infusion: 12 mg/kg every 12 hrs for 3–5 doses, then 12 mg/kg/dAy.
Surgical prophylaxis
IV adult: 400 mg, to be administered up to 30 minutes before the procedure.
Surgical prophylaxis in open fractures
IV adults: 800 mg, to be administered up to 30 minutes before skeletal stabilisation and definitive soft-tissue closure.
Peritonitis associated with peritoneal dialysis (added to dialysis fluid)
Teicoplanin
- S/e
Common: Fever; pain; skin reactions
Uncommon: Bronchospasm; diarrhoea; dizziness; eosinophilia; headache; hearing impairment; hypersensitivity; leucopenia; nausea; thrombocytopenia; vomiting
Rare: Abscess; red man syndrome(10-30min, pruritus, an erythematous rash that involves the face, neck, and upper torso)
FNK: Agranulocytosis; angioedema; chills; neutropenia; overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms; renal impairment; seizure; severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs); thrombophlebitis
Gentamicin
- Indications & dose
- a. Bacterial eye infections (staph a, strep pneu? both GP)
For Adult: 1 drop at least every 2 hours, reduce frequency as infection is controlled and continue for 48 hours after healing, less severe infection 3–4x daily is generally sufficient.
b. Bacterial infection in otitis externa (Pseudomonas aeruginosa GN and Staphylococcus aureus GP)
Ear for Child: 2–3 drops 4–5x day, (including a dose at bedtime).
For Adult: Apply 2–3 drops 4–5 times a day, (including a dose at bedtime).
c. Gram-positive bacterial endocarditis or HACEK endocarditis (in combination with other antibacterials)
IM injection, IV injection, IV infusion Adult: 1 mg/kg every 12 hrs, IV injection to be administered over at least 3 minutes, to be given in a multiple daily dose regimen.
Septicaemia,
Meningitis and other CNS infections,
Biliary-tract infection,
Acute pyelonephritis,
Endocarditis,
Pneumonia in hospital patients,
Adjunct in listerial (bacteria 3rd commonest cause of) meningitis,
Prostatitis
IV infusion, or by slow IV injection, or by IM injection adult: 3–5 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses, to be given in a multiple daily dose regimen, divided doses to be given every 8 hours, intravenous injection to be administered over at least 3 minutes.
By intravenous infusion
For Adult
Initially 5–7 mg/kg, subsequent doses adjusted according to serum-gentamicin concentration, to be given in a once daily dose regimen.
CNS infections (administered on expert advice)
Intrathecal injection adult: 1 mg/day, increased if necessary to 5 mg daily, seek specialist advice.
Surgical prophylaxis
Slow IV injection adult
1.5 mg/kg, intravenous injection to be administered over at least 3 minutes, administer dose up to 30 minutes before the procedure, dose may be repeated every 8 hours for high-risk procedures; up to 3 further doses may be given.
Surgical prophylaxis in joint replacement surgery
IV infusion adult: 5 mg/kg for 1 dose, administer dose up to 30 minutes before the procedure.
Central retinal artery occlusion:
- What time is there irreversible loss of vision?
- Most common microorganism which causes conjunctivitis (bacterial)
- Irreversible damage after 90 minutes
but even 24 hours after symptoms begin, vision can still be saved or partially restored.
- Common: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae.
Rare/ hyperacute: Neisseria gonorrhoeae/ meningitidis
red sclera
gritty fealing
Aminoglycosides display concentration-dependent bactericidal activity against?
most gram-negative aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacilli
not against gram-negative anaerobes
most gram-positive bacteria
e.g. gram negative anaerobe Prevotella (oral, vaginal, and gut microbiota and) are often recovered from anaerobic infections of the respiratory tract. These infections include aspiration pneumonia, lung abscess, pulmonary empyema, and chronic otitis media and sinusitis.
- Contra indications of gentamicin
a. For all aminoglycosides
b. For GENTAMICIN - MOA
- s/e
For all AMINOGLYCOSIDES (BY INJECTION)
- a. Myasthenia gravis (aminoglycosides may impair neuromuscular transmission)
b. When used by ear: patent grommet, perforated tympanic membrane - prevents bacteria from making protein
- Common: Hearing impairment
Uncommon: Nausea; skin reactions (very common in children); vomiting
Rare: Anaemia; eosinophilia; fever; headache; hypomagnesaemia; paraesthesia; renal impairment
Frequency not known: Bronchospasm; confusion; lethargy; nephrotoxicity
Gentamicin
- pregnancy?
