Disorders of the lumbar spine Flashcards
ageing physiology of the spine
Nucleus pulposus dehydrates with age
- Loss of disc height- DISC BULGE
- Increased load stresses reactive marginal osteophytosis at the endplates SYNDESMOPHYTES
- Increased load stress on facet joint FACET JOINT ARTHRITIS
Mechanical Back Pain
back pain when the spine is loaded (sitting, standing and not lying)
relieving and aggravating factors of mechanical back pain
that worsens with activity and is relieved with rest.
how common is mechanical back pain
- 50% of the UK population report lumbar back pain at least 24 hours in a year
- 80% will experience LBP lasting >24 hours in lifetime
- It is not abnormal to have episodes of mechanical LBP
risk factors of mechanical back pain
poor posture, sedentary lifestyle, poor lifting technique and being overweight.
Natural history of mechanical back pain
intermittent. Often triggered by innocuous activity e.g. tying shoes- predisposition in overweight, unhealthy lifestyle, deconditioned core muscles
management of mechanical back pain
Management involves lifestyle modifications and pain management, commonly with NSAIDS.
Spondylosis
Spondylosis is the name for chronic degenerative osteoarthritis (spinal osteoarthritis) affecting intervertebral discs of the lumbar (or cervical) spine.
risk factors of spondylosis
having a genetic tendency
having obesity or being overweight
having a sedentary lifestyle with a lack of exercise
having injured the spine or undergone spinal surgery
smoking
having a job that requires repetitive or weight-bearing movements that involve the spine
having a mental health condition, such as anxiety or depression
having psoriatic arthritis
causes of spondylosis
It is usually caused by disc degeneration and marginal osteophytosis (bony spurs developing adjacent to the end plates of the disc).
As a person ages, the discs become drier, thinner, and harder, and they lose some of their cushioning ability. This is why an older person is more likely to have a compression fracture of the vertebra than a younger person.
A vertebral compression fracture results from bone collapsing in the spine. It commonly occurs with osteoporosis.
The facet joints between the vertebrae also function less well with age because of wear and tear on their cartilage surfaces.
As the cartilage erodes, the bones start to rub together, causing friction. This can result in the formation of bony growths, called bone spurs.
The loss of rubbery tissues and the development of spurs make the spine stiffer. Back movement also becomes less smooth, and friction increases.
marginal osteophytosis
bony spurs developing adjacent to the end plates of the disc
symptoms of spondylosis
- It can present with radiculopathy causing dermatome/myotome symptoms.
- Stiffness and mild pain that gets worse following certain movements or long periods without moving, while sitting for a long time, for example.
- More severe symptoms include:
- a grinding or popping feeling when moving the spine
- weakness in the hands or legs
- poor coordination
- muscle spasms and pain
- headaches
- loss of balance and difficulty walking
- loss of bladder or bowel control
spotting spondylolysis
- Trace the outline of scottie dog in oblique view of the spine
- Displaced fractures through the pars interarticularis (i.e. spondylolysis), look like a collar on a dog (look at blue outline)

X-ray of spondylosis

Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is the anterior displacement of the above vertebra on the below vertebra (commonly the 5th lumbar vertebra on the sacrum).
causes of spondylolisthesis
Causes are divided into five categories: congenital/dysplastic, isthmic, degenerative, traumatic and pathological.
congenital cause of spondylolisthesis
congenital instability of the facet joints
Isthmic causes of spondylolisthesis
A defect in the pars interarticularis
degenerative causes of spondylolisthesis
results from facet joint arthritis and joint remodelling (age >50
years)
traumatic causes of spondylolisthesis
Acute fractures in the neural arch, other than the pars
interarticularis
pathological causes of spondylolisthesis
Infection or malignancy
iatrogenic causes of spondylolisthesis
Caused by surgical intervention e.g. if too much lamina and facet joint is excised during a laminectomy operation
difference ebtween spondylolysis and spondylolisthetis
Spondylolysis- A complete fracture in this location without displacement
Spondylolisthesis- Once anterior displacement (usually forward) of the upper vertebra occurs, this is Spondylolisthesis may, or may not, be associated with gross instability of the vertebral column.
signs and symptoms of spondylolisthesis
It can be asymptomatic, but may present with lower back pain, sciatica and/or neurogenic claudication (pain/paraesthesia in the legs when standing or walking that is relieved by rest).
diagnosis of spondylolisthesis
Diagnosis can involve performing a straight leg raise test which is often painful if spondylolisthesis is present but is confirmed with a standing X-ray which will show the displacement.
x-ray of spondylolisthesis

treatment of spondylolisthesis
Treatment depends on severity, but often starts with rest, painkillers and physiotherapy. If very severe, surgery can be recommended to fuse the slipped vertebra to the adjacent vertebra using metal screws and rods.
Spotting spondylolisthesis
Trace line of the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments and thereby detecting the ‘step’ at the site of displacement

Prolapsed intervertebral disc (slipped disc)
A prolapsed (herniated) disc occurs when the outer fibres of the intervertebral disc are injured, and the soft material known as the nucleus pulposus, ruptures out of its enclosed space.
The prolapsed disc or ruptured disc material can enter the spinal canal, squashing the spinal cord, but more frequently the spinal nerves.

