Cornea Degeneration and Ectasia Flashcards
which layer of the cornea is capable of regeneration? which ones are not?
epithelium is the only layer to undergo mitotic division (Bowman’s, stroma, Descemet’s and endothelium do not regenerate)
what are the cell junctions present in the corneal epithelium?
desmosomes and gap junctions and connect to Bowman’s layer via hemidesmosomes
what type of pumps are in the corneal endothelium and what is the purpose?
Na-K-ATPase pumps to keep the stroma from having too much fluid
what is a degneration?
a process in which normal elements of corneal tissue are converted (age-related or metabolic diseases) - can be benign or detrimental to normal function
what are 7 corneal degenerations that are non-sight threatening?
crocodile shagreen, arcus, limbal girdle of vogt, farinata, terriens marginal degeneration, moorens ulcer and amyloid
what are 2 non-sight threatening corneal degenerations that have the possibility of turning to sight threatening?
mooren’s ulcer and amyloid
what are 3 exmples of degenerations that are opacificiations and sight threatening?
salzmanns nodular, spheroidal and band keratopathy
what is crocodile shagreen?
age related, benign, common condition, easily seen with slit lamp = plaques of fibrous tissue

where is crocodile shagreen located anteriorly and posteriorly?
anterior = bowman’s layer
posterior = posterior corneal stroma and descemet’s
what are the symptoms and treatment for crocodile shagreen?
no symptoms and no treatment required
what is arcus?

lipid/cholesterol deposits in Bowman’s (not common under age 40)
why does arcus have a lucid interval between the limbus?
the lipid deposition ends at bowman’s - it has an abrupt ending
what does type 1 limble girdle of vogt look like?
has a lucid interval - deposition ends at bowman’s swiss cheese holes and sharp edges centrally early form of band keratopathy

what does type 2 limble girdle of vogt look like?
goes to limbus - elastoid degeneration of sub-epithelial collagen extensions centrally

what is farinata?
white dust-like particles, pre-descemet’s and occurs with aging (may resemble pigment dispersion syndrome)

what is the leading line of a pterygium called?
stocker line (iron line)

what is a hudson-stahli line?
occurs in the interpalpebral zone from tear stagnation (iron deposits in tear film) = typically after chronic inflammatory condition

what is Terrien’s marginal degeneration?
thinning of the cornea (starts superiorly then circumferential), asymptomatic, bilateral and epithelium stays intact, fine line of lipid deposit, superficial vascularization, males >> females and 40+

what is a differential diagnosis for Terrien’s marginal degeneration?
Mooren’s ulcer
what symptoms will patients have with Mooren’s ulcer?
non-infectious (unknown etiology - autoimmune likely), painful, red, photophobia
where does Mooren’s ulcer begin?
near limbus, typically progressive (circumferentially and centrally) = thinning, stromal melting, potentially perforation (epithelium is not intact)

what is Mooren’s ulcer type 1?
typically seen in older patients, unilateral and better responses to treatment
what is Mooren’s ulcer type 2?
seen in younger (african descent) 20-30 y/o, bilateral and poor response to treatment (rare)
how do you differentiate between Mooren’s and Terrien’s?
Terriens has intact epithelium, no NaFl staining, rarely painful/inflammatory, and rarely perforates
what type of systemic work up is needed to Mooren’s ulcer?
vasculitis or collagen vascular disease (autoimmune diseases)
what is the treatment for Mooren’s ulcer?
mostly supportive = topical steroids, conjunctival resection/radiation, bandage CL, topical cyclosporine or systemic immunosupression (perforation = cyanoacrylateor lamellar keratoplasty)
what is polymorphic amloid degeneration?
occurs deep stroma, bilateral and appears similar to lattice degeneration - mostly benign

what is spheroidal degeneration?
common from UV exposure (actinic), usually interpalpebral, golden brown deposits

what is Salzmann’s nodular degeneration?
elevated white masses on cornea - tend to be peripheral (milky/glossy), can have a red/irritated eye