- Renal?
- aminoglycosides: risk of auditory or vestibular nerve damage(highest risk streptomycin) 2nd/3rd tri
- aminoglycosides: Excretion via the kidney and accumulation occurs in renal impairment. Ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity occur commonly in patients with renal failure.
Benzylpenicillin
- Indications & dose
- Mild to moderate susceptible infections,
Throat infections,
Otitis media,
Cellulitis,
IM injection, slow IV injection, or by IV infusion adult: 0.6–1.2 g (can inc) every 6 hrs, single doses over 1.2 g IV only
Endocarditis (+/- antibacterial if necessary)
slow IV injection/ IV infusion adult: 1.2 g every 4 hrs, if necessary to 2.4 g every 4 hrs
Anthrax (Bacillus anthracis)
Slow IV injection/ IV infusion adult: 2.4 g every 4 hrs.
Intrapartum prophylaxis against group B streptococcal infection
slow IV injection/ IV infusion adult: 3 g for 1 dose, then 1.5 g every 4hrs until delivery.
Meningitis, Meningococcal disease
slow IV injection/ IV infusion adult: 2.4 g every 4 hrs

Anthrax: Bacillus anthracis
signs and symtoms?

Skin: small blister with surrounding swelling that often turns into a painless ulcer with a black center.
Lungs: fever, chest pain, & SOB
GI: diarrhea which may contain blood, abdominal pains, & N+V
Injection: fever & an abscess at puncture site

benzylpenicillin
- s/e of penicillin
2. s/e of benzylpenicillin
- pregnancy? breastfeeding?
- Renal impairment
- Common: Diarrhoea; hypersensitivity; nausea; skin reactions; thrombocytopenia; vomiting
Uncommon: Antibiotic associated colitis; leucopenia
Rare: Agranulocytosis; angioedema; haemolytic anaemia; hepatic disorders; nephritis tubulointerstitial; neutropenia; seizure; severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs)
- Common: Fever; Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction
Rare: Neurotoxicity
Frequency not known: Coma
- safe
- Accumulation of sodium from injection can occur in renal failure.
High doses may cause neurotoxicity, including cerebral irritation, convulsions, or coma.
- Flucloxacillin (bactericidal)
- a. Infections due to beta-lactamase-producing staphylococci including otitis externa, Adjunct in pneumonia, Adjunct in impetigo, Adjunct in cellulitis
PO adult: 250–500 mg 4x/day
IM injection: 250–500 mg every 6 rs
slow IV injection, infusion adult: 0.25–2 g every 6 hrs
b. Endocarditis (+ antibacterial)
slow IV injection/ IV infusion adult:
(body-weight up to 85 kg) 8 g/day in 4 divided doses
(body-weight 85 kg and above) 12 g/day in 6 divided doses
c. Osteomyelitis
IV injection/IV infusion adult: Up to 8 g daily in 3–4 divided doses.
Surgical prophylaxis
slow IV injection/ IV infusion
Adult: 1–2 g, to be administered up to 30 mins before the procedure, then (by mouth or by intramuscular injection or by slow intravenous injection or by intravenous infusion) 500 mg every 6 hours if required for up to 4 further doses in high risk procedures.
Metronidazole
- Indications
- Anaerobic infections adult:
PO: 400 mg every 8 hrs, alternatively 500 mg every 8 hrs usually treated for 7 days (for 10–14 days in C.difficile infection)
PR: 1 g 3 times a day for 3 days, then 1 g twice daily, for usual total treatment duration of 7 day
IV: 500 mg every 8 hrs, 7 days (10–14 days in c.difficile infection), to be given over 20 minutes
Helicobacter pylori eradication; in combination with clarithromycin and esomeprazole; or in combination with clarithromycin and lansoprazole; or in combination with amoxicillin and lansoprazole; or in combination with clarithromycin and omeprazole; or in combination with clarithromycin and pantoprazole; or in combination with clarithromycin and rabeprazole
PO: 400 mg 2xday
H.pylori eradication; in combination with amoxicillin & omeprazole
PO: 400 mg 3xday
Fistulating Crohn’s disease
PO: 10–20 mg/kg daily in divided doses, usual dose 400–500 mg 3xday usually given for 1 month but no longer than 3 months because of concerns about peripheral neuropathy.
