Diagnostic Techniques Flashcards
Diagnostic Tequniques
(5)
- Skin scrapings
- Wood lamp
- Cultures
- Patch test
- Skin biopsies
*Note: these techniques are not unique to dermatology, family practice can do many of these as well *
Skin Scrapings
(3 uses, 4 stains)
Uses:
- KOH - fungus
- Tzanck smears - virus (herpes)
- Scabies - protozoa
Tools:
- Microscope
- # 15 blade
- Glass slide and cover slip
- Stains
- KOH stain = Potassium Hydroxide (add after collecting skin)
- Tzanck smear = Giemsa, Wrights, or Sedi stains
- Scabies smear = Mineral Oil, KOH, Saline
- apply oil to skin prior to scraping to keep scabies in tact
KOH Skin Scraping
- Most sensitive office test, if done properly
- Identifies
- Tinea
- Candida
Scraping, Top of Vesicle
(procedure, purpose)
Procedure:
- lance vesicle
- insert #15 blad into vesicle
- scrape bottom surface of the top of the vesicle (celing of carrier dome)
Purpose: KOH prep scraping for tinea
Scraping, leading edge of annular lesion
(procedure, purpose)
Procedure: scrape along outside of lesions, towards area of highest proliferation
Purpose: KOH stain for tinea
Scraping, Nails
(procedure, purpose)
Procedure: get deep scraping of nail underside
- clip nail
- sample “cheesy” substance underneath the clipping
- if nail is not cuttable, scrape as far as you can s hurting pt or removing nail
Purpose: KOH stain for tinea
Tzanck Smear
(funtion, positive finding)
Function: Standard microscopic test for rapid Dx of Herpes infection
- cannot distinguish b/w herpes types (HSV 1, 2, or VSV)
- PCR is usually used instead of this
Positive Test:
- multinucleated giant cells = atypical keratinocytes c large nuclei

Tzanck Smear Procedure
- Sample appropriate area
- Scrape base of vesicle/bulla (“floor of the carrier dome”)
- this will hurt the pt a little bit
- “like spreading peanut butter on break”
- Sample only fresh lesion
- Scrape base of vesicle/bulla (“floor of the carrier dome”)
- Use # 15 blade to correct area and transfer to slide
- Stain
- Giemsa
- Wrights
- Sedi stain
- Cover c slip
- Look for multinucleated giant cell
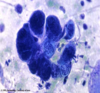
Scabies Smear
(diagnostic method)
Identify Sarcoptes scabiei hominis via microscopic examination
- female mite
- eggs
- fecal matter

Scabes Smear, Procedure
(5 steps)
- Apply mineral oil to sample area
- Sample area in question c # 15 blade
- scrape burrows, vesicles, or papules
- this is where females live (no males)
- have pt point to itchiest area c index finger
- finger webs
- flexural wrists
- genitalia
- use vigorous force, it is okay to cause point bleeding
- scrape burrows, vesicles, or papules
- Coverslip
- +/- stain if mineral oil not used
- KOH
- saline wet mount
- Look for
- female mite
- eggs
- fecal material
Note: look for fragments as well as whole organisms. scraping may cause trauma to the organism
Woods Lamp Exam
(def, purpose)
Def: fluorescing affected area c invisible “black light” (long wave UV radiation)
Purpose: Identify the following pathogens
- Tinea capitis (non-T. tonsurans) = yellow - green
- Tinea versicolor - dull yellow
-
Erythrasma - coral red
- board question
- Pseudomonas - green
- Vitiligo - accentuates epidermal pigment
- good for level 2 skin
Pearls, Bacterial Cultures
(2)
- Best yield when infection is superficial
- Vigorously swab the area of most inflammation
3.
Culture Turnaround Times
- Bacterial ~ 1 week
- Viral ~ 1 week
- Fungal ~ 3 weeks for DTM, 4 week for Sabouraud’s
Viral Culture Pearls
(2)
- Keep refridgerated
- Best to sample base of fresh vesicle or bulla
Fungal Cultures
(list and describe 2 types)
- DTM
- identify presence of a deratophyte (nonspecific)
- test turns red
- Sabouraud’s Dextrose Agar
- identify type of dermophyte (specific)
*These are not always done, empiric tx is popular c fungal infection *