DNA Recombination Flashcards
1
Q
What is DNA recombination?
A
DNA recombination is the exchange of genetic material either between multiple chromosomes or between different regions of the same chromosome.
2
Q
What are the types of DNA recombination?
A
- Homologous - recombination between two strands of DNA with similar or identical sequences
- Non-homologous - insertion of transposons
- Site-specific - site-specific recombinases (eg Cre) perform rearrangement at a short, specific DNA sequence
3
Q
What are the functions of DNA recombination?
A
- Meiotic recombination (independent reassortment)
- DNA repair (Homologous recombination repair)
- Gene regulation (Ig recombination)
4
Q
Describe Robin Holliday’s model of DNA recombination.
A
- Single-stranded nick on each homologous strand
- Holliday junction forms a heteroduplex region
- Depending on how the structure is resolved, the end product will gain either a splice or patch

5
Q
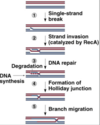
Describe the Messelson-Radding model of DNA recombination.
A
- A single nick frees a single strand to invade the homologous sequence of a non-sister chromatid
- A D-loop is formed from the displacement of the invaded strand
- A portion of the recipient sequence, corresponding to the D-loop, is degraded
- A Holliday junction is formed with a heteroduplex
- Branch migration causes an asymmetric heteroduplex
6
Q
Describe the Szostak model of DNA recombination.
A
- A double-stranded break and nuclease degradation leads to overhangs
- One of the broken strands invades a homologous strand
- DNA repair synthesis forms a D-loop
- Ligation causes the formation of two Holliday junctions with heteroduplex
- Resolution leads to either patch or splice
7
Q
Describe the key difference between the Szostak Double-Strand Break Repair model and Synthesis-Dependent Strand Annealing (SDSA)
A
Rather than forming a double Holliday junction, the 3’ end of the invading strand becomes the template for new DNA synthesis.