Leg ulcers & pressure sores
PO adult: 400 mg every 8 hrs for 7 days.
Bacterial vaginosis (notably Gardnerella vaginalis infection)
PO: 400–500 mg twice daily for 5–7 days, alternatively 2 g for 1 dose.
Bacterial vaginosis
PV vaginal gel: 1 applicatorful daily for 5 days, dose to be administered at night.
PID
PO: 400 mg twice daily for 14 days.
Acute ulcerative gingivitis
400 mg every 8 hours for 3 days
Invasive intestinal amoebiasis,
Extra-intestinal amoebiasis (including liver abscess)
Urogenital trichomoniasis
Giardiasis
Established case of tetanus
rosacea
surgical prophylaxis
Metronidazole
- Cautions
- TOP: avoid exposure to strong sunlight or UV light
PV: avoid intravaginal preparations (particularly those that require the use of an applicator) in young girls who are not sexually active, unless there is no alternative (in children); not recommended during menstruation; some systemic absorption may occur with vaginal gel
Metronidazole s/e
Common
IV: dry mouth; myalgia; nausea; oral disorders; taste metallic; vomiting
PV: pelvic discomfort; vulvovaginal candidiasis; vulvovaginal disorders
Uncommon
IV: asthenia(physical weakness/lack of energy); headache; leucopenia (with long term or intensive therapy)
PV: menstrual cycle irregularities; vaginal haemorrhage
Rare
IV: agranulocytosis; angioedema; appetite decreased; ataxia; diarrhoea; dizziness; drowsiness; encephalopathy; epigastric pain; epileptiform seizure (with long term or intensive therapy); hallucination; hepatic disorders; meningitis aseptic; mucositis; neutropenia; optic neuropathy; pancreatitis; pancytopenia; peripheral neuropathy (with long term or intensive therapy); severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs); skin reactions; thrombocytopenia; urine dark; vision disorders
PO: agranulocytosis; ataxia; cerebellar syndrome; confusion; dizziness; drowsiness; encephalopathy; flushing; hallucination; headache; hepatic disorders; myalgia; neutropenia; pancreatitis; pancytopenia; psychotic disorder; seizure; skin reactions; thrombocytopenia; urine dark; vision disorders
PR: agranulocytosis; ataxia; cerebellar syndrome; dizziness; drowsiness; encephalopathy; flushing; hallucination; headache; hepatic disorders; myalgia; neutropenia; pancreatitis; pancytopenia; psychotic disorder; seizure; skin reactions; thrombocytopenia; urine dark; vision disorder
Metoclopramide (hydrochloride)
- Indications?
- Important safety information
cant give for vomiting due to gi obstruction as it is a prokinetic
Symptomatic treatment of nausea and vomiting including that associated with acute migraine,
Delayed (but not acute) chemotherapy-induced nausea & vomiting,
Radiotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting,
Prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting
PO, IM injection, slow IV injection:
Adult (body-weight <60 kg): Up to 500 micrograms/kg/day in 3 divided doses, when administered by slow IV injection, to be given over at least 3 mins
Adult (body-weight =< 60 kg ): 10 mg up to 3x day
Hiccup in palliative care
PO, IM, SC adult: 10 mg every 6–8 hrs
Nausea and vomiting in palliative care
PO: 10 mg 3xday
SC infusion: 30–100 mg/24 hrs
- risk of neurological effects such as extrapyramidal disorders & tardive dyskinesia outweigh the benefits in long-term or high-dose treatment

Metoclopramide
- Contra-indications
- Cautions
- MOA
- 3–4 days after GI surgery, GI haemorrhage, GI obstruction, GI perforation; phaeochromocytoma
- Asthma; atopic allergy; bradycardia; cardiac conduction disturbances; children; elderly; epilepsy; may mask underlying disorders such as cerebral irritation; Parkinson’s disease; uncorrected electrolyte imbalance; young adults (15–19 yrs old)
- ANTIEMETIC: antagonist activity at D2 receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone in the central nervous system
Gastroprokinetic: D2 receptor antagonist activity, and 5-HT4 receptor agonist activity
inc the tone of the LOS
inc peristalsis of the duodenum & jejunum,
increases tone and amplitude of gastric contractions
relaxes the pyloric sphincter and duodenal bulb
Metoclopramide
- s/e
- pregnancy? breastfeeding?