four stages of disc herniation
- Disc degeneration– intervertebral discs dehydrate and bulge, decreasing disc height and altering load stresses on the joint.
- Disc prolapse– protrusion of the nucleus pulposus (still within the annulus fibrosis).
- Disc extrusion– nucleus pulposus exits the annulus fibrosis.
- Disc sequestration– nucleus pulposus enters the spinal canal.

who is affected by prolapsed discs
0ccurs in 30 to 50 years olds
which discs are most commonly herniated in the lumbar spine
- Most commonly occurs at L4/L5 or L5/S1
Most common type of herniation
the most common type of herniation is a para-central prolapse, meaning that the disc prolapse is off-centre (96% of cases), but can be a central prolapse (2% of cases) or a lateral prolapse (2% of cases).

signs and symptoms
Disc herniation commonly presents with unilateral back pain and paraesthesia that radiates into dermatomes supplies by the nerve roots affected.
CT of prolapsed disc
A CT or MRI scan provides the most conclusive evidence for diagnosis of a disc herniation, but X-rays may also be used.

treatment of prolapsed disc
Cauda equina
Cauda equina syndrome is an absolute emergency and involves the compression of the cauda equina (a bundle of spinal nerves at the base of the spine), often due to a prolapse of a disc or a tumour that is impinging on the spinal canal .
what does the cauda equina look like

presentation of cauda equina
- It presents with bilateral sciatica
- perianal numbness (saddle numbmness)
- painless retention of urine
- faecal incontinence and
- or erectile dysfunction.
what does cauda equina look like on a MRI
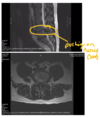
managment of cauda equina syndrome
Diagnosis is confirmed by a CT or MRI scan. Urgent surgical decompression (within 48 hours of sphincter symptoms) is recommended to prevent long term neurological damage.
lumbar canal stenosis
Abnormal narrowing of the spinal cord that compresses either the spinal cord or nerve roots (cauda equina) narrowing
risk factors of lumbar canal stenosis
- Occurs in the elderly
- Gradual
- Body compensates – not cauda equina
- Due to:
- Disc bulging
- Facet joint osteoarthritis
- Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy
- Other causes:
- Compression fractures of vertebrae bodies
- Spondylolisthesis
- Trauma
symptoms of lumbar canal stenosis
Symptom depend on the region of the cord or nerve roots that are affected.
- Discomfort whilst standing
- Discomfort or pain in shoulder, arm or hand (cervical stenosis) or lower limb (lumbar)
- Bilateral symptoms in approx. 70%
- Numbness at or below the level of stenosis
- Weakness at or below the stenosis
- Neurogenic claudication
prognosis of lumbar stenosis (most common type of spinal stenosis)
- 70% of symptoms stay unchanged
- 15% get worse
- 15% improve with time
sciatica
Sciatica is pain/paraesthesia caused by compression of the sciatic nerve or by one or more of the contributing spinal nerves (L4-S3).
symptoms of sciatica
It presents with pain in the lower back and buttocks that radiates to one or more of the following dermatomes:
- L4: Anterior thigh and knee, and medial leg
- L5: Lateral thigh and leg, and dorsum of the foot
- S1: Posterior thigh and leg, and sole of the foot

in sciatica pain is experienced in a
continuous line from the lumbar spine to the affected dermatome, as follows:
- L4 Sciatica: Lumbar spine Anterior thigh anterior knee medial leg
- L5 Sciatica: Lumbar spineLateral thigh lateral legdorsum of foot
- S1 Sciatica: Lumbar spine Posterior thigh posterior leg heel lateral border and sole of foot
in sciatic parasthesia is only experienced
in the affected dermatome (see dermatome map)
prognosis and management of sciatica
Sciatica usually self resolves within 4-6 weeks, but if severe the GP may suggest exercises and stretches, prescribe additional painkillers and refer to physiotherapy.
Neurogenic claudication
A symptom rather than diagnosis
- Pain/ pins and needles in legs on prolonged standing and on walking- radiating in a sciatica distribution
why does neurogenic claudication occur
- Compression of the spinal nerves as they emerge from the lumbosacral spinal cord
- Stenosis
- Disc bulging
- Facet joint osteoarthritis
- Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy
- Stenosis
- Leads to venous engorgement of the nerve roots during exercise, leading to reduced arterial inflow and transient arterial ischaemia.
- Ischaemia results in pain/ paraesthesia
what relieves neurogenic claudication
- A change in position and by flexion of the spine e.g. cycling, pushing a trolley and climbing stairs
- Stops vein engorgement
- Increased blood supply

Spinal Infection
Infections of the spine include:
- vertebral osteomyelitis (infection of the bone)
- discitis (infection of the disc)
- epidural abscesses.
causes of spinal infections
They are most commonly caused by haematogenous spread (via the blood) of an infection from another location but can also be due to direct inoculation during an invasive spinal procedure (e.g. a lumbar puncture) or via spread from adjacent soft tissues.
presentation of spinal infection
They can present with neurological damage as well as systemic symptoms such as pyrexia.
Treatment of spinal infection
includes IV antibiotics and in severe cases surgical intervention may be required.
lumbar puncture
The withdrawal of fluid from the subarachnoid space of the lumbar cistern- important diagnostic test for a variety of CNS disorders inc:
- Meningitis
- MS
outline how a lumbar puncture is performed
Layers the lumbar puncture needs passes
- After passing 4–6 cm in adults (more in obese persons), the needle “pops”through the:
- ligamentum flavum
- then punctures the dura and arachnoid,
- and enters the lumbar cistern.
Lucy did a long cough


