Digestion of Carbohydrates, Proteins and Lipids Flashcards
What drives the entire absorption process of carbs and proteins? What is the one exception to this?
- Na+/K+ ATPase
- Fructose is only one not dependent on ATPase, and has it’s own channel
Describe glucose absorption.
- Glucose absorption is not directly dependent on energy
- Glucose absorption is secondary to active transport
How does insulin affect glucose transport in the stomach and kidney?
It does not
What does insulin primarily affect?
Adipose tissue
resting muscles
Where is protein digested?
The lumen
Does glucose require digestion for absorption?
Nope
What digests sucrose prior to absorption?
Brush border enzymes
These are directly absorbed by cell then broken down inside cell, what are they?
Oligopeptides
These are broken down before absorption cell then resynthesize original molecule. What are they?
TAGs
All chemical digestion and nutrient absorption occurs in the small intestine, what developments allow for greater surface area?
- Circular folds of mucosa
- Villi
- Microvilli
Juice secreted by small intestine does not contain any digestive enzymes. The synthesized enzymes act within the brush-border membrane of epithelial cells. What are the three enzymes we covered?
- Enterokinase
- Disaccharidases
- Aminopeptidases
Peptidase
breaks down peptides into amino acids
Sucrase, maltase, lactase
break down disaccharides into monosaccharides
Lipase
breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol
Enterokinase
converts trypsinogen to trypsin
Somatostatin
hormone that inhibits acid secretion by stomach
Cholescystokinin
hormone that inhibits gastric glands, stimulates pancreas to release enzymes in pancreatic juice, stimulates gallbladder to release bile
Secretin
stimulates pancreas to release bicarbonate ions in pancreatic juice
What does the small intestine absorb?
- 80 % ingested water
- Electrolytes
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Carbonates
- active/facilitated transport
- monosaccharides
•Proteins
- di-/tripeptides
- amino acids
•Lipids
- monoglycerides
- fatty acids
- micelles
- chylomicrons
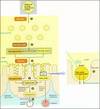
Fill in the boxes with the appropriate enzymes


What are the two steps of carbohydrate digestion?
- Intraluminal hydrolysis of starch to oligosaccharides by amylases
- membrane digestion of oligo to mono by brush border disaccharidases
What are the four brush border oligosaccharidases?
- Lactase
- Glucoamylase
- Sucrase
- Isomaltase
What are the two steps of carbohydrate absorption?
- Uptake across apical membrane into epithelial cell
- coordinated exit across basolateral membrane
Where does protein digestion begin?
In the stomach, when pepsin digests proteins to form polypeptides