- hepatic or renal impairment
- Common: Asthenia; depression; diarrhoea; drowsiness; hypotension; menstrual cycle irregularities; movement disorders; parkinsonism
Uncommon: Arrhythmias; hallucination; hyperprolactinaemia; level of consciousness decreased
Rare: Confusion; galactorrhoea; seizure
Frequency not known: Atrioventricular block; blood disorders; cardiac arrest; gynaecomastia; hypertension; neuroleptic malignant syndrome; QT interval prolongation; shock; syncope
- safe, avoid
- avoid or use low dose

Cyclizine
- indications
- contra indications
- general s/e
- specific s/e
- Nausea,
Vomiting,
Vertigo,
Motion sickness,
Labyrinthine disorders
PO adult: 50 mg up to 3 x day, for motion sickness, take 1–2 hrs before departure.
IV injection, IM injection adult: 50 mg 3 x day
Nausea & vomiting associated with palliative care (adult)
SC: 150 mg, dose to be given over 24 hours.
PO: 50 mg up to 3 times a day
- Neonate (due to significant antimuscarinic activity) (in neonates)
- Rare: Angle closure glaucoma; depression
4.
Dalteparin
- indications
Unstable CAD (including NSTEMI)
SC injection adult: 120 units/kg every 12 hrs (max. per dose 10 000 units twice daily) for up to 8 days.
Patients with unstable CAD (including NSTEMI) awaiting angiography or revascularisation and having already had 8 days treatment with dalteparin
SC: Adult (body-weight =>70 kg & male)
7500 units every 12 hours until the day of the procedure (max. 45 days)
Adult (body-weight 80 kg and above and female)
7500 units every 12 hours until the day of the procedure (max. 45 days).
Prophylaxis of DVT in surgical patients—moderate risk
SC adult: Initially 2500 units for 1 dose, dose to be given 1–2 hours before surgery, then 2500 units every 24 hours.
Prophylaxis of DVT in surgical patients—high risk
SC adult: Initially 2500 units for 1 dose, dose to be administered 1–2 hours before surgery, followed by 2500 units after 8–12 hours, then 5000 units every 24 hours, alternatively initially 5000 units for 1 dose, dose to be given on the evening before surgery, followed by 5000 units after 24 hours, then 5000 units every 24 hours.
Prophylaxis of DVT in medical patients
SC adult: 5000 units every 24 hrs.
Treatment of deep-vein thrombosis,
Treatment of pulmonary embolism
SC adult:
(body-weight 69–82 kg)
15 000 units once daily until adequate oral anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonist established (at least 5 days of combined treatment is usually required).
(body-weight 83 kg and above)
18 000 units
Extended treatment of DVT and prevention of recurrence in patients with solid tumours
Treatment of venous thromboembolism in pregnancy -> not licensed
Dalteparin sodium
- Contra-indications, For all HEPARINS
- breastfeeding and preganncy
- cleared by?
- Acute bacterial endocarditis; after major trauma; epidural anaesthesia with treatment doses; haemophilia and other haemorrhagic disorders; peptic ulcer; recent cerebral haemorrhage; recent surgery to eye; recent surgery to nervous system; severe hypertension; spinal anaesthesia with treatment doses; thrombocytopenia (including history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia)
- not know to be harmful but best to avoid
- kidneys - unfractionated heparin may be preferable.

Normal and diabetic blood sugar ranges before and after eating
Ketone ranges
• Healthy individuals
◦ Between 4.0 - 5.4 mmol/L when fasting
◦ Up to 7.8 mmol/L 2 hours after eating
• People with diabetes
◦ Before meals: 4 - 7 mmol/L (T1DM/T2DM)
◦ After meals: <9 mmol/L (T1DM) / <8.5 mmol/L (T2DM)
• Blood ketones
◦ <0.6 = normal
◦ 0.6 -1.5 = extra insulin
◦ >1.5 = DKA
Metformin
- First line for?
- Benefits?
- How to take?
- Types and administration
- Mechanism
- S/e
- Monitoring?
