Derm in Review Kodas / Path Flashcards
1
Q

A
Acne
2
Q

A
Rosacea
3
Q

A
Rhinophyma
4
Q

A
HS
5
Q

A
psoriasis
6
Q

A
Reactive arthritis
7
Q

A
Erythema annulare centrifugum
8
Q

A
lichen planus
9
Q

A
lichen planus
10
Q

A
atrophic lichen planus
11
Q

A
lichen planus
12
Q

A
pityriasis rubra pilaris
13
Q

A
pityriasis rubra pilaris
14
Q
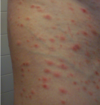
A
PLEVA
15
Q

A
PLC
16
Q

A
atopic derm
17
Q

A
atopic derm
18
Q

A
seborrheic dermatitis
19
Q

A
vitiligo
20
Q

A
vitiligo (wood’s lamp)
21
Q

A
lupus - malar rash
22
Q

A
DLE
23
Q

A
dermatomyositis - heliotrope
24
Q

A
dermatomyositis - Gottron papules
25

dermatomyositis - poikiloderma
26

morphea
27

linear morphea
28

Parry-Romberg
progressive hemifacial atrophy, dyspigmentation
29

sclerodactyly
scleroderma, MCTD
30

Raynaud's
CREST, scleroderma
31

vulvar lichen sclerosus
32

livedo reticularis
33

LCV
34

HSP
35

cryoglobulinemia
36

calciphylaxis
37

purpura of primary systemic amyloidosis
38

macular amyloid
39

lichen amyloid
40

pyoderma gangrenosum
41

pyoderma gangrenosum
42

relapsing polychondritis
a/w: tracheal, nasal collapse; aortic insufficiency, dissecting aortic aneurysm
43

Behcet's
44

acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis
45

erythema nodosum
46

granuloma annulare
47

granuloma annulare
48

generalized granuloma annulare
49

lupus pernio
50

necrobiosis lipoidica
51

tuberous xanthomas
52

xanthelasma
53

CTCL
54

urticaria pigmentosa
55

elastosis perforans serpiginosa
56

urticaria
57

dermatographism
58

angioedema
59

angioedema
60

erythema marginatum
61

erythema migrans
62

actinomycetoma
63

actinomycosis
64

anthrax
65

lyme (erythema migrans)
66

cellulitis
67

erysipelas
68

folliculitis
69

impetigo
70
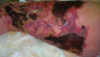
necrotizing fasciitis
71

paronychia
72

pitted keratolysis
Kytococcus sedentarius, Dermatophilus congolensis, Corynebacterium, Actinomyces
73

rhinoscleroma
Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis
74

scarlet fever
75

staph scalded skin
76

trichomycosis axillaris
## Footnote
*Corynebacterium (C tenuis, C propinguum, C flavescens) or Serratia marcescens*
77

tularemia
78

leprosy
79

HSV
80

VZV
81

exanthem subitum / roseola
HHV-6
82

Kaposi's
HHV-8
83

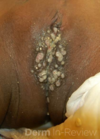
hand-foot-mouth
## Footnote
*coxsackievirus*
84

herpangina
## Footnote
*enteroviruses (coxsackie, adeno, echo)*
85

measles / rubeola
## Footnote
*paramyxovirus*
86

molluscum
87

Erythema infectiosum / Fifth's disease
## Footnote
*Parvovirus B19*
88

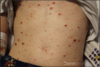
rubella
89

syphilis
90

chancroid
## Footnote
*haemophilus ducreyi*
91

yaws
## Footnote
*Treponema pallidum pertenue*
92

leishmaniasis
93

larva migrans
## Footnote
*hookworms: ancylostoma*
94

onchocerciasis
## Footnote
*Onchocerca volvulus*
95

onchocerciasis
Onchocerca volvulus
96

rocky mountain spotted fever
97

tinea versicolor
98

tinea versicolor
99

white piedra
## Footnote
*trichosporon*
100

tinea nigra
## Footnote
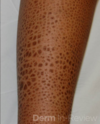
*Exophiala phaeoannellomyces*
101

tinea capitis
102
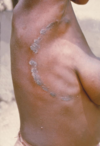
tinea corporis
103

tinea imbricata
## Footnote
*Trichophyton concentricum*
104

tinea pedis
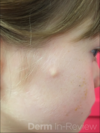
105

Erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica
## Footnote
*Candida*
106

