Custom Cards (random) Flashcards
(31 cards)
DRAG DROP - Drag and drop the descriptions from the left onto the correct QoS components on the right. Select and Place:


DRAG DROP - Drag and drop the characteristics from the left onto the correct infrastructure deployment types on the right. Select and Place:


DRAG DROP - Drag and drop the characteristics from the left onto the infrastructure types on the right. Select and Place:


DRAG DROP - Drag and drop the characteristics from the left onto the correct infrastructure deployment type on the right. Select and Place:


DRAG DROP - Drag and drop the QoS mechanisms from the left onto their descriptions on the right. Select and Place:


Refer to the exhibit. On which interfaces should VRRP commands be applied to provide first hop redundancy to PC-01 and PC-02?
A. G0/0 and G0/1 on Core
B. G0/0 on Edge-01 and G0/0 on Edge-02
C. G0/1 on Edge-01 and G0/1 on Edge-02
D. G0/0 and G0/1 on ASW-01 pic 12
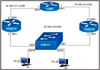
C. G0/1 on Edge-01 and G0/1 on Edge-02
Refer to the exhibit. pic 14 Assuming that R1 is a CE router, which VRF is assigned to Gi0/0 on R1?
A. default VRF
B. VRF VPN_A
C. VRF VPN_B
D. management VRF

A. default VRF
DRAG DROP - Drag and drop the LISP components from the left onto the functions they perform on the right. Not all options are used. Select and Place:

eference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Data_Center/DCI/5-0/LISPmobility/DCI_LISP_Host_Mobility/LISPmobile_2.html#:~:text=% E2%80%93%20Proxy%20ITR%20(PITR)%3A%20A,devices%20deployed%20at%20LISP%20sites.

Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer configures a GRE tunnel and enters the show interface tunnel command. What does the output confirm about the configuration?
A. The keepalive value is modified from the default value.
B. The physical interface MTU is 1476 bytes.
C. The tunnel mode is set to the default.
D. Interface tracking is configured.

C. The tunnel mode is set to the default.
MTU has been configured on the underlying physical topology, and no MTU command has been configured on the tunnel interfaces. What happens when a 1500-byte IPv4 packet traverses the GRE tunnel from host X to host Y, assuming the DF bit is cleared?
A. The packet is discarded on router B
B. The packet arrives on router C without fragmentation
C. The packet arrives on router C fragmented
D. The packet is discarded on router A

C. The packet arrives on router C fragmented
Drag and drop the descriptions of the VSS technology from the left to the right. Not all options are used. Select and Place:


Refer to the exhibit. An engineer must assign an IP address of 192.168.1.1/24 to the GigabitEthernet1 interface. Which two commands must be added to the existing configuration to accomplish this task? (Choose two.)
A. Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
B. Router(config-vrf)#address-family ipv4
C. Router(config-vrf)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
D. Router(config-if)#address-family ipv4
E. Router(config-vrf)#address-family ipv6 pic 23

A. Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
D. Router(config-if)#address-family ipv4
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer must simplify the IPsec configuration by enabling IPsec over GRE using IPsec profiles. Which two configuration changes accomplish this? (Choose two).

B. Apply the crypto map to the tunnel interface and change the tunnel mode to tunnel mode ipsec ipv4.
D. Create an IPsec profile, associate the transform-set, and apply the profile to the tunnel interface.
Refer to the exhibit. Which configuration must be applied to R1 to enable R1 to reach the server at 172.16.0.1?

