Dermatology Flashcards
Skin Epithelial Cells Skin Disorders Pigment Disorders Vascular Lesions Skin Infections Blistering Disorders Hypersensitivity Disorders Skin Cancer Neurocutaneous Disorders
What is the largest organ?
Skin
What is the function of skin?
Barrier against infection
prevent water loss
What are the layers of the skin?
Epidermis - keratinocytes (squamous epithelial cells)
Dermis - connective tissue, vessels
Subcutaneous fat - aka hypodermis or subcutis
What are the layers of the epidermis?
“Come Lets Get Sun Burnt”

what is contained in the stratum basale?
basal cells = stem cells that can regenerate the skin
stratum basale is the layer of the epidermis that sit on top of the dermis
what is contained in the stratum spinosum?
desmosomes (connect keratinocytes) form spines
what is contained in the stratum granulosum?
keratohyalin granules - form keratin filaments
what is the stratum lucidum?
clear layer of dead skin cells
what is in the stratum corneum?
anucleated cells filled with keratin filaments
*nucleated cells are abnormal
what is contained in the dermis?
connective tissues and blood vessels
this is why things that cause leaky vessels affect the dermis not the epidermis
what is hyperkeratosis?
Thickening of stratum corneum
excess quantity of keratin
(ex: psoriasis, callus)
What dermatopathology is seen here?

hyperkeratosis
What dermatopathology is seen here?

parakeratosis
can see nucleated cells in the stratum corneum
What is parakeratosis?
hyperkeratosis + retained nuclei in stratum corneum
indicates hyperproliferation
seen in skin diseases (psoriasis) and malignancies
What is Hypergranulosis?
increased thickness of stratum granulosum
hypergranulosis is a classic finding in what disorder?
lichen planus
What is spongiosis?
Fluis accumulation (edema) of epidermis
seen in eczema, and other skin condtions
What dermatopathology is seen here?
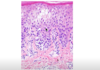
spongiosis
what holds keratinocytes together?
desmosomes
retained nuclei iin the stratum corneum indicates what?
hyperproliferation - cells are moving up from the basal layer to the stratum corneum before they have lost their nuclei
seen in psorisasis and some malignancies
what is acantholysis?
loss of connection between keratinocytes - often loss of desmosomes
what is the dermatopathology?

acantholysis
what are the clinical histopathologicial feathures of acantholysis?
rounded keratinocytes
detached, floating freely epidermis
**key feature of pemphigus vulgaris
acantholysis is classicly seen in what disorder?
pemphigus vulgaris
What is the dermatopathology?

Acanthosis - diffuse epidermal hyperplasia
elongated Rete Ridges
spinous layer thickening

what are rete ridges?
where the epidermis pokes down into the dermis
they are elongated in acanthosis from spinous layer thickening
what forms elongates rete ridges seen in acanthosis?
spinous layer thickening
Acanthosis Nigricans
hyperpigmented (dark) plaques on skin
intertriginous sites (folds)
classically neck and axillae

what disease is acanthosis nigricans associated with?
insulin resistance - seen in obesity and diabetes
what malignancy is acanthosis nigricans associated with?
gastric adenocarcinoma