onychomycosis
107

median rhomboid glossitis
## Footnote
*Candida*
108

madura foot
bacteria (*actinomycotic mycetoma or actinomycetomas*) and fungi (*eumycetomas or mycotic mycetoma*)
109

histoplasmosis
110
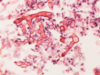
mucormycosis
111

cryptococcosis
112

paracoccidiomycosis
113

negative DIF
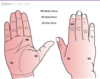
114

ichthyosis bullosa of siemens / ichthyosis exfoliativa
keratin 2
115

progeria
116

pemphigus vulgaris
DSG 1 / 3
117

paraneoplastic pemphigus
118

bullous pemphigoid
may be drug-induced
119

dermatitis herpetiformis
120

epidermolysis bullosa
121

mitten deformity
dystrophic EB
122

Hailey-Hailey
123

Darier's
124

acanthosis nigricans
125

notalgia paresthetica
126

polymorphic eruption of pregnancy
127

pustular psoriasis (of pregnancy)
128

Sweet syndrome
129

dermatomyositis
130

multicentric reticulohistiocytosis
131

cryoglobulinemia
132

necrobiosis lipoidica
133

alopecia areata
134

trichotillomania
135

CCLE
136

Beau's lines
mechanical trauma, proximal fold disease, chemo, systemic illness
137

leukonychia
138

Mee's lines
arsenic, thallium, heavy metal poisoning
139

onycholysis
140

Terry's nails
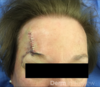
liver failure
141

yellow nail syndrome
+ lymphedema, pulmonary disease (bronchiectasis, pleural effusions)
142

lichen planus
143

stinging nettle leaf (urticaceae)
* most common cause of nonimmunologic (toxic) urticaria*
* trichomes contain* *histamine, serotonin, Ach*
144

stinging nettle trichomes (urticaceae)
* most common cause of nonimmunologic (toxic) urticaria*
* trichomes contain histamine, serotonin, Ach*
145

phytophotodermatitis
## Footnote
* Direct toxic immunogenic reaction*
* UVA + photosensitizers + oxygen → reactive O2 species → epi/dermal damage → hyperpigmentation in linear streaks*
146

prickly pear (opuntia spp.)
## Footnote
* most common cause of mechanical irritant contact*
* may --\> bacterial inoculation*
147

century plant / agave americana / aloe
## Footnote
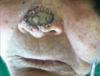
* family Asparagaceae*
* calcium oxalate*
148

century plant
## Footnote
* family Asparagaceae*
* calcium oxalate*
149

daffodil
* family amarillydacea / lilacea, narcissus spp.*
* calcium oxalate*
150

dumb cane (diffenbachia)
## Footnote
* family araceae*
* calcium oxalate*
151

hyacinth
## Footnote
* family amarillydacea / lilacea*
* calcium oxalate*
152

rhubarb
## Footnote
* family Polygonaceae*
* calcium oxalate*
153

buttercups
## Footnote
* family Ranunculaceae*
* protoanemonin, ranunculin*
154

cashew
## Footnote
* anacardiacea*
* urushiol / cashew nut shell oil*
155

poison ivy rash
## Footnote
* family Anacardaciae, toxicodendron spp.*
* allergen: urushiol*
* sensitizer: pentadecylcatechol*
156

poison ivy contact dermatitis
## Footnote
* family Anacardaciae, toxicodendron spp.*
* allergen: urushiol*
* sensitizer: pentadecylcatechol*
157

poison ivy plant
## Footnote
* family anacardaciae, toxicodendron spp.*
* allergen: urushiol*
* sensitizer: pentadecylcatechol*
158

poison oak
## Footnote
* family Anacardaciae, toxicodendron spp.*
* allergen: urushiol*
* sensitizer: pentadecylcatechol*
159

poison oak
## Footnote
* family anacardaciae, toxicodendron spp.*
* allergen: urushiol*
* sensitizer: pentadecylcatechol*
160

poison sumac
## Footnote
* family anacardaciae, toxicodendron spp.*
* allergen: urushiol*
* sensitizer: pentadecylcatechol*
161

chrysanthemum
* family asteraceae*
* sensitizer: sesquiterpene lactone*
* cross-react: permethrin* */ pyrethrins*
162

daisy
## Footnote
* family asteraceae*
* sensitizer: sesquiterpene lactone*
* cross-react: permethrin / pyrethrins*
163

