Conduction Blocks Flashcards
What is a conduction block?
Any obstruction or delay of the normal pathways of electrical conduction
What are the 3 types of conduction blocks?
sinus node block
AV block
bundle branch block
What type of block is this:
sinus node fires normally, but wave of depolarization is blocked and not transmitted to atrial tissue
sinus node block
What type of block is this:
Any conduction block between the sinus node and Purkinje fibers (including AV node & His bundle)
AV block
What type of block is this:
Conduction block in one or both of the ventricular bundle branches
Bundle Branch Block
What type of block is this:
only a part of one of the bundle branches is blocked
fascicular block
**a bundle branch block subtype
What are the 3 types of AV blocks?
First Degree Second Degree (Mobitz I, Mobitz II) Third Degree (a complete block)
What type of AV block is this:
Rhythm is regular, PR interval > 0.2 seconds, QRS is usually normal

1st degree AV block
What AV block is this:
Successively longer PR intervals unil one QRS fails, Rhythm (ventricular) is often irregular, atrial rhythm is ~ regular, QRS is normal, Pwave regular, ventricular wave is not
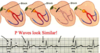
Second Degree AV Block: Mobitz I (Wenckebach)
What type of AV block:
Suddenly dropped QRS, P-waves are punctual and similar, unlike a non-conducted PAC which is EARLY!
Ventricular rhythm = irregular, atrial rhythm is regular
PR interval normal or prolonged, QRS: often abnormal

Second Degree AV block: Mobitz II
(AV block at bundle of His or bundle branches)
What type of AV block:
Atria and ventrilces are depolarizing independently
*No association between atria and ventricles

Third degree av block
aka “complete heart block”
What type of AV block:
Ultimate in heart blocks.
No atrial impulses make it through to activate the ventricles.
Aka Complete heart block.
Third degree av block
What type of AV block:
Ventricles generate an escape rhythm (30-45 BPM).
Atrial and ventricles have nothing to do with each other
Third degree av block
What type of block:
Check QRS first
Look in V1 & V2 (overlie Right ventricle) –> R & R’ wave = bunny ears
Look in V5, V6, and Lead I (lateral leads = Left Ventricle) –> Slurred S wave

Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
What leads will reflect RBBB?
V1, V2: will have R1R’ wave (bunny ears)
V5, V6, Lead I: will have slurred S wave
What type of block:

Left Bundle branch block (LBBB)
What leads will reflect LBBB?
V5, V6, or Lead I: “blunted” positive QRS, T-wave inverted
V1-V3: predominately negative QRS
What block refers to a conduction block of just one of the fascicles of the left bundle branch.
hemiblock
What is the major effect that hemiblocks have on the EKG?
axis deviation
What type of block:
left anterior hemiblock
What type of block:
- Conduction down the left anterior fascicle is blocked and current rushes down the left posterior fascicle to the inferior surface of the heart. Depolarization goes from inferior to superior and right to left in direction.
- Axis of depolarization is directed upward and slightly left, inscribing tall R waves in the left lateral leads and deep S waves inferiorly.
Left Anterior Hemiblock
(results in left axis deviation)
What type of block:
- All of the current rushes down the left anterior fascicle and ventricle myocardial depolarization ensues superior to inferior and left to right in direction.
- The axis of depolarization is down and to the right (RAD), tall R waves in inferior leads and deep S waves in left lateral leads.
Left posterior hemiblock
What type of block:

Left posterior hemiblock
How do you diagnose hemiblocks?
look for Left axis deviation or Right axis deviation
What type of block:
- Normal QRS duration & no ST segment or T wave changes
- LAD
- No other cause of LAD is present
Left anterior hemiblock
What type of block:
- Normal QRS duration and no ST segment or T wave changes
- RAD (no other cause of RAD is present)
Left posterior hemiblock