- T2DM
- ◦ Effective, safe, inexpensive and may reduce the risk of CVS events and death
◦ Has beneficial effects on HbA1C, weight and CVS mortality
- ◦ With food usually breakfast and evening meal
- • Only biguanide on the market
◦ Metform IR (immediate release) - taken up to TDS
◦ Metformin SR (slow release) - taken OD
- ◦ Prevents the production of glucose in the liver
◦ Improves body’s sensitivity towards insulin- benefits for weight management and not hypoglycaemia
◦ Reduces amount of sugar absorbed into the intestine
- ◦ GI upset - main reason it may not be tolerated
◦ Lactic acidosis
◦ Distortion of sense of taste
◦ Reports of altered LFTs
◦ Hepatitis
◦ Skin reactions
◦ Reduced vitamin B12 absorption - Need to monitor renal function before and at least annually during treatment
Sulphonylureas
- Examples
- Mechanism
- How is it taken?
- S/e
- Warning -
- gliclazide, glipizide, glimepiride, tolbutamide
- ◦ Stimulates insulin release from ß cells of the pancreas by closing ATP-sensitive K+ channels and opening of voltage dependent Ca2+ channels:
‣ Require functioning ß cells to work
‣ Need to be taken with meals to prevent hypo
‣ Risk of accumulation and hypo in renal impairment (ELDERLY)
- Just before food with breakfast and evening meal
-
◦ Hypoglycaemia
◦ GI upset
◦ Skin reactions
◦ Reports of decreased hepatic function
◦ Abnormalities
◦ Hepatic failure
◦ Hepatitis
◦ Jaundice
◦ Blood abnormalities
Obesity as a result of increased plasma insulin concentration
- Metabolised by liver with urinary excretion of metabolites, so should be used cautiously in the presence of renal or hepatic dysfunction
- *Thiazolidinediones - pioglitazone**
1. Mechanism
- Adverse effects
- Warning -
- May benefit
- Takes 6 wks to work
◦ Improves metabolic control in patients through improvement of insulin sensitivity
◦ Reduces insulin resistance in adipose tissues/fat, muscle and liver
- ◦ Water retention
◦ Weight gain
◦ Eyesight problems
◦ Reduced sense of touch
◦ Chest pain and infections
◦ Allergic skin reactions - including HF, macular oedema, bone fractures and bladder cancer
- CVS parameters, such as lipids, BP, inflammatory biomarkers, endothelial function and fibrinolytic status but oedema can occur therefore not recommended for patients who have any degree of heart disease
DPP4 -
- Examples
- Mechanism
- Adverse effects
- Warning
- sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin, alogliptin
- Blocks the action of enzyme DPP4 which destroys hormone incretin (a natural hormone that tells the body to release insulin when needed such as after eating and reduces the amount of glucose being produced by the liver when it is not needed)
More incretin
‣ Which inhibits glucagon release
‣ Which increases insulin secretion
‣ Decreases gastric emptying
3.
◦ Potential risk of acute pancreatitis
◦ GI problems - nausea, diarrhoea and abdo pain
◦ Flu-like symptoms, signs of URTI, joint pain
◦ Skin reactions/hives
◦ Signs of UTIs/blood in urine
- ◦ Renal dose adjustment required but can be used in renal impairment (eGFR < 30) - no dose adjustment for linagliptin but adjustment is required for the others
SGLT2 (sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors)
- E.g.
- Mechanism
- Recommended for?
- Adverse effects
- Warnings
- dapagliflozin, canagliflozin, empagliflozin
- Blocks SGLT2 which reduces the reabsorption of glucose by kidneys and increases glucose excretion in the urine
- T2DM not for T1DM
◦ Low risk of hypoglycaemia
◦ Reduction in CVS disease and HF risk
◦ Not recommended for people with kidney disease (not in eGFR < 60)
- ◦ Amputations - stop in diabetic foot
◦ Kidney injury (eGFR >45-60)
◦ Genital and UTI (W>M) can lead to blood infections
◦ Lactic acidosis
◦ Bone fractures
◦ Bladder cancer risk - ◦ SGLT2 in rare cases lead to DKA, this may occur whether the glucose levels are high or healthy (euglycaemic DKA as SGLT2 normalises glucose level in DKA)
◦ Caution with loop diuretics
GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide 1)
- E.g.
- for?