ragweed
## Footnote
* family asteraceae*
* sensitizer: sesquiterpene lactone*
* cross-react: permethrin / pyrethrins*
164

peruvian lily
## Footnote
* family Alstromeriaceae*
* sensitizer: tuloposide / tulipalin A*
* Most common cause of finger dermatitis in florists/ gardeners handling tulip bulbs*
165

primrose
## Footnote
* family Primulaceae*
* sensitizer: primin, turpentine*
* Cross-reacts w/Balsam of Peru*
166

puss moth caterpillar wound
## Footnote
* Dermatitis w/characteristic “tram-track” hemorrhage*
* Spines contain high concentration of oak tannins*
167

gypsy moth caterpillar
168

io moth caterpillar
169

saddleback caterpillar
170

puss moth caterpillar
## Footnote
* Dermatitis w/characteristic “tram-track” hemorrhage*
* Spines contain high concentration of oak tannins*
171

giant silkworm moth (caterpillar)
## Footnote
*Local & severe systemic reaction (renal failure, bleeding diathesis)*
172

pine processionary caterpillar
## Footnote
* Urticaria (immunologic), angioedema, anaphylaxis*
* Lytic bone lesions of the digits*
173

black widow
## Footnote
* α-Latrotoxin → depolarizes neurons*
* Acute pain & edema at bite site (no necrosis)*
* Latrodectism: Chills, vomiting, cramps, spasms, priapism*
* Rx: Antivenin, benzodiazepines, IV calcium gluconate*
174

brown recluse
## Footnote
* Sphingomyelinase D*
* Erythema and edema → vesicle → necrosis and eschar*
* Severe: hemolytic anemia, DIC*
* Rx: Rest, ice, elevation; avoid surgery*
175

hobo spider
## Footnote
* Atracotoxins*
* Painless bite → induration, erythema, numbness → necrotic eschar*
* Severe: Headache, visual disturbances, MI*
* Rx: Supportive*
176

wolf spider
## Footnote
* Histamine*
* Very painful bites → lymphangitis or eschar*
* Rx: Supportive*
177

jumping spider
## Footnote
* Hyaluronidase*
* Painful bite*
* Rx: Supportive*
178

sac spider
## Footnote
* Lipase*
* Painful bite*
* Rx: Supportive*
179

tarantula
## Footnote
* Hairs can penetrate skin --\> wheal and flare*
* Ophthalmia nodosa can lead to blindness*
* Rx: Supportive*
180

brown recluse bite
sphingomyelinase D
181

lone star tick
* Human monocytic ehrlichiosis
* Southern tick-associated rash illness (STARI)
* RMSF
* Tularemia
182

Dermacentor tick
* D. variabilis (dog tick): Major vector for RMSF
* D. andersoni (wood tick): Major vector for Colorado tick fever and RMSF
* Both can cause tick paralysis from release of neurotoxin if attached \>4 days
183

dermacentor / wood tick
* D. variabilis (dog tick): Major vector for RMSF
* D. andersoni (wood tick): Major vector for Colorado tick fever and RMSF
* Both can cause tick paralysis from release of neurotoxin if attached \>4 days
184

deer tick
* Lyme disease
* Babesiosis
* Human granulocytotropic anaplasmosis
185

brown dog tick
* RMSF
* Boutonneuse fever
186

Soft tick
* Borrelial relapsing fever
187

scabies burrow
188

scabies
189

crusted scabies
190

scabies mite
191

chigger bites
192

pediculus humanus
193

phthirus pubis
194

pediculus humanus
195

body lice nits
196

tunga penetrans infestation
## Footnote
*Endemic in Central and South America, Africa, India, Pakistan*
197

tunga penetrans
## Footnote
*Endemic in Central and South America, Africa, India, Pakistan*
198

wound myasis - Infestation of skin by fly larvae
## Footnote
*Caused by screw worm (Cochliomyia hominivorax). Eggs are deposited directly on wound, especially on scalp, and may burrow into brain tissue*
199

fire ant bites
## Footnote
*Inject venom (solenopsin D) --\> histamine release*
200

blister beetle --\> cantharidin
201

bedbug bites
## Footnote
*Possible vector for hepatitis B and Chagas disease*
202

