Continuity Flashcards
(23 cards)
Define continuity at a point.

What are the three requirements for continuity at a point?

When is a function continuous from the left? From the right?

When is a function discontinuous at a point “a”?
A function f(x) is discontinuous at a point x=a if:
- f(x) is undefined at x=a (removable discontinuity)
- The limit of f(x) DNE (non-removable discontinuity)
- The limit of f(x) as “x” approaches “a” ≠ f(a)
What is the definition of continuity over an interval?

What is the greatest integer function?
The greatest integer function is noted by [[x]] or int(x) and is defined as [[x]] = n, where “n” is the greatest integer ≤ “x”.
Examples: 1. [[3.5]] = 3 2. [[-3.5]] = -4
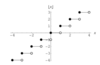
What is the definition of continuity over a closed interval?
A function f(x) is said to be continuous over a closed interval [a,b] if and only if:
- f(x) is continuous on (a,b)
- f(x) as “x” approaches “a” from the right = f(a)
- f(x) as “x” approaches “b” from the left = f(b)
What are the properties of continuity for two functions “f” and “g” at x=a, “c” serving as a constant.

What types of functions are continuous?

Define a polynomial function.
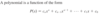
What is the form/definition of a rational function?
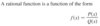
What functions are continuous over their entire domains?
- Polynomials are continuous over (-∞,∞).
-
Rational functions are continuous on (-∞,∞) with the following exceptions:
- D(x)≠0, so except at x=c, such that D(c)=0
- Exponential functions, where a>0 and a≠1 are continuous over (-∞,∞).
- trigonometric functions are continuous where they are defined
- see composite functions

Over what intervals are sine and cosine functions continuous?
sin (x) and cos(x) are continuous over (-∞,∞).
- sin(-θ) = -sinθ
- sin(nπ) = 0 for any integer “n”

Over what intervals are tangent and secant continuous?
tan(x) and sec(x) are continuous for when x≠nπ/2, where “n” is odd.

Over what intervals are cotangent and cosecant continuous?
cot(x) and csc(x) are continuous when x≠nπ, where “n” is any integer.

When are composite functions continuous?
If “g” is continuous at “c” and “f” is continous at g(c), then the composite function f(g(c)) is continuous at g(c).

Explain composite functions.

Explain the intermediate value theorem.

Explain the end-behavior test for polynomials.

What is the definition of a horizontal asymptote?

Define a horizontal asymptote?
The line y = L is called a horizontal asymptote if and only if the limit as “x” approaches ±∞ = L
Note another theorem.
- If r>0 is a rational number, then the limit of 1/(x^r) as “x” approaches ∞ = 0
- If r>0 is a rational number such that x^r is defined for all “x”, then the limit as “x” approaches “-a” =0
What do the highest degrees of rational functions indicate?
For a rational function:
- If the degree of N(x) > D(x), then there is NO horizontal asymptote.
- If the degree of N(x) = D(x), then y = k is the horizontal asymptote, where “k” is the ratio of the coefficients
- If the degree of N(x) < D(x), y = 0 is the horizontal asymptote.