- MOA
- Advantages
- Adverse effects
- Warnings
1.
- Exenatide (byetta & bydureon)
- liraglutide (victoza)
- lixisenatide
- dulaglutide (IV)
- GLP-1 receptor agonists, are normally prescribed for pt who have not been able to control their condition with tablet medication (last resort?)
3.
- Stimulates release of insulin by pancreas,
- inhibits release of gulcagon,
- stomach emptying slows (more satisfied after eating)
- ◦ Relatively low risk of hypo
◦ Strong efficacy/HbA1c reduction
◦ Weight loss
◦ Other possible benefits (ß cell preservation, CVS benefit) being investigated
- ◦ Diarrhoea
◦ N + V
◦ Headaches
◦ Dizziness
◦ Increased sweating
◦ Indigestion
◦ Constipation
◦ Loss of appetite - ◦ Delivered by injection
◦ Nausea/GI s/e (~ decreasing over time)
◦ More expensive than sulphonylureas/metformin
◦ Possibility of slight association with pancreatitis
Insulin
- Rapid acting analogue - e.g.
- Medium acting insulins - e.g.
- Long acting insulins -
- Analogue mixtures - contains rapid acting and slow acting insulin (taken with food)
- Mixed insulins - fast acting and slow acting insulin (taken 20-30 mins before food)
- Within 5 mins of a meal
◦ Novorapid/Aspart
◦ Humalog/Lispro
◦ Apidra/Glulisine
◦ Fiasp/Aspart -
30 mins before food or bed
◦ Insulatard
◦ Humulin I
◦ Insuman Basal - Unusual to have no fast acting insulins with a BG insulin
◦ Lantus/Abasaglar
◦ Levemir//Detemir
◦ Toujeo 300 units/ml
◦ Degludec/Tresiba - ‣ Humalog mix 25
‣ Humalog mix 50
‣ Novomix 30 - 30% FA and 70% LA - Peaks at 1-8 hrs - may stay in system for up to 24 hours (shake thoroughly)
‣ Humulin M3 - given on feeds
‣ Insuman comb 15/25/50
Arrythmia medications

Lipid lowering drugs
Examples, MOA, s/e & dose
Statins
E.g. atorvastatin (Lipitor), fluvastatin (Lescol), lovastatin (Mevacor, Altocor), pravastatin (Pravachol), simvastatin (Zocor),
Mechanism = inhibits cholesterol synthesis in hepatocytes by acting on HMG-CoA reductase which also leads to increased clearance of LDLs
S/e = inc transaminase levels, myopathy, GI complaints, arthralgies, headaches
Atorvastatin - 10mg (can be increased to 80mg) if QRISK >20%
20mg given in ACS primary prevention,
80mg in secondary prevention
◦ Uses = IHD, angina, ACS, TIA, stroke
◦ Simvastatin (take at night), rosuvastatin
Nicotonic acid
• Mechanism = inhibits lipoprotein synthesis and raises HDLs, reduces coronary events
• Side effects = flushing, itching, headache, N+V, hepatotoxicity, GI or peptic ulcer, hyperglycaemia, decreased insulin sensitivity
Ezetimibe
• Mechanism = cholesterol lipase inhibitor which selectively inhibits intestinal cholesterol absorption
• Side effects = headache, abdominal pain, diarrhoea
• Dose = 10mg
PCSK9 inhibitors
• Mechanism = reduces LDL receptors - more cholesterol removed
• Side effects = nasal complaints, oropharyngeal pain, pulmonary reactions, skin reactions
• E.g. alirocumab, evolocumab
What is diltiazem?
Indication?
s/e?
Calcium channel blocker -> relaxing the blood vessels
HTN, angina
Dizziness; flushing; headache; nausea; palpitations; peripheral oedema; rash; tachycardia; vomiting
Some DOAC medications include:

- Apixaban (Eliquis®)
- Dabigatran (Pradaxa®)
- Rivaroxaban (Xarelto®)
- Edoxaban (SavaysaTM)

What is the MOA for DOACs?


What is Enoxaparin? MOA?
LMWH
Enoxaparin binds to and potentiates antithrombin (a circulating anticoagulant) to form a complex that irreversibly inactivates clotting factor Xa. It has less activity against factor IIa (thrombin) compared to unfractionated heparin (UFH) due to its low molecular weight.


