Cushing’s Disease Flashcards
What is Cushing’s Disease?
Cushing’s Disease is a condition in which here is a hypersecretion of cholesterol
What is the aetiology of Cushing’s Disease?
The aetiology of Cushing’s Disease is Tumour in adrenal cortex (primary) Tumour in pituitary gland (secondary) Ectopic ACTH secretion (lung carcinoma) Latogenic - overdose of therapeutic corticosteroids
What is the pathophysiology of Cushing’s Disease?
The pathophysiology of Cushing’s Disease is Oversecresion of ACTH stimulates oversecresion of cholesterol Bilateral adrenal gland hyperplasia
What are the fourteen symptoms of Cushing’s Disease?
The symptoms of Cushing’s Disease are
Thin skin & easy bruising (protein catabolism)
Stretch marks (purple striae)
Red (plethoric) cheeks
Poor wound healing
Hirsutism (male hair patterns)
Headache
Acne
Amenorrhea or impotence
Depression
Oedema (water retention)
Personality changes
Psychosis
Wasting of limb muscles/ proximal myopathy (protein catabolism)
Central fat deposition - Moon face

What are the four signs of Cushing’s Disease?
The four signs of Cushing’s Disease are
Hypertension
Growth arrest in children
Osteoporosis
High Na
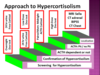
What are the five investigations for suspected Cushing’s Disease?
Overnight Dexamethasone suppression test/ 24 hour urine free cortisol - screening
Low dose dexamethasone test/ 24 hour urine free cortisol - confirm hypercortisolism
Paired morn - midnight ACTH cortisol test - ACTH dependant or not
High dose dexamethasone test - ACTH dependant: pituitary (or ectopic)/ other
MRI sella turcica/ CT adrenals/ CT chest/ BIPSS - localisation