bed bugs
## Footnote
*Possible vector for hepatitis B and Chagas disease*
203

triatomine reduviid bug
## Footnote
* Vector for American trypanosomiasis, Chagas disease*
* Romaña’s sign: Unilateral eyelid swelling*
204

xenopsylla cheopis (fleas)
## Footnote
*Vector for cat scratch disease, endemic (murine) typhus, tungiasis, melioidosis, plague*
205

sandfly
* Sandfly transmits leishmaniasis
* Blackfly transmits onchocerciasis and tularemia
* Deer fly, mango fly, horse fly transmit loiasis and tularemia
* Tsetse fly transmits African trypanosomiasis
206

black fly
* Sandfly transmits leishmaniasis
* Blackfly transmits onchocerciasis and tularemia
* Deer fly, mango fly, horse fly transmit loiasis and tularemia
* Tsetse fly transmits African trypanosomiasis
207

centipede
## Footnote
*Painful bite wounds
Venom contains metalloproteases*
208

millipede
## Footnote
*Do not bite but cause chemical contact dermatitis due to cyanide and quinones*
209

rattlesnake
* Immediate pain / edema at bite site → necrosis, hemorrhage
* Systemic sxs: Hypotension, respiratory distress, neuromuscular blockade depending on species
210

coral snake
* Immediate pain / edema at bite site → necrosis, hemorrhage
* Systemic sxs: Hypotension, respiratory distress, neuromuscular blockade depending on species
211

leeches
* Interfere w/platelet aggregation → purpura and bleeding
* Medical leeches associated with Aeromonas hydrophila wound infection
212

podophyllum peltatum
## Footnote
*podophyllotoxin*
213

sea anemone (cnidaria)
* Have cnidocytes that contain nematocysts = stinging capsule
* Seabather’s eruption: Dermatitis under bathing suit caused by larvae of any cnidarian spp.
214

jellyfish (cnidaria)
* Have cnidocytes that contain nematocysts = stinging capsule
* Seabather’s eruption: Dermatitis under bathing suit caused by larvae of any cnidarian spp.
215

sea urchin (echinodermata)
## Footnote
*spicules cause ICD and foreign body reaction from calcite crystals*
216

blue ringed octopus (mollusca)
## Footnote
*Tetrodotoxin: Deadly neurotoxin in some cone snails, blue-ringed octopus, and pufferfish*
217

sea bather's eruption
stings from nematocysts of larval forms of sea anemones / thimble jellyfishes
218

neonatal lupus
219

neonatal cephalic pustulosis
220

congenital facial milia
Basan syndrome
221

erythema toxicum neonatorum
222

seb derm
223

jacquet's erosive diaper dermatitis
irritant
224
perianal pseudoverrucous papules and nodules (PPPN)
chronic irritation
225

bullous impetigo
226

psoriasis
227

spinal dysraphism
228

aplasia cutis
229

branchial cleft cyst
230

supernumerary nipples
231

staph scalded skin
232

atopic dermatitis
233

atopic dermatitis
234

atopic dermatitis
235

atopic dermatitis
236

nummular atopic dermatitis
237

atopic dermatitis
238

molluscum
239

lichen spinulosus
240

pityriasis rubra pilaris
241

pityriasis lichenoides chronica
242
PLEVA
243

congenital melanocytic nevus
244

congenital melanocytic nevus
245

spitz nevus
HRAS or BAP-1 mutations
pink-red papulonodule vs ink-spot
S-100+, melan-A+, p16+
246

becker's nevus
smooth mm hamartoma + increased basal melanocytes
247

halo nevus
lymphs mingle with melanocytes
248

epidermal nevus
hamartoma epi / pap dermis
249

nevus sebaceous
250

nevus comedonicus
## Footnote
*FGFR2 hamartoma*
251

Buschke-Ollendorf
## Footnote
* LEMD3 mutation (AD) --\> incr TGF-B signaling*
* dermatofibromatosis lenticularis disseminata (collagen-type nevus) + osteopoikilosis*
252

Buschke-Ollendorf
## Footnote
* LEMD3 mutation (AD) --\> incr TGF-B signaling*
* dermatofibromatosis lenticularis disseminata (collagen-type nevus) + osteopoikilosis*
253

spitz nevi
254

collagenoma
MEN-1
255

fibrous hamartoma of infancy
256

mastocytoma
257

urticaria pigmentosa
258

langerhans cell histiocytosis
259

JXG
260

blue nevus
261

ulcerated infantile hemangioma
262

LUMBAR syndrome
## Footnote
* L - Lower segmental hemangioma*
* U - Urogenital anomalies/ulcerations*
* M - Myelopathy*
* B - Bony deformities*
* A - Anorectal defects*
* R - Renal anomalies*
263