C. interface Ethernet0/0 vrf forwarding bank ip address 172.16.0.7 255.255.0.0
router ospf 44 vrf bank network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
Refer to the exhibit. Which configuration allows Customer2 hosts to access the FTP server of Customer1 that has the IP address of 192.168.1.200?
A. ip route vrf Customer1 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.1 global ip route vrf Customer2 192.168.1.200 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.1 global ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 Vlan10 ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 Vlan20
B. ip route vrf Customer1 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.255 172.16.1.1 global ip route vrf Customer2 192.168.1.200 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 global ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 Vlan10 ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 Vlan20
C. ip route vrf Customer1 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.1 Customer2 ip route vrf Customer2 192.168.1.200 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.1 Customer1
D. ip route vrf Customer1 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.1 Customer1 ip route vrf Customer2 192.168.1.200 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.1 Customer2

A. ip route vrf Customer1 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.1 global ip route vrf Customer2 192.168.1.200 255.255.255.255 192.168.1.1 global ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 Vlan10 ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 Vlan20
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer configures a new GRE tunnel and enters the show run command. What does the output verify? pic 27
A. The tunnel keepalive is configured incorrectly because they must match on both sites.
B. The tunnel destination will be known via the tunnel interface. C. The tunnel will be established and work as expected.
D. The default MTU of the tunnel interface is 1500 bytes.

C. The tunnel will be established and work as expected.
DRAG DROP - Drag and drop the virtual components from the left onto their descriptions on the right. Select and Place:


A port channel is configured between SW2 and SW3. SW2 is not running a Cisco operating system. When all physical connections are made, the port channel does not establish. Based on the configuration excerpt of SW3, what is the cause of the problem?
A. The port-channel mode should be set to auto.
B. The port channel on SW2 is using an incompatible protocol.
C. The port-channel trunk is not allowing the native VLAN.
D. The port-channel interface load balance should be set to src-mac. pic 30

B. The port channel on SW2 is using an incompatible protocol.
Refer to the exhibit. pic 31 What are two effects of this configuration? (Choose two.)
A. It establishes a one-to-one NAT translation.
B. The 209.165.201.0/27 subnet is assigned as the outside local address range.
C. The 10.1.1.0/27 subnet is assigned as the inside local addresses.
D. Inside source addresses are translated to the 209.165.201.0/27 subnet.
E. The 10.1.1.0/27 subnet is assigned as the inside global address range.

C. The 10.1.1.0/27 subnet is assigned as the inside local addresses.
D. Inside source addresses are translated to the 209.165.201.0/27 subnet.
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about the OSPF debug output is true?
A. The output displays OSPF hello messages which router R1 has sent or received on interface Fa0/1.
B. The output displays all OSPF messages which router R1 has sent or received on all interfaces.
C. The output displays all OSPF messages which router R1 has sent or received on interface Fa0/1.
D. The output displays OSPF hello and LSACK messages which router R1 has sent or received.

A. The output displays OSPF hello messages which router R1 has sent or received on interface Fa0/1.
Based on this interface configuration, what is the expected state of OSPF adjacency?
A. 2WAY/DROTHER on both routers
B. not established
C. FULL on both routers
D. FULL/BDR on R1 and FULL/BDR on R2
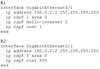
B. not established
Link1 is a copper connection and Link2 is a fiber connection. The fiber port must be the primary port for all forwarding. The output of the show spanning-tree command on SW2 shows that the fiber port is blocked by spanning tree. An engineer enters the spanning-tree port-priority 32 command on G0/1 on SW2, but the port remains blocked. Which command should be entered on the ports that are connected to Link2 to resolve the issue?
A. Enter spanning-tree port-priority 4 on SW2.
B. Enter spanning-tree port-priority 32 on SW1.
C. Enter spanning-tree port-priority 224 on SW1.
D. Enter spanning-tree port-priority 64 on SW2.

B. Enter spanning-tree port-priority 32 on SW1.
Which IP address becomes the active next hop for 192.168.102.0/24 when 192.168.101.2 fails?
A. 192.168.101.10
B. 192.168.101.14
C. 192.168.101.6
D. 192.168.101.18

D. 192.168.101.18
VLANs 50 and 60 exist on the trunk links between all switches. All access ports on SW3 are configured for VLAN 50 and SW1 is the VTP server. Which command ensures that SW3 receives frames only from VLAN 50?
A. SW1(config)#vtp mode transparent
B. SW3(config)#vtp mode transparent
C. SW2(config)#vtp pruning
D. SW1(config)#vtp pruning

D. SW1(config)#vtp pruning










