Correlation and Regression I Flashcards
(17 cards)
What is the Pearson product-moment correlation uses and what are its 5 assumptions?
Population from which the samples are drawn is normally distributed
Data are either interval or ratio
ANOVA is a parametric test so data must have both magnitude and scale
Related pairs
Each participant or observation should have a pair of values
Relationship should be linear
Homoscedasticity
The error should be consistent across all levels of the independent variable
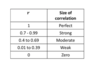
What is the chart for coefficient r ranges correlations?
What is the degrees of freedom for Pearson product correlation?
df=npairs -2
What are the 3 steps in interpreting a Pearson Product moment?
Indicate the type of correlation performed and the variables used
Describe direction and strength & provide relevant statistical information (r, df, p)
Interpret the statistical results relating back to the variables (use 𝑟𝑟^2 to support your statement)
What is Bivariate regression?
When you have two variables, you can use one to predict the other
What is the equation for bivariate linear regression and where can you find the data on a table?
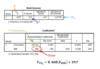
𝑌 = 𝑏𝑋 + 𝐶 b=slope, C=y-intercept
The _______ is a measure of how accurate our sample based prediction is in making predictions about the population
Standard Error of the Estimate (SEE)
Can be used as a confidence interval to measure the upper and lower limits
𝐶= 𝑌𝑝 ±𝑍(𝑆EE)
How do you measure the difference from actual to predicted in a bivariate regression?
(𝑅esidual = 𝑌actual − 𝑌predicted)
What is multiple regression, how is it calculated?
A prediction of the value of a variable based on the value of two or more other variables
𝑌𝑝 = 𝑏𝑋1 + 𝑏2𝑋2 + 𝑏3𝑋3+ … + 𝑏𝑖𝑋𝑖 + C
Yp is the predicted score/value
𝑋𝑖 is the score for each predictor variable
𝑏𝑖 is the weight that each score contributes to the predicted score
𝐶 is the constant (i.e. the Y-intercept)
How to see Multiple regression in a table?

What is the difference between bivariate correlation and partial correlation?
bivariate correlation coefficients would consider the amount of variance in Y only that one variable is being considered independent of all the others
partial correlations of each variable would consider only the amount of unique variance each independent variable explains in Y when the common variance explained by the other variables is removed
What is the basis of multiple regression?
The ability to model the amount of variance in Y explained by a variable (X2) after the variance explained by X1 has already be accounted for is the basis of
True or False: Multiple regression will generate a model that accounts for the contribution of each variable
True
What are the 3 types of multiple regression methods?
Forward: Put in highest bivariate correlation, add next variable that increses R square the most (unique variance)
Backward: All variables are entered into model, the variable that decreases R2 the least is then removed, If the difference between the original R2 and R2 after variable is removed is not significant then variable is removed and the next variable is removed
Stepwise: Add things in sequentially to see the effect it has on the dependant variable
What is the assumption of linear regression?
Relationship between the independent variables and dependent variable is linear
What is multicollinearity and singularity?
Independent variable is correlated with each = harder to the significance of a independant variable
Singularity
- Two or more independent variables are “perfectly” correlated with each other (i.e. one variable is the square of another)
What is a multivariate regression?
Multiple independent variables and multiple dependent variables
Useful for predicting behaviour of variables associated to changes in a predictor variable
- E.g. Can a supermarket owner maintain stock of water, ice cream, frozen foods, canned foods and meat as a function of temperature, tornado risk and gas price in June