PHACE
## Footnote
* P - Posterior fossa malformations*
* H - Hemangioma, segmental (V1-V3)*
* A - Arterial anomalies (carotid, cerebral)*
* C - Cardiac anomalies (coarctation)*
* E - Eye anomalies (cataracts, exophthalmos)*
264

congenital hemangioma
265

port win stain
266

microcystic lymphatic malformation / lymphangioma circumscriptum
## Footnote
*post-excision recurrence common*
267

venous malformations
## Footnote
*associations: maffucci syndrome, blue rubber bleb nevus, multiple cutaneous & mucosal venous syndrome*
268

CM-AVM
269

CM-AVM
270

varicella
271

varicella
272

hand foot mouth
273

hand foot mouth
274

median nail dystrophy
275
X-linked recessive syndromes

276
X-linked dominant syndromes

277

mitten deformity
dystrophic EB
278

collodion baby
279
lamellar ichthyosis
## Footnote
* Type 1: transglutaminase 1 defect*
* Type 2: ABCA12 (copper-binding protein) defect*
280

sparse eyebrows in Netherton Synd
## Footnote
* SPINK5 defect --\> LEKTI serine protease inhibitor*
* Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa + Trichorrhexis invaginata (most common eyebrows) + Atopy*
281

Erythrokeratoderma variabilis
## Footnote
*GJB3 mutation --\> gap junction proteins (connexins)*
282

Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa in Netherton Synd
## Footnote
* SPINK5 defect --\> LEKTI serine protease inhibitor*
* Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa + Trichorrhexis invaginata (most common eyebrows) + Atopy*
283

facial angiofibromas in tuberous sclerosis
284

penile lentigines in PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome
285

axillary freckling and CALM in NF-1
## Footnote
*neurofibromin mutation*
286

plexiform neurofibromas and CALM in NF-1
287

dermal melanocytosis
288

hyperextensible skin / "fishmouth" scars in Ehlers-Danlos
289

Ectrodactyly in Goltz syndrome (focal dermal hypoplasia)
## Footnote
*XLD, defect in PORCN*
290
pilomatricoma
## Footnote
* multiple assoc w/: myotonic dystrophy, Rubinstein-Taybi, Turner Synd, Gardner Synd, Trisomy 9*
* path: "shadow cells" or "ghost cells"*
291

congenital triangular alopecia
## Footnote
*nonscarring, often bilateral*
292

pachyonychia congenita
## Footnote
* Type 1: Jadassohn-Lewandowski, KRT 6A & 16*
* Type 2: Jackson-Lawler, KRT 6B & 17*
* +PPK, hypERhidrosis, plantar pain*
293

congenital malalignment of toenail
## Footnote
*lateral deviation of great toenails, usually b/l*
294
sensory innervation of face

295
facial nerve branches and danger zones

296
temporal nerve danger zone: where to undermine?
Undermine in the **superficial fat** above the superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) to avoid injury

297
Trigeminal trophic syndrome
anesthesia, paresthesia, and erosion of the nasal ala (may clinically mimic BCC)
## Footnote
*damage to CN V at the gasserian ganglion (surgery, injury, encephalitis, leprosy)*
298
Frey’s syndrome (auriculotemporal syndrome)
Pain, vasodilation, and hyperhidrosis of cheeks when eating (gustatory sweating)
## Footnote
* occurs following parotid gland surgery*
* thought to involve haphazard nerve regeneration whereby parasympathetic fibers (rather than sympathetic) reinnervate sweat glands and blood vessels of skin*
299
Cranial Nerve V - name, branches, and function
trigeminal nerve
## Footnote
* 3 branches: primarily sensory, but also motor supply to muscles of mastication*
* ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3)*
300
Cranial Nerve VII - name and function
Facial nerve
* motor innervation to muscles of facial expression
* sensory innervation to conchal bowl and anterior tongue
* taste through chorda tympani branch
* tactile sensation through lingual nerve branch
301
branches of facial nerve

