Danish Ball Bearings Definitions Flashcards
(72 cards)
Pressure groups
A group that tries to influence public policy in the interest of a particular cause.
Job security
Assurance (or lack of it) that an employee has about the continuity of gainful employment for his or her work life.
Job security usually arises from:
- the terms of the contract of employment,
- collective bargaining agreement, or
- labour legislation that prevents arbitrary termination, layoffs, and lockouts.
It may also be affected by general economic conditions.
Technological disaster
Catastrophic event caused by humans that results in the toxic contamination of the environment.
Flow production
Streamlined distribution
based on customer ‘pull’ (demand or requirements)
instead of on sales ‘push.’
CFD is an integral component of lean production

Batch production
A manufacturing process in which components or goods are produced in groups (batches) and not in a continuous stream.
(Hundreds / thousands of the same product are manufactured over a period of time. )

Corporate social responsibility
A company’s sense of responsibility towards the community and environment (both ecological and social)
in which it operates.
Companies express this citizenship
(1) through their waste and pollution reduction processes,
(2) by contributing educational and social programs, and
(3) by earning adequate returns on the employed resources.
Note:
Ethics concern actions which can be assessed as right or wrong by reference to moral principles
CSR is about the organisation’s obligations to all stakeholders – and not just shareholders

Social Contract
Unwritten and tacit agreement said to exist among the members of a community or group
that guides individual behaviour and establishes personal rights and responsibilities.
Social contract is deemed essential for any organised group behaviour and, in democratic societies, is embodied in the national constitution.
Global identity
-
Brand Awareness
Extent to which a brand is recognised by potential customers, and is correctly associated with a particular product.
- Usually expressed as a percentage of target market,
- Primary goal of advertising in the early months or years of a product’s introduction.
Cell production
A lean method of producing similar products using cells, or groups of team members, workstations, or equipment, to facilitate operations by eliminating setup and unneeded costs between operations.
Just in Time Production
Just-in-time is a system which operates on the scheduling of stocks in a precise, coordinated way, so minimising the quantity needed to be held.
Stocks are only ordered a short time period before they are needed for the actual production of the final good.
This technique helps to minimise stocks and therefore reduce the costs of holding stocks.
Just-in-time production requires a close relationship with suppliers to ensure that stocks are available exactly when they are needed.

Downsizing
Associated with delayering.
This happens when the size of the core workforce is reduced.
This can further reduce a firm’s costs because there are fewer core staff who are numerated on full benefits.
Downsizing can lead to more flexible working practices as businesses hire more peripheral and contractual workers. These people are not entitled to the same remuneration as core full time staff.

Globalisation
Globalisation is the integration of the world’s economies in terms of economics, sociology and politics. For businesses, this means that trade is now being conducted on ever widening geographical boundaries. Countries now trade across continents and companies also trade all over the world.
Offshoring
Expanding business by using an overseas firm in another country as the sub-contractor.
Artificial Intelligence
The theory and development of computer systems able to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence,
such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and translation between languages
Unique Selling Point
A unique selling point (USP) is any aspect of or characteristic of a product that differentiates it from the competition.
Firms will often want to stress the USP of their product in their marketing to persuade consumers of the superiority or desirability of their product.
Autocratic Leadership Style
- Autocratic leadership is a form of leadership where the leader makes decisions and sets objectives independently of the others in the firm without involving them in the decision making process.
- This style of leadership can often lead to dissatisfaction as employees do not feel involved in the process of decision-making.
One off Special Order
A One off Special Order is an order that is carried out by a business once, by special request.
Corporate Culture
The corporate culture is all the attitudes, beliefs and values which are a part of the business and the way in which they operate.
It is the culture that is created in the business and forms a part of their day to day operations.
Democratic Leadership style
- Democratic leadership is a style of leadership where a leader encourages others to be involved in the decision making process.
- It is felt that this style of leadership will help to motivate employees as they will feel more involved in the decision-making process,
- requires leaders who are skilled at communication.
Narrow Span of Control
The span of control is the number of people in an organisation for whom one person is responsible.

Wide Span of Control
A wider span of control means that each person is responsible for more people below them and tends to be associated with firms with a flatter hierarchy of management. It is argued that this will give more responsibility to the workers and therefore motivate them to work harder.
Organisational Structure
The hierarchy of a firm from top to bottom into different levels of management.
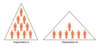
Tall Organisational Structure
A tall hierarchy is one with a lot of levels of management, while a flat hierarchy is one with few levels of management.

















