Digestive system Flashcards
(23 cards)
- The primitive gut tue is formed from the incorporation of the dorsal part of the yolk sac into the embryo due to the craniocaudal folding and lateral folding of the embryo.
- The gut tube extends from the oropharyngeal membrane to the cloacal membrane and is divided into the foregut, midgut, and hind gut
Below is what the gut tube of an 18 day old embryo looks like

18 day old embryo

The epithelial lining and mucosal cells in the GI tract are derived from_____

endoderm

The components of the GI tract that are neither epithelium nor mucosa are derived from___

Visceral (splanchnic) mesoderm

18 month embryo showing derivatives of the foregut

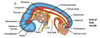
Name the derivatives of the foregut
- Stomach
- Trachea and respiratory tract
- Upper duodenum
- Dorsal and ventral pancreas
- Gall bladder and bile ducts
- Esophagus
- Lungs
- Liver

Name the derivatives of the midgut
- Jejunum
- Appendix
- Ascending Colon
- Proximal 2/3 of transverse colon
- Ileum
- Cecum
- Lower duodenum

Name the derivatives of the hindgut
- Urogenital sinus
- Distal 1/3 of transverse colon
- Descending colon
- Upper anal canal
- Rectum
- Sigmoid colon

What artery supplies foregut derivatives and the intraabdominal portion of the esophagus?
A. Celiac a.
B. Superior mesenteric a.
C. Infereior mesenteric a.
A. Celiac a.

What arteries supply the intrathoracic portion of the esophagus?
A. Celiac a.
B. Superior mesenteric a.
C. Infereior mesenteric a.
D. Branches of the aorta
D. branches of the aorta

What artery supplies midgut derivatives?
A. Celiac a.
B. Sup. mesenteric a.
C. Inf. mesnteric a.
B. sup. mesenteric a.

What artery supplies hindgut derivatives?
A. Celiac a.
B. Sup. mesenteric a.
C. Inf. mesenteric a.
C. Inf. mesenteric a.

It is a derivative of the foregut.
The foregut is divided into the esophagus dorsally and the trachea ventrally by the tracheoesophageal folds, which fuse to form the tracheoesophageal septum.
The esophagus is initially short but lengthens with descent of the heart and lungs. During development, the endodermal lining of the esophagus proliferates rapidly and obliterates the lumen; later recanalization occurs.
Development of the esophagus
The stratified squamous epithelium, mucosal glands, and submucosal glands of the definitive esophagus are derived from____
endoderm

The lamina propria, muscularis mucosae, submucosa, skeletal muscle, and smooth muscle of muscularis externa, and adventitia of the definitive esophagus are derived from___
Visceral (Splanchnic) mesoderm

It’s a derivative fo the foregut. A fusiform dilation forms in the foregut in week 4 that gives rise to the primitive stomach. The dorsal part of the stomach grows faster than the ventral part, thereby resulting in the greater and lesser curvatures, respectively. Dorsal part becomes greater curvature. Ventral part becomes lesser curvature. The primitive stomach rotates 90 degrees clockwise around its longitudinal axis. The 90 degree rotation affects all foregut structures and is responsible for the adult anatomical relaationship of foregut viscera. As a result of this clockwise rotation, the dorsal mesentery is carried to the left and eventually forms the greater omentum. The left vagus n. innervates the ventral surface of the stomach (lesser curvature). The right vagus n. innervates the dorsal surface of the stomach (greater curvature).

Development of the stomach

The surface mucous cells lining the stomach, mucous neck cells, parietal cells, chief cells, and enteroendocrine cells comprising the gastric glands of the definitive stomach are derived from ______.

Endoderm

The lamina propria, muscularis mucosae, submucosa, the outer longitudinal, middle circular, and inner oblique layers of smooth muscle of the muscularis externa, and the serosa of the definitive stomach are derived from______.

Visceral mesoderm

It’s a derivative of the foregut. The endodermal lining of the foregut forms an outgrowth (hepatic diverticulum) into the surrounding mesoderm of the seaptum transversum through induction by fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) FGF-1, FGF-2, and FGF-8 released by cardiac mesoderm. The mesoderm of the septum transversum is involved in the formation of the diaphragm, which explains the intimate gross anatomical relationship betwen the liver and the diaphragm. Cords of hepatoblasts (hepatic cords) from the hepatic diverticulum grow into the mesoderm of the septum transversum, where critical hepatoblast/mesoderm interactions occur. The hepatic cords arrange themselves around the vitelline veins and umbilical veins which course through the septum transversum and form the hepatic sinusoids. Due to the tremendous growth of the liver, the liver bulges into the abdominal cavity, thereby stretching the septum transversum to form the ventral mesentery, consisting of the falciform ligament and the lesseromentum. The falciform ligament contains the l. umbilical vein, which regresses after birth to form the ligamentum teres. The lesser omentum can be divided into the hepatogastric ligament and hepatoduodenal ligament. The hepatoduodenal ligament contains the portal triad: Bile duct, portal vein, and hepatic artery.

Development of the liver

Hepatocytes and the simple columnar or cuboidal epithelium lining the biliary tree of the definitive liver are derived from___.

endoderm

Kupffer cells, hematopoietic cells, endothelium of the sinusoids, and fibroblasts (connective tissue) of the definitive liver are derived from___.

Mesoderm

It’s a derivative of the foregut. The connection betw. the hepatic diverticulum and the foregut narrows to form the bile duct. An outgrowth from the bile duct gives rise to the gall bladder rudiment and cystic duct. The cystic duct divides the bile duct into the common hepatic duct and the common bile duct. During development, the endodermal lining of the gall bladder and extrahepatic bile ducts proliferates rapidly and obliterates the lumen; later recanalization occurs.

Development of the gall bladder and extrahepatic ducts

Simple columnar epithelium lining the definitive gallbladder and simple columnar or cuboidal epithelium lining the definitive extrahepatic bile ducts are derived from___

Endoderm

The lamina propria, muscularis externa, and adventitia of the definitive gall bladder are derived from___.

Visceral mesoderm