302
Muscles supplied by temporal branch of facial nerve

303
Muscles supplied by posterior auricular branch of facial nerve

304
Muscles supplied by zygomatic branch of facial nerve

305
Muscles supplied by buccal branch of facial nerve

306
Muscles supplied by marginal mandibular branch of facial nerve

307
Muscles supplied by cervical branch of facial nerve

308
sensory innervation of ear

309
arterial supply to face

310
The six major arteries supplying the face
1. Facial
* angular aa anastomoses w/dorsal nasal --\> connection btwn ICA + ECA
2. Superficial temporal: from ECA
* branches: transverse facial, frontal
3. Maxillary: from ECA
* branches: infraorbital, buccal, inferior alveolar (mental)
4. Posterior auricular: from ECA
5. Occipital: from ECA
6. Ophthalmic: from ICA
* branches: supraorbital, supratrochlear, palpebral, lacrimal, dorsal nasal --\> anastomoses w/ECA
311
sensory innervation of leg and foot

312
nerve blocks for foot

313
motor innervation of hand
314
external anatomy of penis

315
internal anatomy of penis

316
external anatomy of vulva

317
topographic nail unit anatomy

318
subcutaneous nail unit anatomy

319

O'Brien scissors
## Footnote
*suture removal*
320

straight suture scissors
321

Gradle scissors
## Footnote
*Delicate sharp tips, i.e., skin tag removal*
322

Westcott scissors
## Footnote
*Delicate, spring-loaded tissue scissors with sharp tips, ideal for small delicate sites (eyelid)*
323

Iris scissors
## Footnote
*tissue cutting*
324

Baby Metzenbaum
## Footnote
*sharp or blunt undermining*
325

Metzenbaum
## Footnote
*fine tissues and blunt dissection*
326

bandage scissors
327

Halsey needle holder
## Footnote
* smooth or serrated jaws*
* ideal for small needles and fine suture material (facial reconstruction)*
328

Mayo needle holder
## Footnote
* Larger, more durable*
* for larger needles and suture material (trunk reconstruction)*
329

Castroviejo needle holder
## Footnote
*commonly used in eye surgery and microsurgery*
330

round knurled scalpel handle
## Footnote
*allows control by twisting rather than rocking motion*
331

Beaver blade handle
## Footnote
*Can be rolled with fingertips, providing greater precision and control*
332

#3 blade handle
## Footnote
*Most frequently used in dermatologic surgery*
333

#7 blade handle
## Footnote
*Textured → better control and comfort, cutting angle may be changed by rolling handle with fingers*
334

#10 blade
## Footnote
*Wide & curved, for larger excisions*
335

#15 blade
## Footnote
*Curved, used for most dermatologic surgery*
336

#15c blade
## Footnote
*Curved with finer tip, more delicate areas*
337

#11 blade
## Footnote
*Tapered sharp tip, for I&D*
338

Jeweler's forceps
## Footnote
*Sharp tip, used for suture removal*
339

Adson forceps w/o teeth
## Footnote
*Standard large forceps used for excisional surgery on trunk and proximal extremities*
340

Adson forceps w/teeth
## Footnote
*Standard large forceps used for excisional surgery on trunk and proximal extremities*
341

Bishop-Harmon forceps
## Footnote
*very lightweight, fine-tipped, ideal for delicate work on face and hand*
342

Freer septum elevator (nail elevator)
## Footnote
*thin curved blades that facilitate atraumatic nail avulsion*
343

English nail splitter
## Footnote
*Cutting blade opposed to a flat anvil-like surface, used for partial longitudinal nail avulsion*
344

single-pronged skin hooks
## Footnote
*used for elevating tissue atraumatically*
345

double-pronged skin hook
## Footnote
*used for elevating tissue atraumatically*
346

Fox dermal curette
## Footnote
*Labeled by size, used for tumor removal and debulking*
347

chalazion clamp
## Footnote
*used for immobilizing structures during procedures*
348

mosquito hemostat
## Footnote
*clamping vessels*
349
relaxed skin tension lines of face

