D/O of the Gallbladder & Exocrine Pancreas- Prof Wall & Porth, Chpt 30 Flashcards
What does the so-called Hepatobiliary System consist of?
- Gallbladder
- Left & Right Hepatic Ducts
- come together & form: Common Hepatic Duct
- Cystic Duct
- Bile Duct =’s CBD + CD
What forms the Hepatopancreatic Ampulla?
- Bile Duct
- Main Pancreatic Duct
- Empty into the Duodenum
Can you palpate the Pancreas?
- No!
- Pretty much hiding (posterior region)
- (big issue re: pancreatic CA)
- Pretty much hiding (posterior region)
What type of Organ is the Pancreas?

- Endocrine & Exocrine Organ
What type of Organ is the Pancreas?
Exocrine Function
& Acinar Cells
- Exocrine =
- Acinar cells
- Secrete Digestive Enzymes* into Microscopic Ducts
- Empty into main pancreatic duct
- Secrete Digestive Enzymes* into Microscopic Ducts
-
*Digestive Enzymes:
- Proteolytic (protein)
- Amylase (carbs)
- Lipase (fat)
- Acinar cells
What type of Organ is the Pancreas?
Exocrine Function
& Ductal Epithelial Cells
- Secrete
- Alkaline Solution
- Water, Electrolytes, Sodium Bicarb
- Increase pH in duodenum
- Alkaline solution = majority of what pancreas secretes
- Alkaline Solution
What type of Organ is the Pancreas?
Endocrine Function
- Secretion into bloodstream
- Islets of Langerhans
- B-Cells
- Insulin syn/sec
- A-Cells
- Glucagon
- D-Cells
- Somatostatin
- Inhinits GH & TSH secretion
- Somatostatin
- B-Cells
Pancreas…
So… what does this organ do?

-
Secretes
- aids in digestion, regulation of pH in intestines & blood sugar regulation
DO NOT MAKE THIS ORGAN ANGRY!!!! That would be bad.
Gallbladder
Bile Storage Site
- Bile gets concentrated here
- Filled when Sphinter of Oddi closed
- Contracts to CKK
- Induces drug tolerance to opiods!
Bile

- Breaks up Fats for small intestine digestion
- Secreted from Liver
- Made from:
- Bile salts
- cholesterol
- Bilirubin
- Worn out WBCs
- Alkaline Fluids
- Bile salts
Cholecystic
- Referring to the Gallbladder
Cholecystitis
- Inflammation of Gallbladder
- Chronic or Acute
Cholelithiasis
- Stones in Gallbladder
- aka: cholecystolithiasis
Choledocholithiasis
- Stone in Bile Ducts
Cholecystectomy
- Removal of Gallbladder
Cholecystalgia
- Pain
- aka: biliary colic
Cholelithiasis
Gallstones!

- 10-15% adults get this
- 500,000 cholecystectomies/year
Cholelithiasis
Composition

- Cholesterol
- Most common
- 75% of stones
- Calcium Bilirubinate/Ca Salts
- 25% of stones
- ‘pigmented’ black/brown
Cholelithiasis
Etiology & Pathophyz

- Super Saturation of Cholesterol
- Diet is so important to prevention!
- Nucleation
- Microscopic cholesterol comes together & crystallizes
- Over time… more layers of cholesterol added
- GB hypo-motility
- Slower emptying = more time for stone formation
- pregnancy…
- Slower emptying = more time for stone formation
Cholelithiasis
- The 5 F’s*
- *Risk Factors**
- Female
- Forty
- >40yo
- Fat
- Obesity, or rapid weight loss
- Fair
- White/pasty!
- Fertile

Cholelithiasis
Other Risk Factors
- OCPs
- Preggers
- DM/Insulin Use
- Hemolysis
- Biliary Parasites
- Cirrhosis
- Crohn’s
- Hyperparathyroid Dz
Cholelithiasis
Symptoms/Presentations

- Asymptomatic (50-60%)
-
Symptomatic (~40%)
- Biliary Colic
- Aching pain in RUH/Epigastric
- Referred Pain
- Back, Scapula, R. Shoulder
- Biliary Colic
Cholelithiasis
Symptoms/Presentations
Non-Specific Symptoms

- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fatty Food Intolerance
- Dyspepsia
- Heartburn
- Bloating
- Flatulance
- Belching
Cholelithiasis
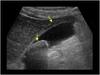
Diagnostics
-
ULTRASOUND!!!!!!!
- RUQ Transabdominal
- >95% sen/spec