what causes salzmann’s nodular degeneration and who typically gets it?
females, > 50 y/o, chronic ocular surface disease/inflammation (especially viral) - hyaline plaques replace bowman’s
what are the symptoms and treatment for salzmann’s nodular degeneration?
symptoms = dry eye symptoms, VA if central treatment = lubricants, steroid, bandage CL (PK if severe)
what is band keratopathy?
interpalpebral CA++ deposits in bowman’s with clear zone separating the limbus - swiss cheese appearance

why does band keratopathy have swiss cheese appearance?
clear areas and small circular areas where nerve endings perforate bowman’s (similar to Vogt 1)
what causes band keratopathy?
inflammatory disease (mercury), systemic conditions that cause increased Ca, chronic ocular pathology and degenerative conditions or idiopathic
what is the treatment/plan for band keratopathy?
monitor, ocular lubricants for mild cases, refer for hypercalcemic work-up, chelation using 2% EDTA for severe cases, PTK
what are 3 corneal ectasias?
keratoconus, keratoglobus, pellucid marginal degeneration
when does keratoconus typically occur and what causes it?
bilateral, usually after puberty (rarely congenital), progressive then stabilizes, males = females, >asians, may have an inheritance pattern

what is the pathology for keratoconus?
irregular epithelium, breaks in bowman’s, fibrosis beneath epithelium, stromal scarring, corneal thinning
what is the pathophysiology for keratoconus?
epithelial lysosomal enzyme expression increase, reduction inhibition of proteolytic enzymes, abnormal corneal collagen, lamellae, keratocyte populations
what is charleaux’s sign?
an irregular red reflex from retinoscopy or retro-illumination in keratoconus

what is Rizutti’s sign?
a triangle of light seen on the distal iris in keratoconus

what is munson’s sign?
when a patient with keratoconus looks down it forms a “V” shape

what is vogt striae and fleischer ring?
lines seen in cornea with keratoconus (fleischer ring = iron deposits around base of cone)

what is the treatment for keratoconus?
optical correction, specialty RGP/hybrid CL, PK, no refractive surgery, intacts, collagen crosslinking
what are corneal hydrops?
spontaneous rupture/break in descemet’s - can result in flattening of cornea, clears on its own - may scar

what is posterior keratoconus?
posterior diffuse or localized curvature (normal anterior surface), unilateral, non-progressive, female > male
what is keratoglobus?
bilateral, congenital or acquired, diffuse corneal thinning > peripheral (1/3 to 1/5 normal thickness)
what does pellucid marginal degeneration look like?
the thinned area is confined to corneal side of inferior limbus (4:00-8:00), pot belly cornea, ATR astigmatism (kissing dove pattern)
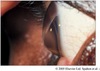
what are dermoids?
collection of ectodermal tissues: sweat glands, hair follicles, sebaceous glands

what is a lipodermoid?
benign fatty tumor beneath conjunctiva laterally

what are trisomy 21, 17-18, and 13?
21 = downs syndrome
17-18 = edwards syndrome
13 = bartholin-patau syndrome
what happens with a vitamin A deficiency?
bitot spot, impaired goblet cell function, keratinization

what disease is caused by sphingolipidoses disorder?
Fabry’s disease

what is fabry’s disease?
x-linked recessive, posterior spoke like deposits in lens along sutures = verticillata
what is cystinosis and alkaptonuria caused by?
diseases of protein and amino acid metabolism
what does cystinosis look like?
cystine crystal deposits throughout cornea

what type of deposits does ciprofloxacin give?
chalky white deposits where epithelium is absent

where do mercury deposits occur? what causes them?
(orange-brown) in bowman’s typically from preservatives

where do silver deposits occur?
argyrosis in descemet’s

what type of deposits occur from epinephrine drops?
adrenochrome
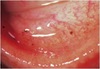
what type of deposits do the drug thorazine cause? and where do they occur?
stellate sub-capsular throughout the stroma

what causes wilson’s disease?
defect in copper metabolism - Cu+ deposit in descemet’s peripherally with no clear interval

what is this picture of?

corneal hydrops
what is this picture of?

band keratopathy
what is this picture of?

crocodile shagreen
what is this picture?

furrow degeneration
what is this topography of?

keratoconus
what is this topography of?

pellucid marginal degeneration
what is this picture of?

Salzmann’s nodular degeneration
what is this picture of?

vogt striae in keratoconus
what is this picture of?

limbal girdle of vogt type 1


