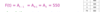demand forecasting Flashcards
(69 cards)
forecasting
consistent, systematic and appropriate forecasting process positively impact performance through decreased operations costs, improved customer service, increased sales, and reductions in inventory. these improvements have positively affected return
what is forecasting?
a method for translating past experience and present events into predictions of the future
observed measurement = systematic part + random part
- forecasting tries to isolate the systematic part
- the random part determines the forecast accuracy
why do we forecast
-to make better decisions
forecasting is important because:
- it is a starting point for business planning
- all business decisions will follow the result of forecasting
- “bad “ forecast can lead to a significant increase in cost
Forecasting is vital to every functional area:
- finance
- marketing
- HR
- production and operations
forecasting error
forecasts are rarely perfect; actual results differ from predicted values
forecasting techniques generally assume that:
the same underlying causal system that existed in the past will continue to exist in the future
Forecasts for ______ items tend to be more accurate than forecast for ______ items
- group of
- individual
_________ forecasts tend to be more _________ accurate than forecasts
- Short-term
- long-term
forecasting methods
- judgmental methods
- time series analysis
- causal relationship
- simulation
judgmental methods:
- sales force estimate
- executive opinion
- market research
- historical analogies
- Delphi method
Delphi method:
Group of experts respond to questionnaire.
A moderator compiles results and formulates a new questionnaire that is submitted to the group
time series:
a time ordered sequence of observations taken at regular intervals of time
assumptions
(i) record of past demand is available and (ii) past demand is a predictor of future demand
the following 5 patterns could be identified in a time series:
- trend
- seasonality
- cycles
- irregular variations
- random variations
trend
long term movement in data (up or down)
seasonality
short-term fairly regular variations in data generally related to factors such as the calendar or time of the day
cycles
wavelike variations of more than one year’s duration. These are often related to a variety of economic, political and agriculture conditions
irregular variations
-caused by unusual circumstances such as severe weather
random variations
-caused by chance that will remain after all other behaviours have been accounted for
fundamental difference between cycles and seasonality is the …
duration of repeating patterns
linear regression
Is a way to model the relationship between two variables. …
The equation has the form Y=a+bt,
- where Y is the dependent variable (that’s the variable that goes on the Y axis),
- t is the independent variable (i.e. it is plotted on the X axis),
- b is the slope of the line and a is the y-intercept
Naïve Method
the Naïve forecasts are simply set to be the value of the last observation
Naïve Method -9 facts
- Simple to use
- This method works remarkably well for many time series.
- Very low cost
- Data analysis is nonexistent
- Easily understandable
- Can serve as a standard for comparison
- Low accuracy (not suitable when the random variation is high)
- Short-term
- Providing a starting point for other forecasting method