350
relaxed skin tension lines of anterior body

351
relaxed skin tension lines of posterior body

352

post-Mohs defect
353

Inferiorly-based rotation flap with dimpling
at site of periosteal tacking stitch to the maxilla (red star)
## Footnote
*used to support weight of flap and counteract downward forces. Over time, dimpling becomes imperceptible as suture is resorbed.*
354
polyglactin 910: brand name
vicryl
355
polyglycolic acid: brand name
dexon
356
polydioxanone: brand name
PDS
357
glycolic acid: brand name
Maxon
358
poliglecaprone 25: brand name
monocryl
359
Absolute indications for prophylactic abx for surgery
* Artificial heart valve (mechanical, bioprosthetic, and homograft valves)
* artificial joint within 2 years
* history of endocarditis
* history of rheumatic fever (RF)
* mitral valve prolapse (MVP) with holosystolic murmur
360
Local anesthetics

361
Recommended maximum dose of lidocaine in adults
* 4.5 mg/kg without epinephrine
* 7.0 mg/kg with epinephrine
* 55 mg/kg tumescent
362
Recommended maximum dose of lidocaine in children
* 1.5 to 2 mg/kg without epi
* 3 to 4.5 mg/kg with epi
363
Phases of wound healing
1. Vascular phase
2. Inflammatory phase
3. Proliferative phase
4. Maturation / Wound contracture and remodeling
364
chemical mediators of inflammation that play a role in wound healing

365
Tip stitch
AKA half-buried horizontal mattress suture
## Footnote
*designed to align tissue at corner of a flap and prevent vascular compromise (i.e., bringing together more than two skin edges)*
366

tip stitch
367

post-mohs defect of chin
368

O-T or A-T advancement flap
369

island pedicle / V-Y advancement flap
370

post-Mohs defect of R alar sulcus
371

Island pedicle/V-Y advancement flap
372

post-mohs defect
373
O-L advancement flap
374

H-plasty
375

post-mohs defect
376

H-plasty
377

post-staged excision defect of L nasal ala/sidewall
378

crescentic advancement flap
379

post-mohs defect
380

bilateral rotation flap (O-Z) elevated at level of galea
381

bilateral rotation flaps held in position w/skin hooks
382

bilateral rotation flaps, closed
383

Mustarde - laterally based rotation flap
384

post-mohs defect of nasal tip
385

dorsal nasal rotation flap
386

Z-plasty
387

post-mohs defect, L preauricular
388

rhombic transposition flap
389

post-mohs defect, R nasal ala
390

bilobed transposition flap
391

post-mohs defect, L nasal ala
392

Nasolabial transposition flap (w/underlying cartilage graft from antihelix to support alar rim)
393

paramedian forehead flap
394

post-mohs defect, L nasal ala
395

Staged melolabial interpolation flap w/pedicle in place (cartilage graft/strut from antihelix supporting alar rim)
in 3 weeks this pedicle is divided and the donor cheek area is linearly closed
396

Full thickness defect of L helix & antihelix
397

mastoid/retroauricular interpolation flap
398

Mastoid/retroauricular interpolation flap s/p pedicle division and healing via secondary intent
399

post-mohs defect of nasal tip and supratip
400
Full-thickness skin graft for nasal tip harvested from R preauricular cheek
401

flap necrosis in smoker
402

surgical wound infection w/dehiscence
403

trapdoor deformity
404

keloid
405

cutaneous horn
406

actinic cheilitis
## Footnote
*hypopigmented, scaly plaque with fissures involving lower lip of a male patient*
407
Common peels

408
Electrosurgery types

409
sunscreen blocking spectrum

410
ocular risk with laser types

411
light wavelength and ocular damage

412
laser wavelength and structures damaged

413

AK, lower magnification
## Footnote
*Focal parakeratosis alternating w/orthokeratosis. Neoplasm confined to epidermis. Prominent solar elastosis in subadjacent papillary dermis. Tumor spares hair follicles.*
414

AK, higher magnification
## Footnote
*Marked parakeratosis and absence of granular layer. Pleomorphism of atypical keratinocytes within basal layer of epidermis.*
415

SCCIS (pink scaly plaque)
416

SCCIS
## Footnote
*Neoplasm confined to epidermis. Atypical keratinocytes proliferating in all layers of epidermis. Some dyskeratotic cells with pyknotic nuclei in upper layers of epidermis. White line: multinucleated tumor cell.*
417

high-risk SCC on lower lip
418

Large, fungating, poorly-differentiated SCC on occipital scalp w/invasion of muscle and bone
419

SCC w/cutaneous horn
420

Invasive, well-differentiated SCC with keratin pearl formation
## Footnote
*Generally: proliferation of cells as slender, long strands or as bulky masses. Individual cells have glassy eosinophilic cytoplasm with large nuclei. Also w/mitotic figures and horn pearls*
421

