Dr. Mhawi 5 Connective Tissue Flashcards
Explain this image
8.5.7
- Primitive CT (undifferentiated)
- Found in the embryo
- Mesodermal origin
- Gives rise to almost all tissue in adult
- Contains elongate MESENCHYME* cells
nLoosely organized and loosely attached
nLarge nuclei
nProminent nucleoli
nThin cytoplasmic processes
•Abundant, viscous extracellular substance with few collagen and reticular fibers
Explain this image

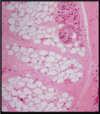
At the upper left corner is a low magnification of a cross section of the umbilical cord in which major blood vessels are visible. The mucoid tissue consists of fibroblasts and mesenchyme cells embedded within a gelatin-like extracellular matrix rich in collagen fibers. Note the simple cuboidal layer of the amniotic cells that cover the umbilical cord.
Explain this image

Mucoid connective tissue. Collagen fibers, appeared light blue, are visible among the fibroblasts. Simple cuboidal amniotic cells are visible at the upper left corner. Trichrome stain.
Explain this image

Mucous tissue. A section of an umbilical cord showing fibroblasts surrounded by a large amount of loose extracellular matrix composed of ground substance and collagen fibers. H&E stain.
Explain this image

Loose (areolar) connective tissue. Whole mount preparation. This tissue is taken from a mesenteric spread. You are looking down on a mesentery that was stretched on the slide, fixed, then stained. The slide shows a random sampling of the cells and fibers that make up loose connective tissue. The thicker fibers which have a reddish color, are collagen fibers. The very thin fibers, which tend to appear dark
Explain this image

Loose (areolar) connective tissue. Whole mount preparation. Collagen fibers appear brown. Elastic fibers dark blue. The stars are placed beside mast cells (appear red).
- Plays important role in:
- immunity
- inflammation
- diffusion of nutrients,
oxygen, CO2, and waste
Diagram of loose connective tissue

_________
Consists mostly of bundles of Type I collagen fibers and fibroblasts
•Collagen fibers and fibroblasts aligned in parallel
nProvide resistance to prolonged or repeated stresses
•poorly vascularized
nRepair of injury is slow
Regular dense connecitve tissue
•Found in:
nTendons
nLigaments
nAponeuroses (flat tendons)
Explain this image

Longitudinal section of regular dense connective tissue from a tendon. A: Thick bundles of parallel collagen fibers fill the intercellular spaces between fibroblasts. Low magnification. B: Higher magnification view of a tendon of a young animal. Note active fibroblasts with prominent Golgi regions (G), nucleus (N) and dark cytoplasm rich in RNA. PT stain.
Explain this image

Longitudinal section of tendon. BV, blood vessel; TC, tendon cell nuclei. dashed line, arbitrary cross-sectional cut of tendon (see next slide).
Explain this image

Dense regular connective tissue of tendon (cross section). BV, blood vessel; Ent, endotendineum; TC, tendon cell nuclei.
Explain this image

Electron micrograph of a fibrocyte (cross-sectioned) in regular dense connective tissue. The sparse cytoplasm of the fibrocytes is divided into numerous thin cytoplasmic processes that interdigitate among the collagen fibers. x25,000.
Explain this image

Section of dense irregular connective tissue. This figure shows fibroblasts (arrow) with many thin cytoplasmic extensions (arrowheads). As these cells are pressed by collagen fibers, the appearance of their cytoplasm depends on the section orientation; when the section is parallel to the cell surface, parts of the cytoplasm are visible. PT stain. Medium magnification.
Explain this image

Irregular dense connective tissue. Note the irregular arrangement of the collagen fibers (green). N, nucleus of fibroblast responsible for synthesizing the fibers; BV, blood vessel.
Explain this image

None lactating mammary gland showing loose connective tissue (arrows around and between the glandular tissue) and irregular dense connective tissue (upper and lower right parts of the micrograph). Masson trichrome. X 200. Human breast glandular epithelium.
What are the 3 fibers that surrounds and support the connective tissue and the 2 ground substances
8.5.7
•Fibers: collagen fibers
elastic fibers
reticular fibers
•Ground substance: proteoglycans
multiadhesive glycoproteins
- fibronectin
- laminin
Explain this image
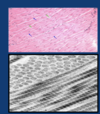
Upper panel: light micrograph of bundles of collagen fibers (blue arrows). Note the wavy appearance. Fibroblasts, responsible for their synthesis, are indicated by the green arrows. Lower panel: At the TEM level collagen fibers are composed of fibrils. The latter are cut in cross (upper left) and longitudinal (lower right) sections. When cut longitudinally each fibril appears to consist of regular alternating dark and light bands. Ground substance completely surrounds the fibrils. x100,000.
Synthesis of collagen molecules is _______
vitamin C-dependent
8.5.7
Explain. this image

TEM of a fibroblast which is responsible for the synthesis of collagen molecules in the rER and for the assembly of these molecules EXTRACELLULARLY into collagen fibers.
______ collagen is most common
•occurs in:
nloose & dense connective tissue
nbone
______ collagen is present in
- hyaline & elastic cartilage
- Vitreous body of the eye
Type I
Type II
______– (reticular fibers) reticular connective tissue
•Synthesized by fibroblasts
______ – meshwork sheets – basal/external laminae
•Synthesized by epithelial cells, muscle cells, Schwann cells
______ – fibers – dense irregular connective tissue, placenta, blood vessel walls
•Synthesized by fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells
______ – anchoring fibrils – epidermal-dermal interface
•Synthesized by fibroblasts
Type III
Type IV
Type V
Type VII
______ forms the Stroma of certain organs (support

Reticular fibers
Reticular fibres in the spleen. The spleen is covered by dense connective tissue capsule (left) from which a trabecula is extended into the parenchyma of the organ.
Explain this image

Reticular fibres form a delicate supporting framework (network) for many highly cellular organs such as liver (this picture).
In loose CT, reticular fibers they are formed by _____, in hematopoietic and lymphatic tissues they are formed by______
fibroblast
reticular cells