KA
422

KA
423

nodular BCC
424

superficial BCC
425

nodular BCC
426

multiple pigmented BCCs
427

morpheaform BCC
428

BCC with squamous differentiation
## Footnote
*Metatypical variant = basosquamous carcinoma: Merging of basaloid tumor areas with squamoid areas with keratinization*
429
AJCC-8 staging for cutaneous SCC

430
BWH staging for cutaneous SCC

431

nodular melanoma with regression
432

acral lentiginous melanoma
433

Pagetoid melanoma.
## Footnote
*Neoplastic proliferation of melanocytes forming irregular nests in the basal layer. Single atypical melanocytes are spreading within all the layers of the epidermis. Cells have large atypical nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and a surrounding halo resembling cells of Paget disease.*
434

merkel cell carcinoma
435

Small cell MCC
## Footnote
*Basophilic aggregates of small-round cells. The tumor cells have prominent round, vesicular nuclei and scant, ill-defined cytoplasm. Occasional mitoses are present. The neoplastic cell islands connect to each other via anastomosing cords.*
436

dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
437
AJCC melanoma staging

438
melanoma margins

439

large multinodular DFSP
440

DFSP
## Footnote
*monomorphic spindle cells arranged in “storiform” or “cartwheel” pattern. Some cells may show slight atypia. At later stages, cells infiltrate SQ adipose tissue --\> honeycomb pattern of entrapped adipocytes*
441

DFSP, higher magnification
## Footnote
*Neoplasm composed of ill-defined, dense, spindle cells w/i reticular dermis extending toward SQ fat. Tumor cells are monomorphic and may be arranged in whorl-like pattern. Neoplastic cells invade SQ fat lobules in lace-like fashion.*
442

microcystic adnexal carcinoma
443

microcystic adnexal carcinoma
444

MAC
## Footnote
*Keratocysts and variably-sized basaloid tumor nests and ducts surrounding nerves within a fibrotic desmoplastic stroma*
445

MAC
## Footnote
*Higher magnification reveals neoplastic cells with prominent oval nuclei*
446

Extramammary Paget’s disease presenting as erythematous, well-demarcated, scaly plaque on suprapubic area
447

Angiosarcoma
## Footnote
*Ill-defined neoplastic proliferation of plump, cuboidal, mostly pleomorphic endothelial cells intermingled with slit-like spaces with many erythrocytes*
448

Kaposi's sarcoma
449

patch and plaque Kaposi's sarcoma
450

traditional vertical sectioning/breadlofing of specimen
451
FDA-approved molecular therapies for cutaneous malignancy

452
best biopsy technique for suspected tumor type

453

Mohs specimen sectioning
454
infections transmitted by plant contact

455
plants that cause irritant contact dermatitis

456
plants that cause allergic contact dermatitis

457
Cross-reactants to Anacardiaceae

458
other mites of significance

459
important genera of mosquito
1. Anopheles transmits malaria
2. Culex transmits filariasis
3. Aedes transmits yellow fever, dengue
460

Acute spongiotic dermatitis
* Spongiosis (intercellular edema) and basket-weave stratum corneum (acute)
* Intraepidermal vesicles filled with mononuclear cells
* May see lymphocyte exocytosis
* Perivascular lymphocytes ± interstitial eosinophils
461

Subacute spongiotic dermatitis
* Epidermal acanthosis with spongiosis
* Parakeratosis
* May see lymphocyte exocytosis
* Perivascular lymphocytes ± interstitial eosinophils
462

Eosinophilic spongiosis
* Epidermis may show features of acute or subacute spongiotic dermatitis
* Eosinophils are seen percolating between epidermal keratinocytes
463

Chronic dermatitis (lichen simplex chronicus)
* Acanthosis and hypergranulosis
* Stratum corneum resembles acral skin but hair follicles are evident
* May not see any spongiosis
* Vertical streaking of the collagen in papillary dermis
464

Pityriasis rosea
* Subacute spongiotic dermatitis (spongiosis may be basilar and not always full thickness)
* Mounds of scale with parakeratosis
* Erythrocyte extravasation in the papillary dermis
* Lymphocyte exocytosis
465

Stasis dermatitis
* Subacute spongiotic dermatitis
* Nodular proliferation of vessels in the papillary dermis
* Interstitial hemosiderin


